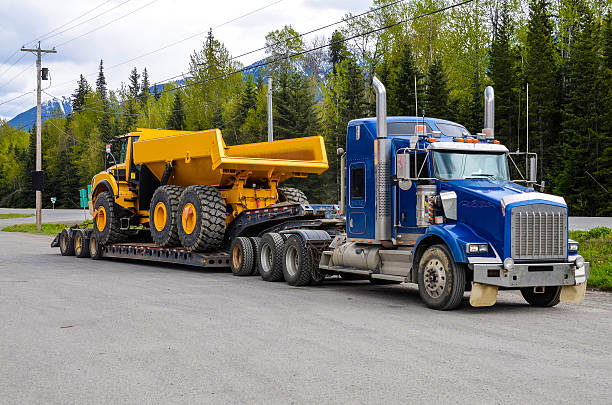
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heavy Duty Truck
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing heavy-duty trucks presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether navigating fluctuating market prices, assessing varying specifications, or identifying reliable suppliers, the intricacies of this sector can be overwhelming. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the heavy-duty truck market by providing insights into different types of trucks, their applications across industries, and critical factors to consider when selecting the right vehicle for your operations.
From the rugged terrains of Africa to the bustling logistics networks of Europe and South America, the demand for reliable and efficient heavy-duty trucks is paramount. Buyers will benefit from detailed evaluations of leading models, including their towing capacities and fuel efficiency, as well as an overview of emerging technologies such as integrated powertrains designed for enhanced performance and lower emissions.
Additionally, this guide will cover essential aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance tips, empowering buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. By the end of this guide, B2B buyers will have the tools and knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the heavy-duty truck market, ensuring they invest wisely in vehicles that drive their business forward.
Understanding heavy Duty Truck Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy-Duty Pickup Trucks | High towing capacity, robust construction, luxury options | Construction, agriculture, logistics | Pros: Versatile, comfortable, high payload. Cons: Higher initial cost, fuel consumption. |
| Class 8 Trucks (Semi-Trucks) | Designed for long-haul transport, powerful engines, trailers | Freight transport, logistics, distribution | Pros: Excellent fuel efficiency, high capacity. Cons: Requires special licensing, higher maintenance. |
| Dump Trucks | Equipped with a hydraulic dump bed, high payload capacity | Construction, mining, waste management | Pros: Efficient unloading, robust design. Cons: Limited to specific tasks, can be costly. |
| Flatbed Trucks | Open bed design for versatile cargo transport | Construction, agriculture, shipping | Pros: Easy loading/unloading, adaptable for various loads. Cons: Limited protection for cargo, exposure to elements. |
| Tanker Trucks | Specialized for transporting liquids, pressure-resistant | Oil, chemicals, food and beverage transport | Pros: Safe transport of hazardous materials, various sizes available. Cons: Regulatory compliance, specialized training needed. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Heavy-Duty Pickup Trucks?
Heavy-duty pickup trucks are characterized by their robust construction and high towing capacities, making them ideal for demanding B2B applications in industries such as construction and agriculture. They often come with luxury features that enhance driver comfort, making them suitable for both work and personal use. When considering a purchase, buyers should assess the truck’s payload capacity, engine performance, and fuel efficiency, as these factors directly impact operational costs and productivity.
How Do Class 8 Trucks Serve the Freight Transport Industry?
Class 8 trucks, commonly known as semi-trucks, are engineered for long-haul freight transport. Their powerful engines and ability to tow large trailers make them essential for logistics and distribution businesses. Buyers should focus on fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and the truck’s ability to comply with local and international regulations when making a purchasing decision. These trucks are ideal for companies looking to optimize their supply chain and reduce operational costs.
What Makes Dump Trucks Essential for Construction and Mining?
Dump trucks are specifically designed with a hydraulic dump bed, allowing for the efficient unloading of heavy materials. Their high payload capacity makes them indispensable in construction, mining, and waste management sectors. When evaluating dump trucks, buyers should consider factors such as payload capacity, durability, and the ease of operation. While they are excellent for specific tasks, their versatility may be limited compared to other truck types.
Why Choose Flatbed Trucks for Versatile Cargo Transport?
