Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for lhd Truck
In the complex landscape of global mining operations, sourcing the right Load Haul Dump (LHD) truck can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With varying terrain, regulatory requirements, and operational demands across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting an LHD that meets both efficiency and safety standards is crucial. This guide is designed to equip international buyers with the insights needed to navigate the intricate market for LHD trucks, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore various types of LHD trucks available, from diesel-powered models to innovative electric alternatives. We will delve into their applications across different mining environments, highlighting key performance metrics such as load capacity, maneuverability, and environmental impact. Additionally, we will provide essential tips on vetting suppliers, assessing cost structures, and understanding local market conditions, empowering you to identify reliable partners in your procurement journey.
By leveraging the information presented here, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of the LHD truck market, ensuring that their investments enhance operational productivity and align with sustainability goals. Whether you’re operating in Brazil’s vast mines or Nigeria’s challenging terrains, this guide will serve as your roadmap to sourcing the right LHD truck tailored to your unique business requirements.
Understanding lhd Truck Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel LHD | Powered by diesel engines, high torque, and load capacity | Underground mining, tunneling | Pros: Strong power output, widely available. Cons: Higher emissions, noise levels. |
| Electric LHD | Battery-powered, lower emissions, quieter operation | Sustainable mining operations, urban sites | Pros: Eco-friendly, reduced operating costs. Cons: Limited range, higher initial investment. |
| Hybrid LHD | Combines diesel and electric power sources | Versatile applications in mining | Pros: Flexibility in fuel use, lower emissions. Cons: More complex maintenance requirements. |
| Narrow Vein LHD | Designed for confined spaces, compact frame | Narrow vein mining, small-scale operations | Pros: Excellent maneuverability, optimized for tight areas. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Continuous Loader LHD | Continuous loading mechanism, high efficiency | Large-scale excavation, rapid material transport | Pros: Increased productivity, reduced cycle times. Cons: Higher upfront costs, requires specialized training. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Diesel LHD Trucks?
Diesel Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks are known for their robust power and high torque, making them ideal for demanding underground mining operations. These trucks typically feature large load capacities, allowing them to transport significant amounts of material efficiently. When considering a diesel LHD, B2B buyers should focus on fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and the availability of service support in their region, especially in areas with limited access to parts.
Why Choose Electric LHD Trucks for Sustainable Mining?
Electric LHD trucks are rapidly gaining traction due to their lower emissions and quieter operation, making them suitable for both underground mining and urban construction sites. These trucks rely on battery power, which significantly reduces operational costs over time. However, buyers must consider the charging infrastructure required and the initial investment costs, which can be higher compared to traditional diesel models. The long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can offset these initial expenses.
What Advantages Do Hybrid LHD Trucks Offer?
Hybrid LHD trucks provide a unique solution by combining diesel and electric power sources, offering versatility in fuel usage. This adaptability allows operations to switch between power sources based on availability and cost, making hybrid LHDs suitable for a variety of mining applications. Buyers should evaluate the complexity of maintenance and the potential for increased downtime due to the dual systems, but the benefits of reduced emissions and operational flexibility can be significant.
How Do Narrow Vein LHD Trucks Enhance Mining Operations?
Narrow vein LHD trucks are specifically designed for operations in confined spaces, offering a compact frame that enhances maneuverability. These trucks are ideal for small-scale mining operations where space is at a premium. B2B buyers should assess the load capacity and operational efficiency, as these trucks may not handle larger loads compared to standard models. However, their ability to navigate tight spots can lead to increased productivity in suitable environments.
What Makes Continuous Loader LHD Trucks Efficient?
Continuous Loader LHD trucks employ a continuous loading mechanism that allows for rapid excavation and material transport. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in large-scale mining operations where time is critical. Buyers should consider the upfront investment and the necessity for specialized training to operate these machines effectively. Despite higher initial costs, the potential for increased productivity and reduced cycle times makes continuous loaders an attractive option for large mining enterprises.
Key Industrial Applications of lhd Truck
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of lhd Truck | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining | Underground ore transportation | Increases efficiency and reduces operational costs | Equipment durability, maintenance support, and parts availability |
| Tunneling | Material handling in tunnel construction | Enhances productivity and accelerates project timelines | Size and maneuverability, safety features, and operator comfort |
| Construction | Material and debris removal in confined spaces | Improves site safety and operational efficiency | Compact design, load capacity, and fuel type options |
| Waste Management | Transporting waste in underground facilities | Supports sustainable operations and compliance | Environmental impact, vehicle emissions, and serviceability |
| Quarrying | Loading and hauling aggregates | Maximizes output and minimizes downtime | Adaptability to different terrains, reliability, and load capacity |
How is LHD Truck Used in Mining Operations?
