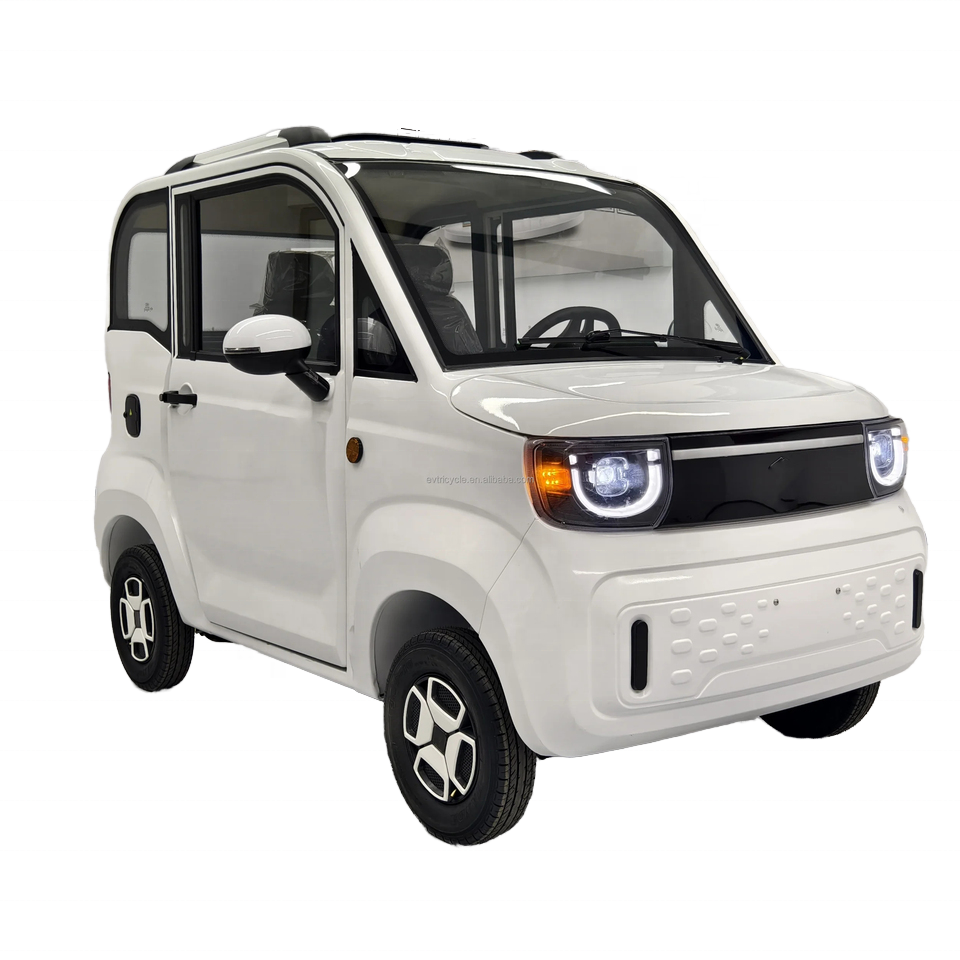
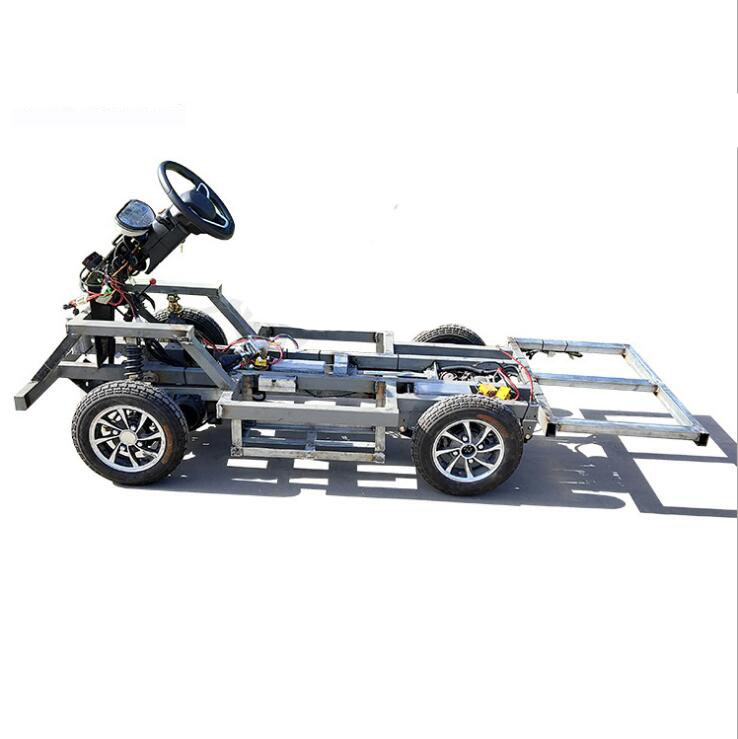
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small electric car chip price
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing small electric car chips at the right price poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers strive to meet the growing demand for affordable, efficient, and high-performance vehicles, understanding the intricacies of chip pricing becomes essential. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of small electric car chips, their applications in diverse vehicle models, and key factors influencing their costs.