Flatbed trucks feature an open bed design that allows for easy loading and unloading of various cargo types. They are particularly popular in construction and agriculture due to their adaptability for transporting oversized or irregularly shaped loads. Buyers should evaluate the truck’s weight capacity and compatibility with loading equipment. Although flatbeds provide flexibility, they offer less protection against the elements, which may be a concern for sensitive cargo.
What Are the Advantages of Tanker Trucks in Liquid Transport?
Tanker trucks are specialized vehicles designed for the safe transport of liquids, including hazardous materials. They are built with pressure-resistant tanks and comply with strict safety regulations, making them suitable for industries such as oil, chemicals, and food and beverage transport. When purchasing tanker trucks, buyers must consider the tank’s capacity, safety features, and compliance with local regulations. While they provide secure transport options, the need for specialized training and regulatory adherence can be a drawback for some companies.
Key Industrial Applications of heavy Duty Truck
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heavy Duty Truck | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Material Transport | Efficient transportation of heavy materials to job sites | Load capacity, durability, and maintenance support |
| Agriculture | Crop Transportation | Timely delivery of harvested crops to markets | Fuel efficiency, off-road capability, and reliability |
| Mining | Mineral Hauling | Safe and efficient transport of minerals from site to processing | Safety features, rugged design, and payload capacity |
| Logistics & Supply Chain | Freight Delivery | Enhanced supply chain efficiency and reduced delivery times | Towing capacity, fuel consumption, and driver comfort |
| Oil & Gas | Equipment Transport | Reliable movement of heavy equipment to remote locations | Versatility, off-road performance, and maintenance ease |
How are Heavy Duty Trucks Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, heavy-duty trucks are essential for transporting materials such as concrete, steel, and timber to various job sites. These trucks solve the problem of moving large quantities of heavy materials efficiently, which is crucial for project timelines. Buyers in this industry should prioritize trucks with high load capacities, robust durability to withstand tough environments, and reliable maintenance support to minimize downtime.
What Role Do Heavy Duty Trucks Play in Agriculture?
Heavy-duty trucks are pivotal in agriculture for transporting harvested crops from farms to processing facilities or markets. Timeliness is critical in this sector, as delays can lead to spoilage. Buyers should consider trucks with excellent fuel efficiency and off-road capabilities to navigate uneven terrains, ensuring that they can operate effectively in rural areas while maintaining reliability during peak harvest seasons.
How are Heavy Duty Trucks Utilized in Mining Operations?
In mining, heavy-duty trucks are used to haul minerals and ores from extraction sites to processing plants. These trucks need to handle rugged terrain and carry significant payloads, addressing the challenges of transporting heavy materials safely. Buyers should look for trucks with advanced safety features, a rugged design for harsh conditions, and substantial payload capacities to meet operational demands in this sector.
What is the Importance of Heavy Duty Trucks in Logistics & Supply Chain?
Heavy-duty trucks are integral to logistics and supply chain management, facilitating the efficient delivery of goods across long distances. They help reduce delivery times and enhance overall supply chain efficiency. Buyers should focus on trucks with high towing capacities, favorable fuel consumption rates, and features that enhance driver comfort, as these factors contribute to long-haul success and operational cost savings.
How Do Heavy Duty Trucks Support the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, heavy-duty trucks transport equipment and materials to remote drilling locations. Their reliability and ability to navigate challenging terrains are critical for maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize trucks that offer versatility for various tasks, excellent off-road performance, and ease of maintenance, ensuring they can rely on their vehicles in demanding environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heavy Duty Truck’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Finding the Right Heavy Duty Truck for Specific Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle to identify the most suitable heavy-duty truck for their unique operational needs. With numerous models available, each equipped with different capabilities such as towing capacity, cargo space, and engine type, it can be overwhelming to determine which truck aligns best with their business requirements. For example, a logistics company may need a truck that can handle heavy loads over long distances while maintaining fuel efficiency, whereas a construction firm might prioritize a vehicle that can maneuver easily on rough terrain. This decision-making process is compounded by the pressure to minimize costs while maximizing operational efficiency.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before starting their search. This involves evaluating the specific applications the truck will be used for, such as load types, distances, and road conditions. Once these criteria are established, buyers can consult with reputable truck manufacturers and dealers to get expert advice tailored to their needs. Utilizing resources such as detailed specifications sheets, comparison tools, and customer testimonials can also help in making informed decisions. Additionally, investing in test drives and utilizing fleet management software can provide real-world insights into performance, ensuring that the chosen truck meets operational expectations.
