Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for used Cargo Truck
Navigating the global market for used cargo trucks presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. With fluctuating prices, varying quality standards, and diverse regulations across regions, sourcing the right vehicle can feel daunting, particularly for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Saudi Arabia and Vietnam. This guide aims to simplify the process of acquiring used cargo trucks by providing an in-depth exploration of the types available, their applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
From box trucks to cargo vans, understanding the different vehicle types will empower buyers to make informed choices that align with their operational needs. Additionally, we will delve into cost factors, maintenance considerations, and best practices for ensuring long-term reliability. By addressing these critical aspects, this guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights to navigate the complexities of the used cargo truck market effectively.
With a focus on enhancing purchasing decisions, we aim to provide clarity and confidence, enabling businesses to optimize their logistics and transportation strategies. Whether you are looking to expand your fleet or replace aging vehicles, this resource serves as your comprehensive roadmap to successfully sourcing used cargo trucks that meet your business requirements.
Understanding used Cargo Truck Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
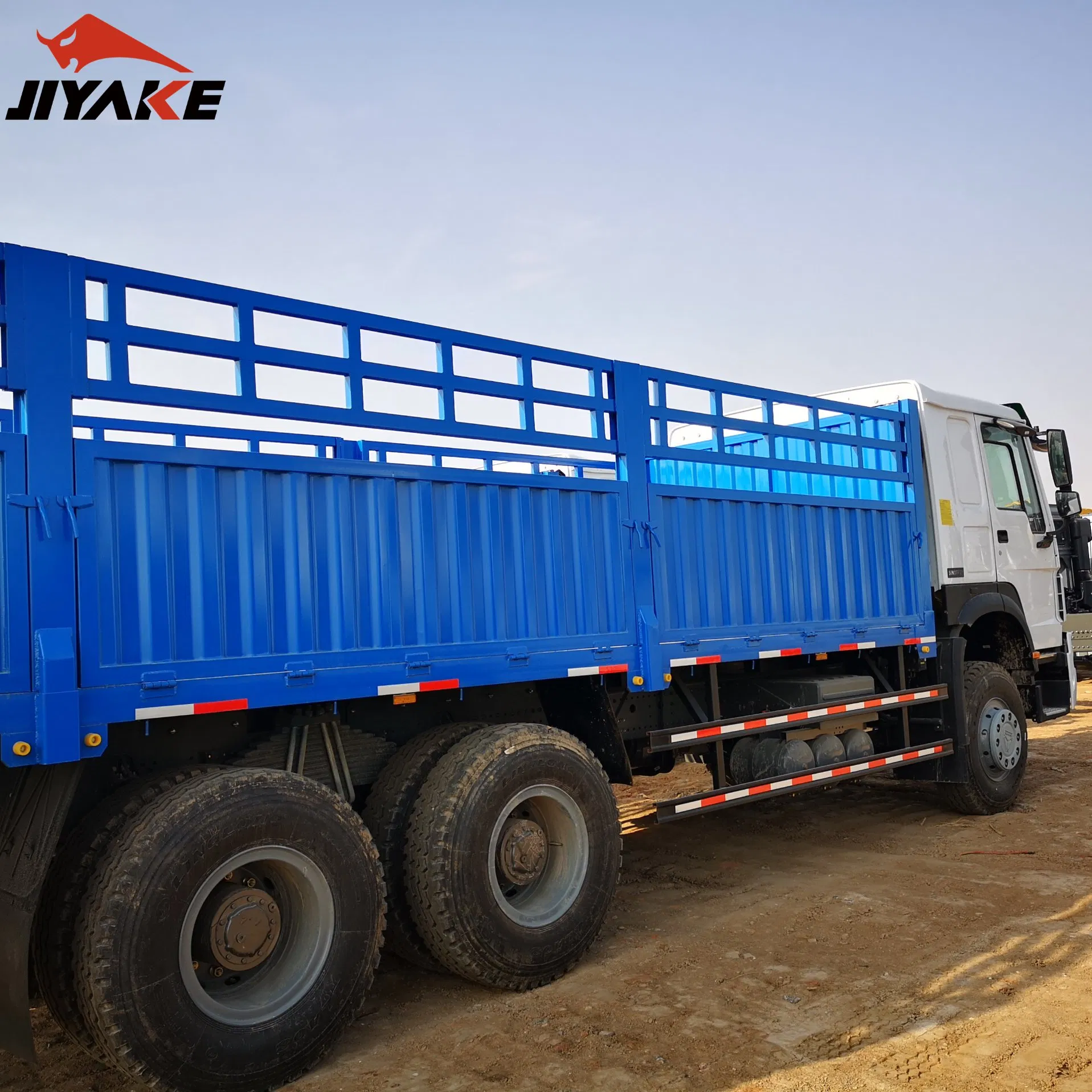
| Box Truck | Enclosed cargo area, varying sizes (10′-26′), high payload | Moving, delivery, logistics | Pros: Secure cargo, versatile. Cons: Limited access for larger items. |
| Cargo Van | Compact, usually 2-3 tons, easy maneuverability | Urban deliveries, service industry | Pros: Easy to drive, good fuel economy. Cons: Less cargo space than box trucks. |
| Flatbed Truck | Open platform, no sides or roof, versatile loading | Construction, heavy equipment transport | Pros: Easy loading/unloading. Cons: Exposed cargo, less secure. |
| Dump Truck | Hydraulic bed for unloading, typically larger in size | Construction, waste management | Pros: Efficient for bulk materials. Cons: Limited to specific cargo types. |