In the mining sector, Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks are essential for transporting ore from underground mines to surface facilities. Their compact design allows them to navigate narrow tunnels and confined spaces, maximizing operational efficiency. By streamlining ore transport, LHDs help reduce labor costs and improve overall productivity. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable models that require minimal maintenance is crucial due to challenging operational environments.
What Role Does LHD Truck Play in Tunneling Projects?
In tunneling applications, LHD trucks facilitate the rapid removal of excavated material, crucial for maintaining project timelines. Their ability to operate efficiently in tight spaces enhances productivity while ensuring worker safety. Buyers should prioritize models that offer ergonomic features and advanced safety systems, especially in regions with strict regulatory requirements. Selecting the right LHD can significantly impact project delivery and cost-effectiveness.
How Do LHD Trucks Support Construction Activities?
Within the construction industry, LHD trucks are employed for debris removal and material handling, particularly in urban or confined construction sites. Their versatility in transporting various materials helps maintain workflow and site safety. When sourcing LHDs for construction, businesses should consider factors such as size, load capacity, and operator comfort to ensure optimal performance in diverse environments, especially in developing regions where construction activities are booming.
What Are the Benefits of LHD Trucks in Waste Management?
LHD trucks are increasingly utilized in waste management, particularly for transporting waste materials from underground facilities. Their design minimizes environmental impact and supports compliance with local regulations. For international buyers, especially those in the Middle East, it is essential to consider the emissions profile and serviceability of the vehicles to align with sustainability goals and operational efficiency.
How Are LHD Trucks Used in Quarrying Operations?
In the quarrying sector, LHD trucks play a vital role in loading and hauling aggregates efficiently. Their robust construction and high load capacities allow for maximum output while minimizing downtime. Buyers should focus on LHD models that can adapt to various terrains and provide reliable performance, as this will directly affect productivity and profitability in regions like Europe and Africa, where aggregate demand is high.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘lhd Truck’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Equipment Reliability in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in sectors like mining often face the challenge of ensuring that their Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks can withstand harsh underground conditions. These environments are typically characterized by extreme temperatures, high dust levels, and rough terrain, which can lead to frequent breakdowns and maintenance issues. This reliability problem not only disrupts operational efficiency but also increases costs associated with repairs and downtime, ultimately impacting productivity and profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate reliability issues, it’s crucial to select LHD trucks specifically designed for robust performance in challenging environments. Buyers should focus on equipment that offers advanced features such as heavy-duty frames, enhanced cooling systems, and protective covers that shield critical components from dust and debris. Additionally, opting for manufacturers that provide comprehensive maintenance support and readily available spare parts can significantly reduce downtime. Regular training for operators on best practices for handling and operating LHD trucks in these environments can also enhance equipment longevity and reliability.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Training Leading to Safety Risks
The Problem: Safety is paramount in underground operations, yet many B2B buyers encounter the issue of inadequate operator training when it comes to using LHD trucks. Improperly trained operators can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and even injuries. This situation is particularly concerning in regions where mining operations are scaling up and hiring new staff rapidly, creating a potential gap in safe operational practices.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize comprehensive training programs that include both theoretical and practical components tailored to LHD operations. Collaborating with equipment manufacturers or third-party training organizations can provide structured training modules focusing on safe operating procedures, emergency response, and equipment maintenance. Furthermore, implementing regular safety drills and refresher courses can ensure that operators remain well-versed in safe practices. Utilizing simulators for training can also provide a risk-free environment for operators to gain experience before operating the actual LHD trucks.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Appropriate Equipment for Specific Needs
The Problem: Sourcing the right LHD truck that meets specific operational requirements can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. Factors such as load capacity, size constraints for narrow veins, and fuel type (diesel vs. electric) can complicate the decision-making process. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the array of options available, leading to potential mismatches between the equipment and their operational needs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the selection process, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment prior to sourcing equipment. This involves evaluating operational requirements, such as the expected load capacity and dimensions of the mining site. Engaging with manufacturers to understand the specifications of various models can provide clarity. Buyers should also consider visiting existing operations using the equipment to observe performance in real-world conditions. Furthermore, leveraging technology, such as simulation tools or software that models operational scenarios, can aid in visualizing how different LHD trucks will perform in their specific environments. Establishing a relationship with a trusted dealer can provide ongoing support and insights into the latest equipment options that align with evolving operational needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for lhd Truck
What Are the Key Materials Commonly Used in LHD Trucks?
When selecting materials for Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material can significantly impact performance, durability, and overall operational efficiency. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of LHD trucks: steel, aluminum, composite materials, and rubber.
How Does Steel Perform in LHD Truck Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in LHD truck construction due to its excellent strength and durability. Key properties of steel include high tensile strength, good weldability, and resistance to wear and tear under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Pros: Steel offers exceptional durability and longevity, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, which is crucial for budget-conscious buyers in regions like Africa and South America.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. This can lead to increased maintenance costs over time. Additionally, steel is heavier than alternatives like aluminum, which may affect fuel efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for harsh mining environments. However, buyers should consider protective coatings or treatments to enhance corrosion resistance.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for LHD Trucks?