By exploring critical topics such as supplier vetting processes, market trends, and pricing strategies, this guide equips buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Brazil—with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Navigating the global market for small electric car chips requires an awareness of emerging technologies and regional market dynamics, as well as the ability to evaluate suppliers based on quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
As Chinese manufacturers continue to gain traction in the EV sector, with competitive pricing and innovative technologies, understanding the landscape of chip pricing will be vital for businesses looking to secure a foothold in this evolving market. This guide serves as a valuable resource for B2B buyers, enabling them to effectively navigate the complexities of small electric car chip pricing while maximizing their investment and ensuring the success of their electric vehicle offerings.
Understanding small electric car chip price Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microcontrollers | Low-cost, integrated circuits; essential for basic functions | Entry-level EVs, budget models | Pros: Affordable, sufficient for basic needs. Cons: Limited functionality for advanced features. |
| Power Management ICs | Regulate power distribution; enhance battery efficiency | Mid-range and high-performance EVs | Pros: Improved efficiency, longer battery life. Cons: Higher cost compared to basic chips. |
| System-on-Chip (SoC) | Combines multiple functions into a single chip; high integration | Premium EVs, autonomous vehicles | Pros: Compact design, reduced space requirements. Cons: Complexity can lead to higher failure rates. |
| Communication Chips | Facilitate vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication | Smart city initiatives, fleet management | Pros: Enhances connectivity, supports advanced features. Cons: May increase overall vehicle cost. |
| Sensor Chips | Enable advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) | Safety-focused EVs, luxury vehicles | Pros: Enhances safety, supports autonomous driving. Cons: Can be expensive, requires integration with existing systems. |
What Are Microcontrollers and When Should B2B Buyers Consider Them?
Microcontrollers are fundamental components in small electric cars, providing essential control for basic functions such as battery management and motor control. These chips are cost-effective, making them ideal for entry-level electric vehicles targeting budget-conscious consumers. B2B buyers should consider microcontrollers when developing budget models where performance demands are minimal, balancing cost and functionality effectively.
How Do Power Management ICs Benefit Mid-Range Electric Vehicles?
Power Management Integrated Circuits (ICs) are crucial for enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles by regulating power distribution from the battery to various components. They are particularly beneficial for mid-range and high-performance EVs, where battery life and energy efficiency are paramount. B2B buyers should assess their long-term operational costs versus initial investment when considering these chips, as they can lead to significant savings through improved battery management.
Why Choose System-on-Chip (SoC) Solutions for Premium Electric Vehicles?
System-on-Chip solutions combine multiple functionalities into a single integrated circuit, allowing for a more compact design and reduced space requirements in premium electric vehicles. These chips are essential for advanced features such as autonomous driving and high-performance applications. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced complexity against the higher costs and potential reliability issues that can arise from integrating multiple functions into a single chip.
What Role Do Communication Chips Play in Smart Electric Vehicles?
Communication chips are vital for enabling vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, which is essential for smart city initiatives and fleet management solutions. These chips facilitate real-time data exchange between vehicles and infrastructure, improving safety and traffic efficiency. B2B buyers should consider the added value these chips bring in terms of connectivity and advanced features, although they may increase the overall vehicle cost.
How Do Sensor Chips Enhance Safety in Electric Vehicles?
Sensor chips are integral to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), providing the necessary data for features like collision avoidance and lane-keeping assistance. They are particularly important for safety-focused electric vehicles and luxury models. B2B buyers must evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of integrating sensor chips, as while they enhance safety and support autonomous driving capabilities, they can also significantly increase the vehicle’s overall cost.
Key Industrial Applications of small electric car chip price
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of small electric car chip price | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration in Electric Vehicle (EV) production | Reduces overall production costs, enhances vehicle performance | Quality assurance, compliance with international standards |
| Fleet Management | Cost analysis for electric fleet upgrades | Optimizes budget allocation and maximizes ROI on fleet investments | Long-term partnerships with suppliers, local market knowledge |
| Battery Technology | Development of affordable battery management systems | Increases energy efficiency, prolongs battery life | Supplier reliability, technological compatibility |
| Public Transportation | Implementation in electric public transport vehicles | Improves operational efficiency, lowers maintenance costs | Government regulations, local sourcing options |
| Consumer Electronics | Embedded systems in EV-related smart devices | Enhances consumer experience, drives additional revenue streams | Innovation capability, competitive pricing |
How Is Small Electric Car Chip Price Applied in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the small electric car chip price is pivotal for integrating advanced technologies into electric vehicles (EVs). Manufacturers leverage these chips to enhance performance while maintaining competitive pricing. This is crucial for companies looking to optimize production costs without compromising on quality. International buyers must consider sourcing chips that meet stringent quality standards and regulatory compliance in their respective markets, especially in regions like Europe and South America.