| Cab & Chassis | Base vehicle without a cargo area, customizable | Specialized applications (e.g., tow trucks) | Pros: Highly customizable. Cons: Requires additional investment for body. |
What are the Characteristics of Box Trucks for B2B Buyers?
Box trucks are characterized by their enclosed cargo area, which provides protection from the elements and theft. They come in various sizes, typically ranging from 10 to 26 feet, making them suitable for diverse applications such as moving, deliveries, and logistics operations. B2B buyers should consider factors like payload capacity and loading access when purchasing box trucks, as these vehicles are ideal for transporting furniture, appliances, and other bulk items.
Why Choose Cargo Vans for Urban Deliveries?
Cargo vans are compact vehicles designed for ease of maneuverability in urban environments. They usually have a payload capacity of 2 to 3 tons and are perfect for businesses that require quick deliveries and service calls. Their fuel efficiency is another significant advantage for B2B buyers looking to minimize operational costs. However, it’s essential to recognize that cargo vans offer less space compared to box trucks, which may limit their use for larger shipments.
How Do Flatbed Trucks Serve Various Industries?
Flatbed trucks are distinguished by their open platform design, allowing for easy loading and unloading of cargo. This type of truck is particularly beneficial in construction and heavy equipment transport, where items may not fit in enclosed vehicles. B2B buyers appreciate the versatility of flatbed trucks, but they should be aware of the security risks associated with exposed cargo. Investing in tarps or securing mechanisms can mitigate these concerns.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Dump Trucks?
Dump trucks are specifically designed to transport bulk materials and feature a hydraulic bed that allows for easy unloading. Commonly used in construction and waste management, these trucks can handle heavy loads. B2B buyers should consider the type of materials they will be transporting, as dump trucks are less versatile for general freight. Their efficiency in moving large quantities of materials makes them indispensable for certain industries.
Why Consider Cab & Chassis Trucks for Custom Applications?