Aluminum is increasingly popular in LHD truck design due to its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. Key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal conductivity.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved fuel efficiency and reduced operational costs. Furthermore, its natural resistance to corrosion minimizes maintenance needs, which is particularly beneficial in humid climates.
Cons: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, which can be a significant factor for buyers in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, while aluminum is strong, it may not withstand the same levels of impact as steel, making it less suitable for extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it a preferred choice for operations in coastal or wet regions. Buyers should ensure that the specific aluminum alloy used meets local standards for strength and durability.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance LHD Truck Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are gaining traction in the mining industry for their unique properties. These materials are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics.
Pros: Composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored for specific applications, enhancing performance. They are also resistant to corrosion and chemical damage, reducing maintenance costs.
Cons: The main drawback of composites is their high manufacturing complexity and cost. This can be a barrier for buyers in developing markets where budget constraints are a concern.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in specialized applications where weight reduction is critical. However, international buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material usage.
What Role Does Rubber Play in LHD Truck Design?
Rubber is primarily used in the tires and certain components of LHD trucks due to its flexibility and shock-absorbing properties. Key properties include high elasticity and resistance to wear.
Pros: Rubber provides excellent traction and shock absorption, improving operational safety and comfort for operators. It is also relatively inexpensive and widely available.
Cons: Rubber can degrade over time, especially when exposed to extreme temperatures or chemicals. This necessitates regular replacement, which can increase long-term costs.
Impact on Application: The use of rubber in tires is essential for optimizing performance in uneven terrains typical in mining operations. Buyers should consider the specific rubber compounds used to ensure they meet local environmental conditions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for LHD Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for lhd Truck | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components and chassis | High durability and cost-effectiveness | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Body panels and lightweight structures | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency | Higher cost, lower impact resistance | High |
| Composite | Specialized components and panels | Tailored performance and corrosion resistance | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Rubber | Tires and shock-absorbing components | Excellent traction and comfort | Degrades over time, requires replacement | Low |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for lhd Truck
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing LHD Trucks?
The manufacturing process for Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks is intricate and involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets the rigorous demands of underground mining operations. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials such as steel and aluminum alloys, which are essential for the durability and performance of LHD trucks. The materials undergo processes like cutting, machining, and surface treatment to enhance their strength and corrosion resistance. The choice of materials is critical as it directly impacts the truck’s performance and longevity in harsh mining environments.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they are shaped into components using various forming techniques. These may include stamping, welding, and casting. Advanced methods like hydroforming and laser cutting may also be employed to create complex shapes that contribute to the structural integrity and efficiency of the LHD truck. Precision in this stage is crucial, as any deviation can lead to performance issues or increased wear.
Assembly
The assembly stage brings together the formed components into a cohesive unit. This process typically involves multiple sub-assemblies, such as the hydraulic system, electrical components, and the chassis. Skilled technicians utilize jigs and fixtures to ensure accuracy during assembly. Automated systems may also be integrated to enhance productivity and reduce human error. This phase is where the integration of technology, such as battery-electric systems, is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves several finishing processes, including painting, coating, and quality checks. A robust coating system is applied to protect against corrosion and wear, which is essential for vehicles operating in underground conditions. This stage often includes rigorous testing to ensure that the LHD trucks meet all specifications and are ready for deployment.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for LHD Trucks?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of LHD trucks, ensuring that every unit produced meets international standards and customer expectations. Key standards include ISO 9001, CE marking, and industry-specific certifications like API.
ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers of LHD trucks must establish processes that enhance customer satisfaction by consistently providing products that meet regulatory and customer requirements. This certification is essential for B2B buyers as it reflects the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
CE Marking
For products sold in Europe, CE marking demonstrates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. LHD trucks bearing the CE mark indicate that they have undergone rigorous testing and meet the necessary EU regulations, providing assurance to buyers in Europe and beyond.
API Standards
The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for equipment used in oil and gas operations, which can apply to certain LHD truck configurations. Compliance with API standards ensures that trucks are built to withstand the specific demands of these industries, offering an additional layer of confidence for buyers in sectors like mining and oil extraction.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured in LHD Truck Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral aspect of the manufacturing process, with multiple checkpoints established to maintain standards throughout production. Common QC checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This step ensures that all incoming materials meet specified quality standards before being used in production. Inadequate materials can lead to failures in the final product, making this checkpoint vital.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC checks are conducted at various stages. This includes monitoring the forming and assembly processes to ensure compliance with design specifications. Technicians may use statistical process control (SPC) methods to identify variations and rectify issues in real-time, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is the last line of defense before the LHD trucks are shipped to customers. This stage includes comprehensive testing, such as performance assessments, safety checks, and compliance verifications. FQC ensures that every unit meets the required standards and is ready for operational use.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in LHD Truck Production?