Scenario 2: Managing Maintenance and Downtime of Heavy Duty Trucks
The Problem:
One of the most pressing concerns for businesses operating heavy-duty trucks is the potential for unexpected breakdowns and maintenance issues. Downtime can lead to significant financial losses, not only due to repair costs but also from lost revenue and delayed deliveries. B2B buyers often find it challenging to establish a reliable maintenance schedule and may struggle to source parts quickly, especially in regions with limited access to dealerships or service centers. This situation creates a sense of urgency to find solutions that ensure trucks are not only operational but also compliant with safety standards.
The Solution:
To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should implement a proactive maintenance strategy that includes regular inspections and servicing based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. Establishing a partnership with a reliable service provider or dealership can facilitate quicker access to parts and expertise. Furthermore, investing in telematics systems can help monitor vehicle performance in real-time, allowing businesses to anticipate potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs. Training drivers on best practices for operating heavy-duty trucks can also extend the life of the vehicle and reduce the frequency of maintenance needs.
Scenario 3: Rising Fuel Costs Impacting Operational Budgets
The Problem:
As fuel prices fluctuate, businesses that rely on heavy-duty trucks often find their operational budgets strained. This can be particularly challenging for companies in regions where fuel prices are consistently high or volatile. B2B buyers may feel pressured to optimize fuel efficiency without compromising on performance, leading to frustration when faced with the limited options available in the market. The challenge is exacerbated by the need to balance cost savings with the demands of transporting heavy loads across various terrains.
The Solution:
To address rising fuel costs, B2B buyers should focus on selecting heavy-duty trucks that feature advanced fuel-efficient technologies, such as turbocharged engines or hybrid powertrains. Researching models known for their fuel economy, like the latest iterations of the Ram HD or Ford Super Duty, can lead to significant savings in the long run. Additionally, implementing fuel management systems can help track consumption patterns and identify areas for improvement. Regular driver training on fuel-efficient driving techniques, such as maintaining optimal speeds and minimizing idling, can also contribute to lower fuel expenses. Finally, exploring alternative fuels or electric heavy-duty options may provide long-term savings and sustainability benefits.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heavy Duty Truck
What Are the Key Materials Used in Heavy Duty Trucks?
When selecting materials for heavy-duty trucks, various factors such as performance, durability, and cost play crucial roles. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of heavy-duty trucks, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Heavy Duty Truck Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in heavy-duty truck manufacturing, particularly for the chassis and frame. Its key properties include high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and good weldability. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros: Steel is durable, cost-effective, and readily available. Its manufacturing processes are well-established, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in humid or saline environments. This can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including diesel and hydraulic fluids, making it ideal for heavy-duty trucks that operate in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary significantly, selecting corrosion-resistant coatings may be essential.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Heavy Duty Truck Construction?
Aluminum is increasingly used in heavy-duty trucks due to its lightweight properties, which enhance fuel efficiency. Key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized.
Pros: Aluminum reduces the overall weight of the truck, leading to better fuel economy and payload capacity. Its resistance to corrosion minimizes maintenance needs.
Cons: The primary limitation of aluminum is its higher cost compared to steel, which can impact the overall budget for truck manufacturing. Additionally, welding aluminum requires specialized techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as fuel tanks and body panels, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is vital. Buyers in Europe may also prefer aluminum for its recyclability, aligning with sustainability goals.
Why Is Composite Material Gaining Popularity in Heavy Duty Trucks?
Composite materials, including fiberglass and carbon fiber, are gaining traction in heavy-duty truck applications due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Composites offer excellent durability and can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemical damage.
Cons: The major drawback is the high manufacturing cost and complexity associated with composite materials. Repairing composite components can also be more challenging than traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for non-structural components like body panels and interior elements, where weight savings and aesthetics are important.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of varying standards for composite materials, such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties. In markets like the Middle East, the high initial cost may be offset by long-term savings in maintenance.
How Does High-Strength Steel Compare in Heavy Duty Truck Design?