What Role Does Small Electric Car Chip Price Play in Fleet Management?
Fleet management companies are increasingly analyzing the small electric car chip price to make informed decisions about upgrading their electric fleets. By understanding the cost implications of these chips, businesses can better allocate budgets and maximize return on investment (ROI). Buyers in this sector should focus on establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers who can provide consistent quality and support, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and the Middle East.
How Does Small Electric Car Chip Price Influence Battery Technology Development?
In the battery technology industry, the small electric car chip price is critical for developing cost-effective battery management systems. These chips help improve energy efficiency and extend battery lifespan, which is vital for both manufacturers and consumers. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers known for reliability and technological innovation, ensuring that products are compatible with existing systems and meet international standards.
What Are the Benefits of Small Electric Car Chip Price in Public Transportation?
Public transportation systems are adopting small electric car chips to enhance their electric vehicle fleets. The incorporation of these chips leads to improved operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs, which are essential for sustainable transportation solutions. Buyers in this sector should be aware of government regulations that may influence sourcing decisions, as well as the importance of local sourcing to support community economies.
How Can Consumer Electronics Leverage Small Electric Car Chip Price?
In the consumer electronics domain, small electric car chips are being integrated into EV-related smart devices, enhancing user experiences and driving new revenue streams. Understanding the pricing dynamics of these chips enables businesses to innovate while keeping costs manageable. Buyers should seek suppliers that not only offer competitive pricing but also demonstrate a strong capacity for innovation, ensuring they stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small electric car chip price’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Fluctuating Chip Prices in the Electric Vehicle Market
The Problem: B2B buyers in the electric vehicle (EV) sector often face the challenge of fluctuating prices for small electric car chips. This volatility can severely impact budgeting and financial forecasting, particularly for manufacturers who rely on these components to remain competitive. For example, a manufacturer may have planned a production run based on a certain chip price, only to find that prices have surged due to supply chain disruptions or increased demand. This can lead to unanticipated costs, project delays, and ultimately, reduced market competitiveness.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of price fluctuations, B2B buyers should consider establishing long-term contracts with chip suppliers that include price lock mechanisms. Engaging in strategic partnerships with manufacturers allows for better forecasting and inventory management. Additionally, buyers can diversify their supplier base to reduce dependency on any single source, thus spreading risk. It’s also beneficial to stay informed about industry trends and market dynamics, as this insight can enable buyers to make timely purchasing decisions before prices escalate. Utilizing data analytics to predict price trends based on historical data can further enhance decision-making.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality while Managing Costs
The Problem: A common concern for B2B buyers is the delicate balance between cost and quality when sourcing small electric car chips. Lower-priced chips may seem attractive, but they can compromise the vehicle’s performance, safety, and longevity. This is particularly critical for companies aiming to enter markets with stringent regulatory requirements, such as Europe. A poorly performing chip can lead to recalls, reputational damage, and financial losses, making it essential for buyers to ensure that cost-cutting does not come at the expense of quality.
The Solution: To ensure quality while managing costs, buyers should adopt a comprehensive supplier evaluation process that includes quality audits and performance testing of the chips. Establishing clear specifications and performance criteria in the procurement process is crucial. Collaborating with suppliers to understand their manufacturing processes can also provide insights into their quality control measures. Furthermore, buyers should invest in pilot programs to test chips in real-world conditions before full-scale deployment. This approach not only safeguards product integrity but can also help negotiate better pricing based on proven performance.
Scenario 3: Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions remain a persistent issue affecting the availability and pricing of small electric car chips. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics can create bottlenecks in production and distribution, leading to increased lead times and costs. For B2B buyers, this unpredictability complicates planning and can result in production delays, impacting delivery schedules and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To combat supply chain disruptions, B2B buyers should implement a robust risk management strategy that includes diversifying their supply chain. Identifying alternative suppliers across different geographic regions can provide a buffer against localized disruptions. Additionally, maintaining a safety stock of critical components can help mitigate immediate impacts from supply shortages. Buyers should also engage in regular communication with suppliers to monitor their capacity and any potential issues that may arise. Leveraging technology, such as supply chain management software, can enhance visibility and allow for proactive adjustments to sourcing strategies in response to emerging risks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small electric car chip price
When selecting materials for small electric car chips, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and overall impact on performance. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in chip manufacturing, providing insights tailored for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Silicon in Small Electric Car Chips?
Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material due to its excellent electrical properties and thermal stability. It can operate effectively at high temperatures, typically rated up to 150°C, making it suitable for automotive applications. Silicon also exhibits good corrosion resistance, which is crucial for longevity in various environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons:
Silicon’s primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes. However, its limitations include a lower electron mobility compared to other materials, which can affect performance in high-speed applications. Additionally, the complexity of the manufacturing process can lead to increased production times.
Impact on Application:
Silicon’s compatibility with standard electronic components makes it a reliable choice for various applications, including power management and signal processing in electric vehicles.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers in Europe, for instance, may prefer silicon chips that meet stringent automotive safety standards.
How Does Gallium Nitride Enhance Performance in Electric Car Chips?
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is emerging as a superior alternative to silicon, particularly in high-frequency and high-power applications. It can withstand higher voltages and temperatures, often rated up to 200°C, which is beneficial for electric vehicle systems that require efficient power conversion.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of GaN is its high efficiency and fast switching capabilities, which can lead to smaller and lighter components. However, GaN is more expensive than silicon and requires more complex manufacturing techniques, which can increase overall costs.
Impact on Application:
GaN chips are particularly effective in applications like onboard chargers and power inverters, where efficiency is paramount. Their ability to handle high frequencies also allows for better thermal management.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that GaN components comply with local regulations and standards, especially in regions with strict electronic waste management laws.
What Role Does Silicon Carbide Play in Electric Vehicle Chip Design?
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is another advanced material that offers significant advantages for electric vehicle applications. It can operate at higher temperatures (up to 200°C) and voltages, making it suitable for high-performance power electronics.
Pros and Cons:
SiC’s primary advantage is its ability to reduce energy losses, thereby improving the overall efficiency of electric vehicles. However, it is more costly than both silicon and GaN, and its manufacturing process is less mature, which can lead to supply chain challenges.
Impact on Application:
SiC is ideal for applications requiring high power density, such as traction inverters and DC-DC converters, where efficiency and thermal performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider the availability of SiC components in their regions, as supply chains may vary significantly. Additionally, understanding the specific certifications required for automotive applications in different countries is essential.
How Do Conductive Polymers Impact Chip Performance in Electric Vehicles?
Conductive polymers are gaining traction in the development of flexible and lightweight electronic components. They offer good conductivity and can be engineered to provide specific electrical properties.
Pros and Cons:
The main advantage of conductive polymers is their lightweight nature, which can contribute to overall vehicle efficiency. However, they generally have lower thermal stability and mechanical strength compared to traditional materials, which may limit their application in high-performance settings.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly suited for applications in sensors and flexible electronics, where weight and form factor are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the varying performance standards for conductive polymers in automotive applications across different regions, particularly in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Small Electric Car Chips
| Material | Typical Use Case for small electric car chip price | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Power management and signal processing | Cost-effective and widely available | Lower electron mobility and longer manufacturing time | Low |
| Gallium Nitride (GaN) | Onboard chargers and power inverters | High efficiency and fast switching capabilities | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Traction inverters and DC-DC converters | Reduced energy losses and high power density | More expensive and less mature manufacturing process | High |
| Conductive Polymers | Sensors and flexible electronics | Lightweight and customizable electrical properties | Lower thermal stability and mechanical strength | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials relevant to small electric car chip pricing, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small electric car chip price
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Small Electric Car Chips?
Manufacturing small electric car chips involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and efficiency. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of high-purity semiconductor materials, typically silicon or gallium nitride. These materials are essential for producing reliable and efficient chips. The preparation involves several steps, including cleaning, slicing, and doping the silicon wafers to enhance their electrical properties. This phase is crucial, as impurities can significantly affect the performance of the final product.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage takes place. This involves photolithography, where light-sensitive chemicals are applied to the wafer surface. Patterns are then etched onto the wafers using various techniques, including dry and wet etching. This stage also includes ion implantation, where ions are embedded into the silicon to alter its electrical characteristics. Each step must be executed with precision to maintain the integrity of the chip design.
Assembly
After forming, the chips undergo assembly. This process involves cutting the wafers into individual chips, followed by the attachment of bonding wires and encapsulation to protect the chips from environmental factors. Automated equipment is commonly used during this stage to ensure consistency and speed. The assembly process is critical, as any defects can lead to failures in the final product.
Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which includes testing and packaging the chips. This phase ensures that all chips meet the required specifications and are ready for integration into electric vehicles. The chips are typically packaged in protective casings that facilitate thermal management and electrical connectivity.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Small Electric Car Chip Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of small electric car chips, given the stringent requirements for performance and reliability in automotive applications. The QA process adheres to various international standards, including ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system.
International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO 9001, manufacturers often pursue industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) to demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards. These certifications are particularly important for B2B buyers looking to ensure that their suppliers meet international quality benchmarks.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with multiple checkpoints established to monitor quality at various stages. Key QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards. Any subpar materials are rejected, preventing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC monitors critical parameters to ensure each stage is performed correctly. This includes real-time inspections and measurements to detect deviations from the specified process.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, the final products undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet all performance specifications. This stage often includes electrical testing, thermal cycling, and reliability testing to ensure long-term performance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Chip Quality Assurance?