Testing methods in the production of LHD trucks are diverse and tailored to assess various performance aspects. Common methods include functional testing, load testing, and environmental testing.
Functional Testing
This involves verifying that all systems, including hydraulic, electrical, and mechanical, operate as intended. Functional testing is crucial for ensuring that the LHD truck performs effectively in real-world scenarios.
Load Testing
Load testing assesses the truck’s ability to carry specified weights under operational conditions. This testing simulates actual mining environments to ensure that the truck can handle the stress and demands of its intended use.
Environmental Testing
Given the harsh conditions of underground mining, environmental testing evaluates the truck’s performance under extreme temperatures, humidity, and dust. This ensures that the equipment can operate reliably in various environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Buyers can employ several strategies, including audits, requesting quality reports, and utilizing third-party inspections.
Conducting Supplier Audits
Audits allow buyers to evaluate a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems firsthand. An on-site audit can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality, adherence to standards, and overall operational efficiency.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports can help buyers assess the supplier’s quality performance over time and identify any recurring issues.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes. These services often include pre-shipment inspections, which can identify potential issues before the product reaches the buyer.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may vary by region. Understanding local regulations, quality standards, and cultural differences can significantly impact procurement decisions.
Regional Regulations
Different regions have distinct regulations regarding safety, environmental impact, and product standards. Buyers must familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties.
Quality Standards Variability
While international standards like ISO 9001 are widely recognized, some suppliers may adhere to local standards that do not align with global practices. Buyers should clarify which standards the supplier meets and ensure they align with their own requirements.
Cultural Considerations
Cultural differences can influence business practices, including communication styles and expectations regarding quality. Establishing clear lines of communication and understanding cultural nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and help mitigate misunderstandings.
By considering these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring LHD trucks, ensuring they select suppliers that prioritize quality and reliability in their manufacturing processes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘lhd Truck’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers aiming to procure Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks. LHD trucks are essential for efficient underground mining operations, and making informed purchasing decisions can significantly impact productivity and operational costs. By following these steps, buyers will ensure they select the right equipment and supplier for their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate LHD truck. Consider factors such as payload capacity, dimensions, and engine type (diesel vs. electric). Knowing your operational requirements helps narrow down your options and ensures compatibility with existing equipment.
- Payload Capacity: Determine the weight you need to haul to select an LHD with the right capabilities.
- Dimensions: Ensure the truck fits within your mining environment, considering tunnel sizes and turning radii.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated on the latest trends in LHD technology, including advancements in electric and hybrid models. Understanding current market offerings can help you identify options that improve efficiency and sustainability.
- Efficiency Improvements: Look for models that offer enhanced performance metrics, such as lower fuel consumption or faster cycle times.
- Sustainability Features: Consider LHDs equipped with eco-friendly technologies that may reduce operational costs in the long run.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions to assess their reliability and expertise.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering LHD trucks to your specific market.
- After-Sales Support: Evaluate the level of support offered post-purchase, including maintenance services and spare parts availability.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the LHD trucks you consider comply with local mining regulations and safety standards. Non-compliance can lead to significant delays and penalties.
- Safety Standards: Confirm that the equipment meets safety regulations applicable in your region.
- Environmental Compliance: Check for adherence to environmental guidelines to avoid operational disruptions.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trial periods for the LHD trucks you are considering. This allows you to assess their performance in real-world conditions before making a financial commitment.
- Performance Evaluation: Pay attention to how the equipment operates under load and in various conditions.
- Operator Feedback: Gather insights from operators who will be using the equipment daily, as their input can be invaluable.
Step 6: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
When evaluating different LHD trucks, consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance costs, fuel efficiency, and potential downtime.
- Maintenance Expenses: Look into the average maintenance costs associated with each model.
- Fuel Efficiency: Assess how fuel consumption impacts overall operational costs over time.
Step 7: Finalize Negotiations and Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier and model, focus on negotiating favorable terms. Ensure that the contract outlines all aspects, including warranties, delivery schedules, and service agreements.
- Warranties: Confirm what is covered under warranty and for how long.
- Delivery Terms: Clarify timelines and logistics for equipment delivery to avoid unexpected delays.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for LHD trucks with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance their mining operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for lhd Truck Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for LHD Truck Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing LHD trucks, such as steel and specialized alloys, significantly impact the overall cost. The quality and sourcing of these materials can vary based on regional availability and market conditions.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the production of LHD trucks. Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographic location, labor laws, and the availability of skilled workers in the manufacturing region.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. These overhead costs can differ among manufacturers depending on their operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The investment in tooling is a critical factor, as it involves the creation of molds and machines necessary for production. Advanced tooling can enhance precision but may increase initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that LHD trucks meet industry standards and certifications incurs additional costs. Effective QC processes can prevent defects and enhance product reliability, leading to potential long-term savings.