Cab & chassis trucks serve as a base vehicle without a cargo area, providing businesses with the flexibility to customize according to their specific needs. These vehicles are often used for specialized applications, such as tow trucks or delivery vehicles. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment for additional bodywork against the long-term benefits of a tailored solution. The ability to customize makes cab & chassis trucks a valuable option for companies with unique operational requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of used Cargo Truck
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of used Cargo Truck | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Transportation | Last-mile delivery services | Reduces operational costs while ensuring timely deliveries | Evaluate payload capacity, fuel efficiency, and maintenance history. |
| Retail | Mobile retail operations | Expands market reach by bringing products directly to consumers | Ensure the vehicle has sufficient storage space and branding opportunities. |
| Construction | Transportation of materials and equipment | Streamlines project timelines by facilitating quick transport | Consider the truck’s load capacity and durability for rough terrains. |
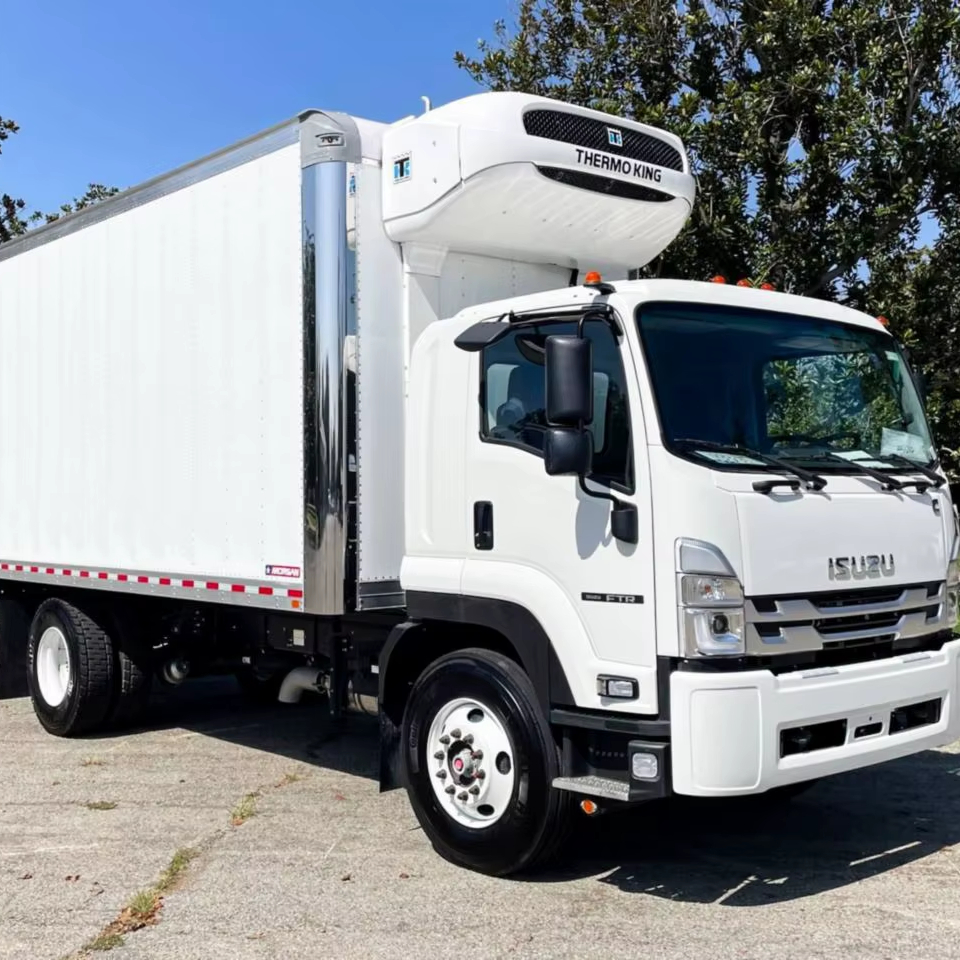
| Food & Beverage | Mobile catering and food delivery | Enhances customer service by providing on-site food options | Assess refrigeration capabilities and compliance with health regulations. |
| Agriculture | Transport of produce and farming equipment | Increases efficiency in supply chain management | Focus on vehicle adaptability for off-road conditions and load security features. |
In the Logistics & Transportation sector, used cargo trucks are pivotal for last-mile delivery services. These vehicles enable businesses to reduce operational costs while ensuring timely deliveries to consumers. Buyers should prioritize evaluating payload capacity, fuel efficiency, and maintenance history to ensure reliability and operational success.
In the Retail industry, used cargo trucks serve as mobile retail operations, allowing businesses to expand their market reach by bringing products directly to consumers. This approach enhances customer engagement and can lead to increased sales. When sourcing, it’s important to ensure that the vehicle has sufficient storage space and opportunities for branding to attract customers.
For the Construction sector, used cargo trucks are essential for transporting materials and equipment to job sites. They streamline project timelines by facilitating quick transport of necessary supplies. Buyers in this sector should consider the truck’s load capacity and durability, especially when navigating rough terrains typical of construction sites.
In the Food & Beverage industry, used cargo trucks are commonly utilized for mobile catering and food delivery services. This application enhances customer service by providing on-site food options at events or busy locations. Buyers should assess the truck’s refrigeration capabilities and compliance with health regulations to ensure food safety and quality.