Testing methods are vital for validating the performance and reliability of small electric car chips. Common techniques include:
-
Functional Testing: This method assesses whether the chip performs its intended function under various conditions. It simulates real-world scenarios to ensure reliability.
-
Burn-In Testing: This involves subjecting the chips to elevated temperatures and voltages to accelerate aging and identify early failures. This method helps ensure long-term reliability.
-
Environmental Testing: Chips are tested under extreme conditions, including temperature fluctuations and humidity, to evaluate their durability in different environments.
-
Electrical Testing: This includes measuring parameters like current, voltage, and power consumption to ensure the chip operates within specified limits.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial for ensuring product reliability and compliance. Here are several strategies to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Audits can reveal adherence to international standards and highlight areas for improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes. These reports should outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can evaluate suppliers’ facilities and processes, providing unbiased assessments of quality control measures.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances when it comes to quality control in chip manufacturing. Understanding local regulations, certification requirements, and cultural differences in business practices is essential.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be aware of specific regulations governing electronic components in their respective regions. For instance, Europe has stringent standards for electronic waste and recycling, which manufacturers must comply with.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality assurance. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication about quality standards and expectations.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Ensuring proper documentation and traceability is crucial for international transactions. Buyers should require that suppliers maintain detailed records of production and quality control processes, which can be invaluable for audits and compliance checks.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing small electric car chips, ensuring they receive high-quality components that meet international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small electric car chip price’
The procurement of small electric car chips is a critical process for businesses involved in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. This guide provides a structured approach to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing these essential components, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their technical requirements and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the first step in sourcing small electric car chips. Identify the specific functionalities required, such as processing power, energy efficiency, and compatibility with your vehicle’s architecture. This clarity will enable you to communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the chips meet your engineering standards.
- Consider performance metrics: Look for parameters like processing speed, power consumption, and thermal management.
- Evaluate integration needs: Ensure the chips can seamlessly integrate into your existing systems without requiring extensive modifications.
Step 2: Research the Market Landscape
Understanding the market landscape is crucial for making strategic sourcing decisions. Conduct thorough research on current suppliers, emerging technologies, and pricing trends. This knowledge will help you identify potential partners and anticipate future developments in the small electric car chip sector.
- Identify leading manufacturers: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the EV industry.
- Monitor price fluctuations: Stay informed about global supply chain dynamics that may affect pricing, such as material shortages or geopolitical factors.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from previous clients in similar industries. This step will help you gauge the reliability and reputation of each potential supplier.
- Assess quality assurance practices: Inquire about their quality control processes and certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Review case studies: Look for examples of successful partnerships that demonstrate their ability to meet technical specifications and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their small electric car chips for testing. This hands-on evaluation will allow you to assess the chips’ performance in real-world applications, ensuring they meet your specifications.
- Conduct rigorous testing: Evaluate factors such as durability, temperature resistance, and overall performance under load.
- Gather feedback from engineering teams: Involve your technical team in the testing process to gain insights into any integration challenges.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Negotiating pricing and terms is a critical step in the procurement process. Engage in discussions with your selected suppliers to reach a mutually beneficial agreement that considers your budget constraints and the supplier’s capabilities.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Look beyond the initial price and factor in aspects like warranty, support services, and potential future upgrades.
- Establish clear delivery timelines: Ensure that the supplier can meet your production schedules and discuss penalties for delays.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier choice, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. This step is vital to ensure that the chips are manufactured in accordance with safety and quality regulations.
- Check for relevant certifications: Look for certifications such as RoHS, CE, or UL that indicate adherence to industry standards.
- Review compliance records: Request documentation that confirms their compliance history and any audits they have undergone.
Step 7: Monitor Supplier Performance Post-Purchase
After procurement, maintain ongoing communication with your supplier to monitor performance and address any issues promptly. This proactive approach will help you build a strong partnership and ensure the continued reliability of your chip supply.
- Set performance metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate delivery, quality, and support.
- Schedule regular reviews: Conduct periodic reviews to discuss performance and any necessary adjustments to the partnership.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for small electric car chips, ensuring they secure high-quality components that align with their business objectives and technical requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small electric car chip price Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Small Electric Car Chip Pricing?