High-strength steel (HSS) is used for critical structural components in heavy-duty trucks, offering enhanced performance without significantly increasing weight. Key properties include improved tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
Pros: HSS provides excellent durability and can withstand higher loads, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It also allows for thinner sections, contributing to weight reduction.
Cons: The increased strength can lead to higher costs and may require advanced manufacturing techniques, complicating the production process.
Impact on Application: HSS is particularly effective in areas subjected to high stress, such as the frame and suspension components, ensuring reliability under heavy loads.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A992 for structural steel. In Europe, adherence to EN 10025 standards is crucial for quality assurance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heavy Duty Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for Heavy Duty Truck | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and frame | High durability and cost-effectiveness | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Fuel tanks and body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Composite | Body panels and interior components | Excellent durability and design flexibility | High manufacturing cost and repair complexity | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Structural components | Enhanced performance without added weight | Higher costs and advanced manufacturing needs | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials commonly used in heavy-duty trucks, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heavy Duty Truck
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heavy-Duty Trucks?
The manufacturing of heavy-duty trucks is a complex process that involves several key stages, ensuring that the final product meets the rigorous demands of commercial applications.
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing high-quality materials. Steel, aluminum, and composite materials are commonly used for various truck components. Suppliers are typically required to provide material certifications, ensuring compliance with international standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO specifications.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are ready, they undergo forming processes. Techniques such as stamping, welding, and machining are employed to create essential components like chassis, body panels, and frames. Advanced technologies, including robotic welding, are increasingly used to enhance precision and reduce human error.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage is critical, as it combines the various components into a complete vehicle. This stage often utilizes modular assembly lines, where parts are assembled in sections before being joined into the final product. It is essential that workers are trained in the latest assembly techniques and that ergonomic considerations are taken into account to minimize workplace injuries.
Finishing Touches
After assembly, trucks undergo finishing processes, which may include painting, coating, and installing interior features. These processes not only enhance aesthetics but also provide protection against corrosion and wear. Quality control during this stage ensures that the trucks meet both functional and aesthetic standards before they are dispatched.
How is Quality Assurance Integrated into Heavy-Duty Truck Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that heavy-duty trucks meet industry standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Guide Heavy-Duty Truck Manufacturing?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, are foundational in establishing a quality management system (QMS). This standard helps manufacturers ensure consistency in their processes and products. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for trucks used in oil and gas applications provide further validation of quality and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Truck Manufacturing?
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers must provide documentation that certifies compliance with relevant standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checkpoints are established to monitor assembly accuracy, weld integrity, and component functionality. This step is crucial for identifying defects early in the production cycle.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the final inspection is conducted. This includes road tests, performance evaluations, and checks for aesthetic quality.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Heavy-Duty Truck Manufacturing?
A variety of testing methods are implemented to ensure that heavy-duty trucks are safe and reliable:
- Static and Dynamic Load Testing: Assess the strength and durability of components under various load conditions.
- Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s resistance to environmental factors, which is particularly relevant for trucks operating in harsh climates.
- Emissions Testing: Ensures compliance with environmental regulations, especially important for international markets with strict emissions standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence when evaluating suppliers to ensure quality and compliance with international standards. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can reveal adherence to quality control processes and standards. Buyers should establish a checklist based on relevant ISO standards and industry requirements.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers. These documents should outline their QA processes, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices. This is particularly important for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe who may not have direct access to the manufacturing site.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local laws and industry standards, which may vary significantly between Europe, Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Language differences and cultural variations can impact the clarity of quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels and documentation practices can help mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Warranty and Support Services: Assess the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by suppliers. A robust support framework can provide additional assurance regarding the quality and reliability of the trucks.
By paying close attention to these manufacturing and quality assurance processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heavy-duty trucks, ensuring that their investments meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heavy Duty Truck’
Introduction
Sourcing heavy-duty trucks is a critical investment for businesses that rely on transportation and logistics. This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a clear, step-by-step checklist to ensure a successful procurement process. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to establish your technical requirements. Consider the type of loads you will transport, the terrain, and whether you need specialized features like advanced towing capacity or specific engine types.
- Key Considerations:
- Payload capacity
- Engine type (diesel vs. gasoline)
- Fuel efficiency ratings
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Understanding the market landscape is crucial for making an informed choice. Research various heavy-duty truck models and manufacturers to identify which vehicles meet your specifications.