Finally, in Agriculture, used cargo trucks are vital for transporting produce and farming equipment. They increase efficiency in supply chain management, ensuring that perishable goods reach markets promptly. Buyers should focus on the vehicle’s adaptability for off-road conditions and features that secure loads, which are crucial for transporting agricultural products safely.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘used Cargo Truck’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Assessing Vehicle Condition Before Purchase
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of assessing the true condition of a used cargo truck before finalizing a purchase. This can be particularly daunting when sourcing trucks from different regions, such as Africa or South America, where local standards for vehicle maintenance may vary. Buyers may worry about hidden damages, mechanical issues, or subpar maintenance records that could lead to costly repairs down the line. The risk of investing in a vehicle that may not meet operational requirements can significantly impact logistics and business efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should prioritize conducting thorough inspections and obtaining detailed vehicle history reports. When considering a used cargo truck, engage a trusted third-party mechanic to perform a pre-purchase inspection, focusing on critical components such as the engine, transmission, brakes, and tires. Additionally, leverage online platforms that offer comprehensive vehicle histories, including accident reports and service records. Building relationships with reputable dealers who provide warranties or guarantees can further enhance confidence in the purchase. For buyers in regions with limited access to reliable vehicle inspections, consider using virtual inspection services that allow for remote assessments, providing greater peace of mind.
Scenario 2: Navigating Import Regulations and Compliance Issues
The Problem: For international B2B buyers, especially those in the Middle East and Europe, navigating the complex web of import regulations and compliance standards can be a significant pain point. Varying regulations regarding emissions, safety standards, and import tariffs can lead to unforeseen delays and additional costs. Misunderstanding these requirements can result in penalties or even the inability to use the purchased vehicle within the intended market.
The Solution: To streamline the import process, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research on the specific regulations applicable in their target country. Consulting with local customs brokers or legal experts can provide valuable insights into compliance requirements. Before purchasing, inquire about the vehicle’s compliance with local emissions standards and safety regulations, ensuring it meets all necessary criteria for importation. Additionally, consider leveraging services that specialize in international vehicle transport, as they often have experience in navigating compliance issues and can offer guidance on paperwork and fees. Establishing a checklist of required documentation and regulations specific to the destination country can help streamline the process and avoid costly missteps.
Scenario 3: Understanding Total Cost of Ownership
The Problem: Many B2B buyers underestimate the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with used cargo trucks, which can lead to budget overruns and operational inefficiencies. Factors such as fuel consumption, maintenance, insurance, and potential financing costs can significantly impact the overall expense of running a fleet. Buyers may focus solely on the initial purchase price, neglecting these ongoing costs that can erode profit margins.
The Solution: To gain a comprehensive understanding of TCO, buyers should conduct a detailed analysis of all potential expenses associated with the used cargo truck. Begin by researching fuel efficiency ratings for the specific models being considered, as this can greatly influence operational costs. Next, create a maintenance budget based on average service intervals and common repair costs for those vehicles. Consulting with other businesses in the same industry can provide insights into realistic operational costs. Additionally, consider the potential resale value of the truck after a few years of use, as this can offset some of the initial investment. Utilizing fleet management software can also help monitor and optimize costs over time, ensuring that the total cost of ownership aligns with business objectives.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for used Cargo Truck
What Are the Key Materials Used in Cargo Trucks and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for used cargo trucks, several options are prevalent in the industry, each with unique properties and implications for performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials: steel, aluminum, fiberglass, and composite materials.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material in Cargo Trucks?
Steel is a widely used material in the construction of cargo trucks due to its exceptional strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s corrosion resistance can be enhanced with coatings, which is crucial for trucks operating in diverse environmental conditions.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and offers excellent structural integrity. It can be easily sourced and manufactured, making it a cost-effective choice for many truck components.
Cons: The weight of steel can be a disadvantage, leading to reduced fuel efficiency. Additionally, untreated steel is prone to rust, which can impact longevity and maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it ideal for truck frames and load-bearing structures. However, international buyers should ensure compliance with local corrosion resistance standards, especially in humid or saline environments, such as coastal regions in Africa or the Middle East.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Cargo Trucks?