When sourcing small electric car chips, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The semiconductor materials used in chip manufacturing, such as silicon and gallium nitride, significantly impact costs. Prices for these raw materials can fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for chip design, manufacturing, and testing. Labor costs vary by region, with higher wages in Europe compared to emerging markets in Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for production lines, including molds and testing equipment, can be substantial. These costs are often amortized over large production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures ensure that chips meet performance standards. This involves testing equipment and procedures, which add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are also significant. The choice of shipping method and distance from suppliers can influence the total logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary widely based on competition, market conditions, and the supplier’s strategic positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Small Electric Car Chip Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of small electric car chips:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers often provide discounts based on volume, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Chips designed for specific applications or with advanced features may carry a premium price. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Chips that meet high-quality standards or industry certifications, such as ISO or IATF, may be priced higher. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are essential for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more due to their reliability and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and responsibility for costs can impact the total landed cost of chips. Different Incoterms can shift costs between buyer and seller, affecting overall pricing.
What Tips Can Help International B2B Buyers Navigate Chip Pricing?
For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate: Leverage volume and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or flexible payment terms for committed buyers.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not only the upfront costs but also the long-term implications of chip performance, reliability, and potential failure rates. A cheaper chip may lead to higher costs if it requires frequent replacements or results in system failures.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand that pricing can vary significantly based on regional factors such as tariffs, local market conditions, and currency fluctuations. Buyers should factor these into their budgeting.
-
Engage Multiple Suppliers: Sourcing from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, technological advancements, and geopolitical factors that may influence prices. This knowledge can inform better purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for small electric car chips can vary widely based on the above factors and market conditions. Buyers should seek quotes tailored to their specific needs and requirements, as indicative prices may not reflect the final cost.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small electric car chip price With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Small Electric Car Chip Pricing
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, understanding the various options available for small electric car chips is essential for B2B buyers. These chips are critical for performance, efficiency, and overall vehicle functionality. However, several alternative technologies and methods can achieve similar goals. This analysis will compare the pricing and value of small electric car chips against two viable alternatives: integrated automotive software solutions and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) components.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Small Electric Car Chip Price | Integrated Automotive Software Solutions | Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency and speed | Variable, dependent on software design | Proven reliability, lower efficiency in comparison |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Potentially lower long-term costs | Typically lower upfront costs, higher long-term fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires advanced integration | Easier integration with existing systems | Established technology, minimal adaptation needed |
| Maintenance | Lower due to fewer moving parts | Ongoing updates and potential licensing fees | Higher due to mechanical wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Optimal for EVs | Suitable for hybrid or multi-platform vehicles | Best for traditional vehicles and fossil fuel reliance |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Integrated Automotive Software Solutions
Integrated automotive software solutions provide a modern approach to vehicle functionality. They enable manufacturers to optimize performance through software updates and data analytics, often resulting in lower costs over time. These solutions can be easier to implement within existing vehicle architectures, as they require less physical modification. However, the reliance on software may lead to performance variability, depending on the design and updates available. Additionally, ongoing maintenance may incur licensing fees, which could offset initial savings.
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Components
Traditional ICE components are well-established within the automotive industry and offer a proven track record of reliability. The upfront costs for these components are often lower than those for electric vehicle technologies, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, ICE systems are less efficient than electric alternatives, leading to higher long-term fuel costs and more frequent maintenance due to mechanical wear and tear. As the world shifts towards sustainability, relying on ICE components may not align with future market demands and regulatory pressures.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Decide on the Right Solution?
Choosing the right solution for small electric car chips involves evaluating performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and specific use cases. B2B buyers should assess their long-term goals, the regulatory environment in their markets, and the specific applications they are targeting. For companies focused on sustainability and efficiency, investing in small electric car chips may be the best choice. Conversely, if initial cost is a primary concern and the market is still heavily reliant on traditional vehicles, ICE components could be a more suitable option. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each alternative will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small electric car chip price
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Small Electric Car Chips?
When evaluating small electric car chips, B2B buyers should focus on several critical specifications that influence performance, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential technical properties:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of a chip, often defined by its semiconductor composition (e.g., silicon, silicon carbide), directly impacts its efficiency and thermal management. High-grade materials can enhance performance, reduce energy losses, and extend the lifespan of chips, making them critical for electric vehicles (EVs) that prioritize sustainability. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and performance parameters of the chip. In the automotive industry, tighter tolerances are crucial for ensuring that chips function correctly under varying conditions, such as temperature changes and vibrations. This is particularly important for safety-critical applications, where even minor deviations can lead to significant failures. -
Power Consumption
– This specification measures the amount of power the chip consumes during operation. Lower power consumption is essential for electric vehicles, as it helps maximize battery life and improve overall vehicle efficiency. B2B buyers should seek chips with optimized power profiles to enhance the performance of their EV offerings. -
Operating Temperature Range
– The operating temperature range indicates the temperatures within which the chip can function reliably. For small electric car chips, a broad range is beneficial as it ensures consistent performance across various environmental conditions, from extreme cold to high heat. This reliability is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and safety. -
Processing Speed
– Processing speed is a critical factor that determines how quickly a chip can execute tasks, such as managing battery systems or controlling electric motors. Faster processing speeds enhance the responsiveness of electric vehicles, providing a better driving experience. B2B buyers should prioritize chips with high processing capabilities to keep up with the growing demands of modern EV technology. -
Integration Level
– Integration level refers to how many functions a single chip can perform. Higher integration levels can reduce the overall number of components needed, leading to lower manufacturing costs and improved reliability. For businesses looking to streamline production and minimize space, choosing chips with a high integration level is advantageous.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Small Electric Car Chip Pricing?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common trade terms that buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of small electric car chips, buyers often source from OEMs to ensure high-quality components that meet specific automotive standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers as it affects inventory management and overall procurement costs. B2B buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for a specific quantity of goods. This is a vital step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and liability during international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to effectively plan their production schedules and ensure timely availability of components. -
Supply Chain Management
– This term encompasses the entire process of production, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products. Effective supply chain management is critical for B2B buyers to ensure that they maintain a steady flow of small electric car chips while minimizing costs and delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing small electric car chips, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness in the evolving electric vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small electric car chip price Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting the Small Electric Car Chip Price Sector?