- Research Tools:
- Industry reports
- Online forums and reviews
- Competitor analysis
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage directly with their sales representatives for deeper insights.
- What to Look For:
- Supplier reputation and experience
- After-sales support and service options
- Availability of spare parts
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the trucks you are considering comply with local and international regulations. This step is vital for avoiding legal issues and ensuring safety standards are met.
- Key Certifications:
- ISO certifications
- Environmental compliance standards
- Emission ratings
Step 5: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, warranties, and delivery timelines. A comprehensive quote will help you compare offers effectively and negotiate better terms.
- Comparison Factors:
- Total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Warranty coverage and terms
- Financing options
Step 6: Arrange for Test Drives
Before finalizing your purchase, arrange for test drives of the shortlisted trucks. This practical step allows you to evaluate performance, comfort, and operational efficiency firsthand.
- What to Assess:
- Handling and maneuverability
- Cabin comfort and technology features
- Noise levels and ride quality
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
After selecting the best truck and supplier, it’s time to finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms are clearly defined, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and after-sales support.
- Important Elements:
- Payment structure (upfront, financing, etc.)
- Delivery timelines and logistics
- Conditions for return or exchange
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for heavy-duty trucks, making informed choices that align with their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heavy Duty Truck Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heavy Duty Truck Sourcing?
When sourcing heavy-duty trucks, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and source of materials significantly influence pricing. Premium materials used in truck frames, engines, and interiors can raise costs but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the skill level required for assembly and manufacturing. Skilled labor in developed countries might be more expensive compared to emerging markets, affecting overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and maintenance of manufacturing facilities. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and equipment are necessary for producing heavy-duty trucks. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, but it is amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that trucks meet industry standards and regulations incurs additional costs. Implementing robust QC processes can prevent costly recalls and warranty claims in the future.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for moving raw materials to the factory and finished products to the buyer can vary widely. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and local infrastructure impact these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, demand, and the specific value proposition of the truck being sold.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Heavy Duty Truck Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of heavy-duty trucks, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate pricing based on expected order volumes to maximize cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as advanced technology, specific engine types, or unique body configurations can lead to higher prices. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these customizations against their operational requirements.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Trucks built with higher-quality materials or those that have received industry certifications (such as ISO) may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established brands with a proven track record may charge more due to perceived value, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international buyers. Incoterms dictate who bears the costs and risks during transportation, which can significantly affect the final price.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Sourcing Heavy Duty Trucks?
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider several strategies when sourcing heavy-duty trucks:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in negotiations to explore potential discounts, especially for bulk orders. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also lead to better terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, fuel efficiency, and resale value. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower operating expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can impact the final cost. It’s advisable to conduct thorough market research and price comparisons across suppliers.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor industry trends and technological advancements in heavy-duty trucks. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for heavy-duty trucks can fluctuate based on various factors, including market demand, raw material costs, and economic conditions. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heavy Duty Truck With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Heavy Duty Trucks for B2B Applications
When evaluating logistics solutions, businesses often consider various alternatives to heavy-duty trucks. These alternatives can offer different advantages in performance, cost, and application suitability. Understanding these options allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Heavy Duty Truck | Light-Duty Truck | Cargo Van |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High towing capacity (up to 36,000 lbs) | Moderate towing capacity (up to 12,000 lbs) | Limited towing capacity (up to 5,000 lbs) |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (starting around $46,300) | Lower initial investment (starting around $30,000) | Moderate investment (starting around $35,000) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific training and licensing | Easier to operate; less stringent regulations | Simple setup and operation; no special licensing needed |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance costs due to complexity | Lower maintenance costs; simpler components | Generally lower maintenance; fewer moving parts |
| Best Use Case | Heavy hauling over long distances | Light to moderate loads; urban delivery | Urban delivery; service-based industries |
What are the Pros and Cons of Light-Duty Trucks Compared to Heavy Duty Trucks?
Light-duty trucks are a viable alternative for businesses that do not require the extreme towing capabilities of heavy-duty trucks. With a lower initial investment and simpler operational requirements, they are suitable for urban deliveries and light hauling tasks. However, their performance limitations may hinder businesses that require heavy cargo transport, making them less versatile in demanding applications.
How Do Cargo Vans Compare to Heavy Duty Trucks?