Aluminum is increasingly favored for its lightweight properties, which can significantly improve fuel efficiency. It has good corrosion resistance and can be treated for enhanced durability, making it suitable for various climates.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight-to-strength ratio, allowing for increased payload capacity without compromising structural integrity. It is also resistant to corrosion, reducing maintenance needs.
Cons: Aluminum tends to be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes can be more complex. Additionally, while it is strong, it may not be as durable under extreme stress compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in cargo truck bodies and panels, especially for companies focused on reducing operational costs through improved fuel efficiency. Buyers should consider local standards for aluminum alloys, particularly in regions like Europe, where specific grades may be mandated.
How Does Fiberglass Compare as a Material for Cargo Trucks?
Fiberglass is a composite material known for its lightweight and strong properties. It is particularly resistant to corrosion and can be molded into various shapes, making it versatile for truck design.
Pros: Fiberglass is lightweight, which contributes to better fuel efficiency. It is also resistant to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for trucks that operate in harsh environments.
Cons: The main drawbacks include higher initial costs and potential brittleness under certain conditions. Repairing fiberglass can also be more challenging compared to metal materials.
Impact on Application: Fiberglass is often used in truck bodies and interior components. International buyers should verify that fiberglass components meet local safety and performance standards, especially in markets with stringent regulations like Europe.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Cargo Truck Construction?
Composite materials, which combine two or more materials to enhance performance, are becoming more common in cargo truck applications. They offer a unique blend of strength, weight reduction, and corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, providing excellent durability and resistance to environmental factors. Their lightweight nature can lead to significant fuel savings.
Cons: The cost of composite materials can be high, and the manufacturing processes may be complex. Additionally, the long-term durability of some composites under heavy loads is still being evaluated.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in specialized applications, such as truck interiors or custom body designs. Buyers should be aware of the specific standards for composites in their region, particularly in areas like South America, where regulations may vary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Used Cargo Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for used Cargo Truck | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Truck frames and load-bearing parts | High strength and durability | Heavy weight, rust potential | Low |
| Aluminum | Truck bodies and panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Fiberglass | Truck bodies and interior components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher initial cost, brittle | Medium |
| Composite | Specialized applications, custom designs | Tailored performance, lightweight | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions with varying standards and environmental considerations. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can significantly impact purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for used Cargo Truck
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Used Cargo Trucks?
Manufacturing used cargo trucks involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets quality and performance standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as steel and aluminum, which are essential for the truck’s structure. Suppliers typically adhere to international standards for material quality, ensuring that they meet specifications for strength and durability.
-
Forming: During this stage, raw materials are shaped into various components. Techniques like stamping, forging, and extrusion are commonly employed to create chassis, body panels, and other parts. Advanced machinery, including CNC machines, is often used to enhance precision and efficiency in forming processes.
-
Assembly: Once the components are formed, they are assembled into a complete vehicle. This stage may involve robotic automation for repetitive tasks, along with skilled labor for more complex assembly processes. Each vehicle is constructed following specific design blueprints to ensure consistency and quality.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage includes painting and coating to protect against corrosion and enhance aesthetics. Quality control measures, such as visual inspections and paint thickness tests, are applied to guarantee the durability of the finish.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of used cargo trucks and encompasses various checkpoints and testing methods throughout the production process.
-
International and Industry-Specific Standards: Manufacturers often adhere to international standards like ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. In addition, industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for certain components, may also apply. Compliance with these standards ensures that the trucks are safe and reliable.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: The QA process typically includes several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Incoming materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications before they enter production.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the assembly process, various inspections are conducted to verify that components are being assembled correctly and meet design specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a thorough inspection is performed to evaluate the overall quality of the finished product. This may include functional tests, safety checks, and performance assessments. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to ensure quality:
– Destructive Testing: This includes tests such as tensile and impact tests to evaluate the material’s strength and durability.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to assess structural integrity without damaging the components.