The small electric car chip price sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. First, the surge in electric vehicle (EV) demand, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is creating an unprecedented requirement for semiconductor chips. In regions like Europe, the push towards electrification and sustainability is accelerating the adoption of small electric cars, which typically require specialized chips for power management, battery control, and autonomous driving features. This growing demand is coupled with supply chain challenges that have plagued the semiconductor industry, causing price volatility and scarcity.
Moreover, international B2B buyers must navigate an increasingly competitive landscape characterized by aggressive pricing strategies from Chinese manufacturers. Companies like BYD are not only dominating the EV market in China but are also expanding aggressively into Europe and South America, leveraging lower production costs and robust supply chains. This has led to a downward pressure on chip prices, as manufacturers look to maintain competitiveness in the face of rising operational costs and fluctuating raw material prices. Buyers must stay attuned to these dynamics, understanding how shifts in production capabilities and market entries can impact sourcing strategies and overall costs.
Additionally, technological advancements in chip manufacturing are emerging as a key trend. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning in chip design is enhancing performance while reducing costs. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who seek to optimize their supply chains and ensure they are sourcing from manufacturers that can provide cutting-edge technology at competitive prices.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing in the Small Electric Car Chip Price Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal factor in the sourcing decisions of international B2B buyers in the small electric car chip price sector. Environmental considerations are no longer optional; they are essential for maintaining brand integrity and compliance with increasingly stringent regulations. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as minimizing carbon emissions during chip production and using recyclable materials.
The importance of ethical sourcing is underscored by the growing awareness of the environmental impact associated with raw material extraction, particularly in the context of lithium and cobalt, which are critical for battery production. Suppliers that can provide transparent supply chain practices and certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming more appealing to buyers. These certifications not only validate a supplier’s commitment to sustainability but also mitigate risks associated with reputational damage and regulatory compliance.
Furthermore, the demand for “green” materials is reshaping the chip manufacturing landscape. B2B buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers that utilize alternative materials or innovative processes that reduce the ecological footprint. This shift towards sustainability is not just beneficial for the environment; it also opens up new market opportunities as consumers increasingly favor brands that prioritize ethical practices.
What Is the Historical Context of the Small Electric Car Chip Price Sector?
The evolution of the small electric car chip price sector can be traced back to the early 2000s when the automotive industry began integrating electronic components into vehicles. However, the real transformation began with the rise of electric vehicles in the last decade. As governments worldwide implemented stricter emissions regulations and incentivized EV adoption, the demand for specialized chips surged.
Initially, the chip market was dominated by a few key players, primarily in North America and Europe. However, the rapid advancement of technology in Asia, particularly in China, has shifted the balance. Chinese manufacturers have capitalized on economies of scale and government support, enabling them to produce high-quality chips at lower prices. This shift has not only increased competition but has also prompted established players to innovate and adapt their sourcing strategies.
Today, the small electric car chip price sector stands at a crossroads, where technological innovation, sustainability, and global market dynamics will dictate its future trajectory. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and navigating the complexities of the current market landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small electric car chip price
-
How do I solve the issue of high small electric car chip prices?
To address high chip prices for small electric cars, consider exploring multiple suppliers to compare costs and negotiate better pricing. Investigate alternative materials or technologies that can reduce manufacturing expenses. Additionally, look for partnerships with manufacturers that offer volume discounts. Collaborating with local suppliers in regions like Africa or South America can also yield cost savings by minimizing shipping expenses and tariffs. -
What is the best approach for sourcing small electric car chips from international suppliers?
When sourcing small electric car chips internationally, begin by identifying reputable suppliers through industry trade shows, online marketplaces, and professional networks. Evaluate their certifications, production capabilities, and experience in the automotive sector. Request samples to assess quality and performance. Establish clear communication channels and consider suppliers who understand the specific regulations and requirements of your target market in regions such as Europe or the Middle East. -
What factors influence the pricing of small electric car chips?