Cargo vans provide an excellent alternative for businesses focused on urban logistics and service industries. Their ease of operation and lower maintenance costs make them attractive for companies that prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. However, they lack the towing capacity and ruggedness of heavy-duty trucks, which may limit their use for heavier loads or long-haul journeys.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the right logistics solution requires a careful assessment of operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Heavy-duty trucks excel in performance and heavy hauling, making them ideal for businesses with significant transport needs. Conversely, light-duty trucks and cargo vans offer cost-effective and efficient alternatives for lighter loads and urban applications. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific use cases, considering factors such as load capacity, frequency of use, and overall cost of ownership to determine the best solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heavy Duty Truck
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heavy Duty Trucks?
When investing in heavy-duty trucks, understanding the technical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Towing Capacity
Towing capacity indicates the maximum weight a truck can safely tow. This is crucial for businesses that require transport of heavy loads, such as construction materials or machinery. A higher towing capacity often correlates with a more robust engine and chassis design, which can enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. -
Payload Capacity
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight a truck can carry, including cargo and passengers. This is vital for logistics companies and contractors who need to ensure their vehicles can handle the weight of their loads without compromising safety or performance. -
Engine Power and Torque
Measured in horsepower (HP) and pound-feet (lb-ft), engine power and torque dictate a truck’s ability to accelerate and maintain speed under load. For heavy-duty operations, trucks with higher torque ratings are preferred, as they provide better performance when starting from a standstill or climbing inclines. -
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency, often expressed in miles per gallon (MPG), is critical for operational cost management. Heavy-duty trucks that offer better fuel economy can significantly reduce long-term fuel expenses, making them more economical for businesses that rely on extensive travel. -
Frame Material and Durability
The frame material impacts the truck’s durability and weight. Heavy-duty trucks typically use high-strength steel or aluminum to withstand extreme conditions. Understanding the material grade can help businesses assess longevity and maintenance needs, which are essential for reducing total cost of ownership. -
Braking System
A robust braking system is essential for safety, especially when hauling heavy loads. Features such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC) enhance braking performance and vehicle control, making them critical considerations for fleet managers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Heavy Duty Truck Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to the company that manufactures the original components of a vehicle. In the heavy-duty truck market, OEMs are crucial as they ensure that parts meet specific quality standards and compatibility, which is vital for maintenance and repairs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a buyer can purchase from a supplier. Understanding MOQ is essential for companies planning to invest in heavy-duty trucks, as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For heavy-duty truck purchases, submitting an RFQ can help businesses gather competitive pricing and terms, which is critical for budget management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost of acquiring heavy-duty trucks, especially in global markets. -
Fleet Management
Fleet management encompasses all aspects of managing a company’s vehicle fleet, including maintenance, logistics, and cost control. Understanding fleet management principles can help businesses optimize their operations and ensure efficient use of heavy-duty trucks. -
Telematics
Telematics refers to the integration of telecommunications and monitoring systems in vehicles. In heavy-duty trucks, telematics can provide real-time data on vehicle location, fuel consumption, and maintenance needs, enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in heavy-duty trucks align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heavy Duty Truck Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Heavy Duty Truck Sector?
The heavy-duty truck market is experiencing a significant transformation driven by various global factors. Key drivers include increasing demand for freight transportation due to global trade growth, urbanization, and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa and South America. Additionally, the focus on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints is reshaping purchasing decisions among international B2B buyers. As a result, manufacturers are investing in advanced technologies, including electric and hybrid powertrains, to meet stricter emissions regulations and changing consumer preferences.
Emerging B2B technology trends, such as telematics and fleet management systems, are becoming essential for optimizing operations and reducing costs. These technologies allow fleet operators to track vehicle performance, monitor fuel efficiency, and enhance overall fleet management. The integration of AI and machine learning into these systems further aids in predictive maintenance, ensuring higher uptime and lower total cost of ownership. International buyers are increasingly seeking trucks equipped with these technologies to stay competitive.