-
Logistics: Transportation of LHD trucks to buyers involves shipping, handling, and customs duties, which vary by destination. Understanding the logistics costs is vital for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can be influenced by market demand, competition, and product differentiation.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect LHD Truck Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of LHD trucks, making it essential for buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized LHD trucks tailored to specific operational needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO standards) can elevate the price. However, investing in quality can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer service life.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capabilities of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in the transaction is crucial for pricing. Different terms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency in LHD Truck Sourcing?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to ensure cost efficiency when sourcing LHD trucks:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to explore discounts, flexible payment terms, or bundled services that can reduce overall costs.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, fuel efficiency, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment in a more reliable truck can yield savings over time.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations in the LHD truck industry. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help in budgeting.
-
Leverage Local Knowledge: For international buyers, understanding local regulations and market conditions can aid in making informed purchasing decisions. Collaborating with local experts can enhance sourcing strategies.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Variations in currency exchange rates can significantly impact the final cost. Buyers should consider locking in prices or hedging against currency risks.
-
Import Duties and Tariffs: Different countries have varied import duties that can affect the total cost. Researching these beforehand can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Local Regulations: Compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and safety standards can affect the choice of LHD trucks and their associated costs.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always approach pricing information with caution, as prices can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare and negotiate effectively.
By understanding the intricacies of cost components, pricing influencers, and effective sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing lhd Truck With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to LHD Trucks
In the competitive landscape of underground mining, companies often seek efficient solutions for material handling. Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks are a popular choice due to their versatility and performance. However, several alternative technologies and methods can also fulfill similar objectives, offering unique advantages and potential drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize operations and reduce costs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | LHD Truck | Battery Electric Truck | Conveyor System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity and flexibility | Lower load capacity, but high efficiency in certain environments | Continuous material flow, less downtime |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and operational costs | Higher upfront cost, lower operational costs | Moderate initial investment, low operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training and infrastructure | Needs charging infrastructure, training for operators | Requires significant installation and setup |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed, moderate complexity | Lower maintenance with electric systems | Low maintenance, but requires regular checks |
| Best Use Case | Versatile for various mining applications | Ideal for environmentally conscious operations | Best for large-scale, continuous operations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Battery Electric Truck
Battery electric trucks are becoming increasingly popular in the mining sector due to their lower emissions and operating costs. These vehicles excel in environments where air quality is a concern, making them suitable for operations in confined spaces. However, the initial investment for battery technology can be significant, and companies must ensure they have the necessary charging infrastructure in place. While they may not match the load capacity of traditional LHD trucks, their efficiency and lower energy costs can make them a compelling choice for environmentally conscious operations.
Conveyor System
Conveyor systems provide a continuous method for transporting materials from one point to another, reducing the need for multiple vehicle trips. This technology is particularly advantageous in large-scale operations where material flow needs to be consistent and efficient. While the initial setup and installation costs can be moderate, the operational costs tend to be lower over time. However, conveyor systems may not be as flexible as LHD trucks, especially in varied terrains or smaller spaces. They also require regular inspections to ensure functionality, which can be a downside in terms of maintenance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the ideal solution for underground material handling, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, cost implications, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs. LHD trucks are a robust choice for their versatility and high capacity, making them suitable for diverse applications. However, alternatives like battery electric trucks and conveyor systems present viable options, especially for operations that prioritize sustainability or efficiency in large-scale environments. Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational goals and environmental considerations of the mining project at hand.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for lhd Truck
What Are the Key Technical Properties of LHD Trucks?
When considering Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks for underground mining operations, several technical specifications are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Below are essential properties to consider:
-
Hauling Capacity
– Definition: This is the maximum weight that an LHD truck can carry, typically measured in tonnes.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right capacity is vital for meeting production targets. Overloading can lead to equipment damage, while underloading may result in inefficient operations and increased costs. -
Engine Power and Type
– Definition: Refers to the engine’s horsepower and whether it’s diesel or electric.
– B2B Importance: The engine type impacts operational costs and environmental compliance. Electric engines, for instance, are increasingly favored for their lower emissions and reduced operational costs, aligning with sustainable practices. -
Breakout Force
– Definition: This is the force exerted by the loader to break through rock or other materials, usually expressed in kilonewtons (kN).
– B2B Importance: A higher breakout force translates to improved efficiency in loading operations, enabling quicker cycles and enhanced productivity in challenging mining conditions. -
Operating Weight
– Definition: The total weight of the LHD truck when fully equipped and operational.
– B2B Importance: Understanding operating weight is essential for assessing the truck’s stability and performance on inclined surfaces, which is common in mining applications. -
Turning Radius
– Definition: This is the smallest circular turn that the truck can make, measured in meters.