– Performance Testing: The trucks are subjected to real-world conditions to evaluate their performance under load and during operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC processes:
-
Conduct Audits: Buyers should consider conducting audits of potential suppliers. This can include on-site visits to review manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed quality reports that outline their QA processes, test results, and certifications. These documents should reflect their adherence to relevant standards and any third-party inspections that have been conducted.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations of the manufacturing process, materials, and final products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances must be considered when navigating quality control in the used cargo truck market:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and compliance requirements specific to their market.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Communication is crucial in ensuring quality. Buyers should be prepared to overcome potential language barriers and cultural differences when engaging with suppliers. Utilizing bilingual representatives or local partners can facilitate smoother negotiations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International buyers should consider how logistics and supply chain factors may impact the quality of used cargo trucks. Issues such as transportation conditions, storage practices, and handling can affect the condition and performance of the trucks upon arrival.
-
After-Sales Support and Warranty: Assessing the supplier’s after-sales support and warranty offerings is essential. A robust warranty and responsive customer service can significantly enhance the buyer’s confidence in the quality of the purchased trucks.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for used cargo trucks are critical for ensuring that these vehicles meet the demands of international B2B buyers. By understanding the manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, and verification strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and expectations. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the reliability of their purchases but also supports sustainable business practices in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘used Cargo Truck’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of used cargo trucks can be a complex process, particularly for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed to streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start sourcing, it’s essential to establish your requirements. Identify the type of cargo truck you need, including specifications such as payload capacity, engine type, size, and body style (e.g., box truck, flatbed). This clarity will help you filter options and focus on vehicles that meet your operational demands.
- Payload Capacity: Ensure the truck can handle the weight of your goods.
- Body Style: Choose a style that suits your transport needs, whether for deliveries or larger freight.
Step 2: Set Your Budget
Establishing a budget is crucial to avoid overspending. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs over time. This holistic view will help you identify vehicles that provide the best value.
- Initial Purchase Price: Look for trucks within your financial range.
- Long-term Costs: Factor in ongoing maintenance and repair expenses.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet your potential suppliers to ensure reliability. Investigate their reputation in the market, their history of transactions, and customer reviews. This step is vital to ensure you partner with trustworthy suppliers who can deliver quality vehicles.
- Supplier Reputation: Seek feedback from previous buyers.
- Certifications: Verify any industry certifications that indicate quality assurance.
Step 4: Inspect Vehicle Condition
Physical inspection of the used cargo truck is non-negotiable. Check for signs of wear and tear, both externally and internally, including the engine, brakes, and tires. Request a detailed vehicle history report to uncover any past accidents or major repairs.
- Visual Inspection: Look for rust, dents, or other damage.
- Mechanical Check: Ensure all critical systems are functioning properly.
Step 5: Verify Ownership and Documentation
Ensure that the seller has clear title and ownership of the vehicle. Request all necessary documentation, including maintenance records, service history, and any warranties. This step protects you from potential legal issues down the line.
- Title Verification: Confirm the truck is not stolen or under lien.
- Maintenance Records: Review to understand the vehicle’s upkeep.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a suitable truck, engage in negotiations. Discuss pricing, payment terms, and any warranties or guarantees. Effective negotiation can lead to better deals and terms that align with your business needs.
- Pricing: Be prepared to make counter-offers based on your research.
- Warranties: Ensure any guarantees are documented and clear.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Arrange Logistics
After agreeing on terms, finalize the purchase and arrange for transportation to your location. Consider the logistics of moving the truck, including customs clearance if sourcing internationally. This final step ensures the truck is delivered efficiently and without unexpected delays.
- Transportation Options: Evaluate local and international shipping methods.
- Customs Regulations: Ensure compliance with local laws if importing.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for used cargo trucks, making informed decisions that contribute to your business’s efficiency and success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for used Cargo Truck Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Used Cargo Trucks?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing used cargo trucks, several components come into play. The primary costs include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in the truck’s construction and any aftermarket modifications. For used trucks, the condition of materials—like the chassis and body—can significantly impact pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve the workforce required to maintain, refurbish, or modify the trucks. Skilled labor is especially important for ensuring that the trucks meet safety and operational standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Understanding this can help buyers gauge the overall cost structure.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools for refurbishing or customizing used trucks can add to the costs. Buyers should inquire about any modifications that may be necessary for their specific operational needs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that used trucks meet safety and operational standards can incur additional costs. Buyers should look for certifications and maintenance records that indicate a truck’s reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary based on the distance between the seller and the buyer, as well as the mode of transport chosen. These costs are critical, especially for international buyers.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically mark up prices to ensure a profit margin. Understanding the standard margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
What Influences Prices for Used Cargo Trucks?