In regions like Europe and the Middle East, there is a notable shift towards smart logistics solutions, emphasizing real-time data analytics and automation. This trend is pushing manufacturers to incorporate advanced safety features and driver assistance systems into their heavy-duty trucks. For B2B buyers, understanding these market dynamics and adapting sourcing strategies accordingly is crucial to capitalize on opportunities in the evolving landscape.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Heavy Duty Truck Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount considerations in the heavy-duty truck sector. As environmental concerns escalate globally, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to reducing their environmental impact. This includes the use of sustainable materials, efficient manufacturing processes, and adherence to environmental regulations. Heavy-duty trucks made with recycled materials or sourced from eco-friendly suppliers are gaining traction in the market.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now demanding transparency in sourcing practices, ensuring that manufacturers uphold labor rights and fair working conditions throughout their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 26000 for social responsibility are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection. By choosing manufacturers with these certifications, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with unethical practices and enhance their brand reputation.
Incorporating green certifications and eco-friendly materials not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also appeals to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers. As the heavy-duty truck market evolves, sustainability will play a critical role in shaping sourcing strategies and influencing purchasing decisions.
What Is the Evolution of the Heavy Duty Truck Market?
The heavy-duty truck market has undergone significant evolution over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional diesel engines, the sector has seen a gradual shift towards more advanced technologies. The introduction of stricter emissions regulations in various regions has prompted manufacturers to innovate, resulting in the development of cleaner, more efficient powertrains, including electric and hybrid models.
Additionally, the rise of globalization and e-commerce has amplified the demand for logistics and freight services, driving the need for more robust and capable heavy-duty trucks. This evolution is marked by the increasing integration of technology, such as telematics and driver assistance systems, which enhance safety and operational efficiency.
As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of the heavy-duty truck market will provide valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities. Embracing innovation while prioritizing sustainability will be key to success in this dynamic sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heavy Duty Truck
-
How do I determine the right heavy-duty truck for my business needs?
To select the best heavy-duty truck, assess your specific operational requirements such as load capacity, towing needs, and the type of terrain you’ll be navigating. Consider factors like engine type (diesel vs. gasoline), fuel efficiency, and comfort features for drivers. Research various models and compare their specifications, focusing on performance metrics such as horsepower, torque, and payload capacity. Additionally, consult with industry peers or experts to gain insights on brands and models that align with your business operations. -
What are the key specifications to look for in heavy-duty trucks?
When evaluating heavy-duty trucks, prioritize specifications such as towing capacity, payload limits, engine performance, and fuel efficiency. Examine the truck’s drivetrain options and available configurations (e.g., cab size, bed length). Safety features, driver comfort amenities, and technology integrations (like GPS and telematics) should also be considered. Ensure that the truck complies with regional regulations and standards, particularly if operating in diverse international markets. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing heavy-duty trucks internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of heavy-duty trucks can vary widely based on the supplier, contract agreements, and buyer-seller relationships. Common arrangements include letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, ensuring that the payment structure aligns with your cash flow needs. Always review the supplier’s payment policies and consider utilizing escrow services for large transactions to mitigate risk. -
How can I vet suppliers for heavy-duty trucks?
To effectively vet suppliers, conduct thorough research into their reputation and track record in the industry. Look for customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies showcasing their previous work. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards, and request references from other businesses. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible, or arrange for a virtual tour to assess their operations and capabilities firsthand. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for heavy-duty trucks?
The minimum order quantity for heavy-duty trucks often depends on the manufacturer and the specific models being purchased. Some manufacturers may have a MOQ of one unit, while others might require bulk orders to offer competitive pricing. When negotiating, express your needs clearly and explore options for flexibility, especially if your business is just starting out or if you’re testing a new market. It’s also beneficial to inquire about financing options for larger orders. -
Can I customize heavy-duty trucks to fit my business requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for heavy-duty trucks to cater to specific business needs. Customizations can include modifications to the truck’s engine, body type, storage solutions, and technology features. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available options and understand any additional costs or lead times involved. Ensure that the customization complies with local regulations and meets your operational demands. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing heavy-duty trucks?
When importing heavy-duty trucks, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Evaluate the best routes for transport and work with reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling heavy equipment. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, is prepared in advance to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in the cost of insurance to protect your investment during transit. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place when purchasing heavy-duty trucks?