– B2B Importance: A smaller turning radius is advantageous in tight underground spaces, allowing for better maneuverability and efficiency in operations. -
Serviceability Features
– Definition: Includes aspects such as ease of access to components for maintenance and repair.
– B2B Importance: Quick and straightforward maintenance reduces downtime, ensuring that operations remain productive and costs are kept under control.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know About LHD Trucks?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and decision-making in the procurement of LHD trucks. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often seek OEM products for their reliability and compatibility with existing machinery, ensuring better performance and easier maintenance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively, especially for large-scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal process where buyers ask suppliers for price quotes on specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms across multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact overall project budgets. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: The purchase price of an asset plus the costs of operation, maintenance, and disposal over its lifecycle.
– Importance: Evaluating TCO helps buyers assess the long-term financial implications of their purchase, ensuring that they choose equipment that fits their budget and operational needs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that operations are not delayed due to equipment shortages.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and drive profitability in their mining operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the lhd Truck Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the LHD Truck Market for International Buyers?
The Load Haul Dump (LHD) truck sector is experiencing a dynamic transformation driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for efficient and sustainable mining practices is propelling the market forward, particularly in emerging economies like Brazil and Nigeria. Technological advancements, such as automation and electrification, are becoming critical in optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. The introduction of battery-electric and hybrid LHD models is not only addressing environmental concerns but also appealing to businesses looking to improve their bottom line.
B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing equipment that enhances productivity and safety. Features like ergonomic design, advanced operator assistance systems, and enhanced payload capacities are becoming essential criteria for procurement. Furthermore, international buyers are seeking suppliers that offer comprehensive service packages, including maintenance, training, and readily available spare parts, to minimize downtime and maximize operational efficiency.
As the LHD market becomes more competitive, buyers are encouraged to leverage digital tools and platforms for sourcing. Online marketplaces and dealer locator services streamline the procurement process, allowing companies to compare different models and prices, ensuring they get the best value for their investment. This trend toward digitalization is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where traditional supply chains may be less established.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the LHD Truck Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it has become a core consideration for B2B buyers in the LHD truck market. The environmental impact of mining operations is under scrutiny, leading companies to prioritize equipment that aligns with their sustainability goals. Buyers are increasingly seeking LHD trucks that feature low-emission technologies, such as electric or hybrid engines, which significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality in mining areas.
Moreover, the importance of ethical sourcing is gaining traction among international buyers. Companies are looking for suppliers that maintain transparent supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ standards are becoming essential benchmarks for evaluating potential suppliers. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sourcing of materials used in LHD trucks, ensuring they are from responsible sources that prioritize environmental stewardship.
Incorporating sustainability into procurement strategies not only enhances a company’s corporate social responsibility profile but can also lead to long-term cost savings. Investments in greener technologies can result in lower operational costs and increased efficiency, ultimately benefiting the bottom line.
What Is the Historical Context of LHD Trucks in Mining Operations?
The Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks have evolved significantly since their inception in the mid-20th century. Initially designed for underground mining, these vehicles have undergone substantial technological advancements, improving their efficiency and safety features. The introduction of hydraulic systems and later, electronic controls, revolutionized their performance, allowing for greater precision in load handling.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the shift toward automation began, with manufacturers introducing features that enhanced operator comfort and reduced physical strain. Today, LHD trucks are at the forefront of the mining sector’s transition toward sustainability, with electric and hybrid models leading the charge. This historical evolution underscores the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the changing demands of the market, particularly for international B2B buyers looking to invest in state-of-the-art equipment.
In summary, understanding the current market dynamics, the push towards sustainability, and the historical context of LHD trucks can empower B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of lhd Truck
-
How do I choose the right LHD truck for my mining operation?
Selecting the appropriate Load Haul Dump (LHD) truck requires careful consideration of several factors. First, assess the specific needs of your mining operation, such as the size of the mine, the type of ore being extracted, and the mining method employed. Evaluate the truck’s capacity, power, and design features that enhance performance in your unique environment. Additionally, consider the availability of parts and service support in your region, as this can significantly impact operational efficiency and maintenance costs. -
What are the benefits of electric vs. diesel LHD trucks?
Electric LHD trucks offer significant advantages, including reduced emissions, lower operational costs, and decreased noise levels, making them ideal for underground environments. They also contribute to a healthier work environment for operators. Conversely, diesel LHD trucks typically provide greater power and longer operational ranges, making them suitable for larger mines or those with extensive haulage requirements. Ultimately, the choice depends on your operational goals, local regulations, and environmental considerations. -
What customization options are available for LHD trucks?
Most manufacturers offer a variety of customization options for LHD trucks to meet specific operational needs. Customizations may include different load capacities, specialized attachments, enhanced safety features, and ergonomic operator controls. It’s also possible to integrate automation technologies for improved efficiency. When considering customization, consult with your supplier to understand the available options and how they can be tailored to your operational requirements. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing LHD trucks?