The pricing of small electric car chips is influenced by several factors, including material costs, manufacturing processes, supply chain dynamics, and demand fluctuations. Additionally, geopolitical factors and trade regulations can affect availability and pricing. Suppliers in regions with established automotive industries, like Germany, may offer competitive prices due to economies of scale, while emerging markets may have variable pricing based on local production capabilities. -
How can I vet potential suppliers for small electric car chips?
To vet potential suppliers, conduct thorough due diligence by researching their company history, financial stability, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients in the automotive industry and analyze their production capacity and quality control processes. Consider visiting their facilities if feasible, and assess their compliance with international standards and certifications, particularly those relevant to your target markets. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for small electric car chips?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for small electric car chips can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific chip model. Typically, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your production needs with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a smaller manufacturer or a startup. Some suppliers may be willing to accommodate lower MOQs for new customers or in exchange for a longer-term contract. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing small electric car chips?
Payment terms when sourcing small electric car chips can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and the balance due upon delivery. For larger orders, suppliers may offer net payment terms ranging from 30 to 90 days. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit, to mitigate risks in international transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when purchasing small electric car chips?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a comprehensive quality control plan that includes supplier audits and regular inspections of production processes. Request detailed specifications and testing data for the chips, and consider third-party testing for compliance with international standards. Implement a clear return policy for defective products and maintain open communication with suppliers to address any quality concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing small electric car chips?
When importing small electric car chips, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose reliable freight forwarders familiar with automotive components to navigate international shipping complexities. Account for potential delays due to customs clearance and ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared in advance. Additionally, factor in warehousing needs and inventory management strategies to optimize supply chain efficiency.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Small Electric Car Chip Price Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Eli – Electric Micro Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Eli launches its electric micro ‘car’ in the US priced at $11,900.
2. Renault – 5 52kWh
Domain: whatcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 1. Renault 5 52kWh:
– Strengths: Grown-up driving manners, great infotainment system, tempting pricing.
– Weaknesses: Rear leg room is tight, small discounts compared to Citroën ë-C3 and Fiat Grande Panda Electric.
– Battery: 52kWh, range up to 253 miles, 100kW peak charging rate (15-80% in 30 mins).
– Price: £22,995, Leasing from £201 pm, Nearly new from £22,999.
2. Hyundai Inste…
3. Accio – Electric Vehicle Essentials
Domain: accio.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key considerations: Unit Price: $4.6 – $25,414; Quantity: Product attributes: Electric motor, Lithium-ion battery, Regenerative braking, Fast charging, 100 km range, 4 seats, 2 doors, 50 kW power, 120 Nm torque, 3.5 m length; Select by: Best Selling, MOQ < 5, Verified Supplier, 5+ Years Supplier Exp., Manufacturer Only, 4.5+ Supplier Rating; Various models with prices ranging from $567 to $8,214, …
4. Nozaki Sss – Electric Vehicle
Domain: discourse.mcneel.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: – Type: Electric Vehicle (EV)
– Design: Created by Nozaki Sss in 2013
– Price: $2000
– Battery Options: Inexpensive lead battery or expensive lithium battery
– Weight: Approximately 300 kg (similar to a large bike)
– Capacity: 2-3 passengers
– Range: About 30 km
– Charging: Can be charged with 200V electricity at home
– Target Market: Designed for use in rural areas, especially for the elderly and…
5. Wafer World – Semiconductor Wafer Services
Domain: waferworld.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Products offered by Wafer World include Silicon, GaAs, Germanium, InP, and Clean Room services. They provide Silicon and Semiconductor Wafer Services, GaAs and InP Reclaim, Germanium, and other materials. Additionally, they offer Clean Room Packaging and Reclaim services for Silicon, GaAs, and InP.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small electric car chip price
In an increasingly competitive landscape, the strategic sourcing of small electric car chips has emerged as a critical factor for success. As manufacturers pivot toward cost-effective solutions, the price dynamics of these components are influenced by factors such as supply chain efficiencies, geopolitical tensions, and evolving technological advancements. B2B buyers must prioritize partnerships with suppliers that offer robust quality assurance and innovation capabilities to navigate these complexities effectively.
The rise of Chinese manufacturers, leveraging economies of scale and state support, underscores the need for established players in Europe, Africa, and South America to adapt swiftly. By embracing strategic sourcing, companies can secure competitive pricing and foster resilience against market fluctuations. Additionally, as electric vehicle adoption accelerates globally, the demand for high-quality chips will only intensify, making it imperative for buyers to remain proactive in their sourcing strategies.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should consider diversifying their supplier base and investing in long-term relationships to enhance supply chain stability. By doing so, they position themselves to capitalize on the evolving electric vehicle market, ensuring they remain at the forefront of innovation and competitiveness. Now is the time to take action—assess your sourcing strategies and align them with the future of electric mobility.