Implementing quality assurance measures is crucial when purchasing heavy-duty trucks. Request detailed specifications and quality certifications from the supplier, and arrange for inspections before delivery. Consider third-party quality assurance services to evaluate the trucks’ condition upon arrival. Establish a clear return and warranty policy with the supplier to address potential defects or issues post-purchase, ensuring your investment is protected.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Heavy Duty Truck Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ford – Inventory of Vehicles for Sale
Domain: victorfordinc.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Ford – Inventory of Vehicles for Sale, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. GMC – 2025 Sierra Heavy Duty 2500 & 3500 Pickup Trucks
Domain: gmc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 2025 GMC Sierra Heavy Duty 2500 & 3500 Heavy-Duty Pickup Trucks
– Starting Price: PRO at $46,300, AT4X at $93,685
– Maximum Towing Capacity: Up to 36,000 lbs.
– Available Engines: Duramax® 6.6L Turbo-Diesel V8 with 975 lb.-ft. of torque and 470 hp
– Standard Features: 6.6L V8 gas engine, Allison® 10-speed automatic transmission, Trailering Package, Trailering Mirrors, Trailer Brake Controller, Bes…
3. International – Heavy-Duty Trucks
Domain: international.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Heavy-Duty Trucks from International® include the LT® Series and RH™ Series. The LT Series focuses on comfort, control, uptime, and efficiency, featuring the S13® Integrated Powertrain, which is the most fuel-efficient powertrain available, offering lower total cost of ownership and reduced emissions. The RH Series is designed for local and regional hauling, optimized for middle-mile and final-mil…
4. Ford – 2026 Super Duty® Truck
Domain: ford.com
Introduction: 2026 Ford Super Duty® Truck
– Max Available Towing: 40,000 lbs (best-in-class diesel-powered gooseneck tow rating)
– Max Available Payload: 8,000 lbs (best-in-class)
– Max Available Diesel Torque: 1,200 lb-ft
– Max Available Diesel Horsepower: 500 hp (best-in-class)
– Models: F-250, F-350, F-450
– Key Features:
– Engine: 6.8L 2V DEVCT NA PFI V8 gas engine
– Transmission: TorqShift®-G 10-speed …
5. Heavy Duty Trucks – 2025 Models
Domain: cars.usnews.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“best_heavy_duty_trucks”: [{“model”: “2025 Ford F-250 Super Duty”, “score”: 9.4, “msrp”: “$45,300 – $78,065”}, {“model”: “2025 Ram 2500”, “score”: 9.4, “msrp”: “$45,565 – $90,205”}, {“model”: “2025 Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD”, “score”: 8.9, “msrp”: “$45,300 – $73,100”}, {“model”: “2025 GMC Sierra 2500HD”, “score”: 8.7, “msrp”: “$46,300 – $93,600”}, {“model”: “2024 Nissan Titan XD”, “score”: 7.0, …
6. Kelley Automotive Group – Used Heavy Duty Trucks
Domain: kelleyautomotivegroup.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Used Heavy Duty Trucks for Sale at Kelley Automotive Group. Inventory includes popular brands like Chevy and GMC. Features include competitive pricing, rotating used vehicle specials, and trade-in options. Customization available through Kelley’s Customs with warranty protection. Financing options available with a payment calculator for personalized plans. Service center with factory-trained techn…
7. Chevrolet – 2025 Silverado HD Models
Domain: chevrolet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: {“models”:[{“name”:”2025 Silverado 2500 HD”,”starting_price”:”$45,300″,”as_shown_price”:”$80,335″},{“name”:”2025 Silverado 3500 HD”,”starting_price”:”$46,500″,”as_shown_price”:”$76,595″}]}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heavy Duty Truck
In the evolving landscape of heavy-duty trucks, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. By focusing on key attributes such as towing capacity, fuel efficiency, and advanced technology, businesses can better align their purchasing decisions with operational needs. The latest models, like the Ram HD and Ford Super Duty, exemplify the blend of power and luxury, catering to diverse market demands across regions.
B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer comprehensive support and robust warranties, ensuring long-term value and reliability. Moreover, understanding regional variations in performance and compliance standards can significantly enhance the procurement strategy, particularly in markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, the heavy-duty truck market is poised for innovation, with advancements in fuel efficiency and smart technology reshaping the industry. As you consider your next purchase, leverage insights from this guide to make informed decisions that not only meet current needs but also anticipate future challenges. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore the best options to drive your business forward in this competitive landscape.