Minimum order quantities for LHD trucks can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may have a MOQ of one unit, while others may require bulk orders to secure favorable pricing. It’s advisable to communicate directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your operational needs and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing LHD trucks internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of LHD trucks can vary widely based on the supplier, the buyer’s creditworthiness, and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include a deposit upfront with the balance due upon delivery or after installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans. Always review the payment terms carefully and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment. -
How can I vet suppliers of LHD trucks to ensure quality and reliability?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation in the industry through customer reviews and testimonials. Request references from other buyers, particularly those in your region. Evaluate their manufacturing processes, quality assurance protocols, and after-sales support. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible, or attending trade shows where they exhibit. Certifications from recognized industry bodies can also indicate a commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing LHD trucks?
Logistics for importing LHD trucks involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. It’s crucial to work with logistics providers experienced in heavy equipment transportation to ensure compliance with international shipping regulations. Factor in costs related to tariffs, taxes, and insurance. Proper planning and coordination with your supplier can help mitigate delays and ensure timely delivery to your site. -
What are the key quality assurance practices to look for in LHD truck manufacturers?
When assessing LHD truck manufacturers, look for established quality assurance practices such as ISO certification and adherence to industry standards. Inquire about their testing protocols for durability and performance under various conditions. A solid warranty program can also be an indicator of confidence in their products. Finally, evaluate their approach to after-sales support, as ongoing service and maintenance are critical to the longevity of your equipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Lhd Truck Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cat – R2900 XE Diesel Electric Loader
Domain: cat.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: This company, Cat – R2900 XE Diesel Electric Loader, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Komatsu – LHDs for Underground Haulage
Domain: komatsu.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
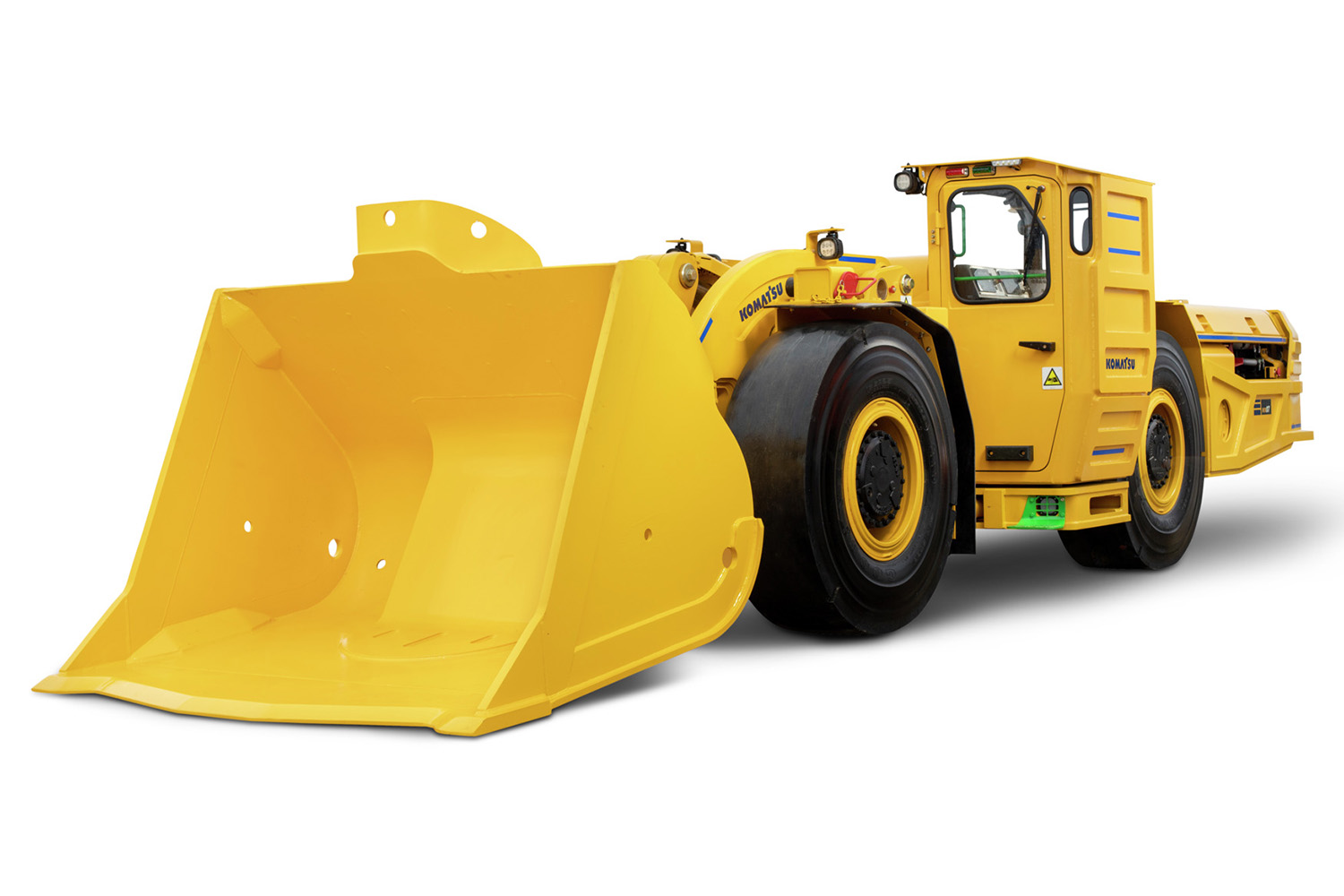
Introduction: Breakout force, speed, reliability, and operator comfort are key features of Komatsu’s LHDs designed for underground hard rock haulage. The product line includes narrow vein designs and super-efficient hybrid drives, catering to various operational needs.
3. Epiroc – Loaders and Trucks
Domain: epiroc.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Loaders and trucks (LHDs) include Electric loaders, Diesel loaders, Continuous loaders, Diesel trucks, and Electric trucks. They are designed for reliable performance in mining applications.
4. MineMaster – GHH LHDs and Dump Trucks
Domain: minemaster.eu
Introduction: GHH LHDs and Dump Trucks are designed for mining and tunnelling operations, known for their robust, durable, and reliable characteristics. Key features include:
– Compact design with ergonomic operator position and side-mounted seat for optimum visibility.
– LHD capacity ranges from 1 to 21 tonnes.
– Applications include underground mining, tunnelling, hydro, and civil engineering projects.
– Vari…
5. Japan Partner – Used LHD Kei-Trucks
6. Boyd CAT – Underground Mining Load Haul Dump Loaders
Domain: boydcat.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Underground Mining Load Haul Dump (LHD) Loaders offered by Boyd CAT include:
1. **R2900 XE Underground Diesel-Electric LHD Loader**
– Engine Model: Cat ® C15
– Engine Power:
– Stage V: 449 hp
– Tier 2/Stage II: 447 hp
2. **R1700 XE Underground Battery-Electric LHD Loader**
– Bucket Capacities: 5.7-7.5 m³ (7.5-9.8 yd³)
– Nominal Payload Capacity: 33,069 lb
– Oper…
7. Custom Truck – Spiradrill LHD-35 Pressure Digger
Domain: customtruck.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘Spiradrill LHD-35 Pressure Digger’, ‘type’: ‘Hydraulic machine’, ‘features’: ‘Truck-mounted, Road Legal, no permits required’, ‘drill_depth’: “35′”, ‘drill_torque’: ‘30,000 FT LBS’, ‘kelly_bar’: ‘3 Bar, 3 1/2” x 5” x 7” square’, ‘drill_diameter’: ’72″‘, ‘maximum_rpm_low’: ’22 RPM’, ‘maximum_rpm_mid’: ’56 RPM’, ‘spin_off_speed’: ‘140 RPM’, ‘main_winch’: ‘12,000 Lbs’, ‘service_winch’: ‘8,0…
8. Car Junction – Total Stock: 1381 Key Brands
Domain: lhd.carjunction.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Total Stock: 1381
Key Brands: Toyota, Nissan, Mitsubishi, Honda, Mercedes Benz, Suzuki, DAF, Daihatsu, Ford, Foton, GMC, Hino, Hyundai, Isuzu, Iveco, Jeep, Kia, Land Rover, Lexus, Lincoln, Mahindra, Man, Mazda, MINI, Neoplan, Opel, Porsche, Renault, Scania, Setra, Subaru, Temsa, Volkswagen, Volvo.
Types of Trucks: Left Hand Trucks, Pickup Trucks, Garbage Trucks, Flatbed Trucks, Box Trucks, Tanker …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for lhd Truck
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your LHD Truck Procurement?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of underground mining, strategic sourcing for Load Haul Dump (LHD) trucks is paramount for maximizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who are not only aligned with their operational needs but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and technological advancement. With options ranging from diesel to electric and hybrid models, the choice of equipment can significantly impact productivity and environmental footprint.
Moreover, leveraging strategic sourcing can facilitate better negotiation terms and foster long-term partnerships with manufacturers. This enables buyers to access the latest innovations, including automated functions and enhanced safety features, which are critical in challenging mining environments.
As we look ahead, the demand for LHD trucks is anticipated to grow, driven by the need for efficient mining solutions in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By investing in robust sourcing strategies today, international buyers can position themselves advantageously in a competitive market. Embrace the future of mining by exploring partnerships with leading LHD manufacturers and ensure your operations are equipped for success.