Several factors can influence the pricing of used cargo trucks, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer better pricing for larger orders, reducing the overall cost per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Trucks that require specific features or customizations will generally command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Trucks made from higher-quality materials or those with certifications (like ISO or safety standards) may be priced higher. However, these trucks often provide better long-term value.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and geographic location of suppliers can impact prices. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived quality, while newer suppliers may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment (like FOB, CIF) is crucial, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during transport. This can significantly affect the total price for international transactions.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Prices on Used Cargo Trucks?
-
Research and Comparison: Buyers should conduct thorough market research and compare prices from multiple suppliers. This information is crucial for effective negotiation.
-
Leverage Volume: If purchasing multiple units, buyers can negotiate lower prices per unit by leveraging their volume.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the initial purchase price, buyers should consider maintenance, fuel efficiency, and potential repair costs to assess the true value of the truck.
-
Timing: Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and seasonal trends. Buyers may find better deals during off-peak times or when suppliers are looking to clear inventory.
-
Be Flexible: Being open to different models or configurations can provide more options and potentially lower prices.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers must navigate additional complexities when sourcing used cargo trucks. Currency fluctuations can affect pricing, and import duties or taxes may add to the overall cost. Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is essential to avoid unexpected expenses.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for used cargo trucks can vary widely based on condition, specifications, and market demand. The figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should not be viewed as fixed. Buyers should conduct their own due diligence and consult multiple sources before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing used Cargo Truck With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Used Cargo Trucks
When considering logistics solutions, B2B buyers often evaluate various transport options to find the most effective and cost-efficient methods for their operations. While used cargo trucks serve a critical role in freight transportation, alternatives such as cargo vans and third-party logistics (3PL) services can offer distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of a business. This analysis compares these alternatives to help buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Used Cargo Truck | Cargo Van | Third-Party Logistics (3PL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity for large loads | Moderate capacity for smaller loads | Variable, dependent on provider |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Lower purchase price and operational costs | Variable, often subscription-based |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires licensing and insurance | Easier to obtain and less regulatory burden | Minimal effort; outsourced entirely |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance costs due to size | Generally lower, but depends on usage | No maintenance required by buyer |
| Best Use Case | Bulk transportation, heavy goods | Urban deliveries, smaller loads | Flexibility in distribution and scalability |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cargo Vans?
Cargo vans present an appealing alternative for businesses that require efficient urban transportation solutions. They generally have a lower purchase price compared to used cargo trucks, making them financially accessible for small to medium enterprises. Their smaller size allows for easier maneuverability in congested areas, which can be a significant advantage in urban logistics. However, the trade-off is a reduced load capacity, limiting their utility for bulk shipments. Maintenance costs are typically lower than those of larger trucks, but frequent use can still lead to significant wear and tear.
How Do Third-Party Logistics Services Compare?
Third-party logistics (3PL) services provide a flexible alternative to owning transport vehicles. Businesses can outsource their logistics operations, allowing them to scale up or down based on demand without the burden of maintaining a fleet. This can significantly reduce overhead costs associated with vehicle maintenance, insurance, and compliance. However, the variability in service quality and potential hidden costs can be a concern. Additionally, businesses may lose some control over their logistics processes, which can affect delivery times and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right transportation solution hinges on the specific operational needs of a business. If a company frequently handles large shipments and values control over its logistics, investing in a used cargo truck may be the best choice. Conversely, businesses focused on urban deliveries or those with fluctuating demand may find greater value in cargo vans or third-party logistics services. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of performance requirements, budget constraints, and logistical flexibility will guide B2B buyers in making the most advantageous decision for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for used Cargo Truck
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Used Cargo Trucks?
When evaluating used cargo trucks, several technical properties are crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Understanding these specifications helps buyers assess the vehicle’s suitability for their business needs and ensures they are getting value for their investment.
-
Payload Capacity: This refers to the maximum weight a cargo truck can carry, including cargo and passengers. It is typically measured in pounds or kilograms. For B2B buyers, knowing the payload capacity is essential for ensuring compliance with local regulations and avoiding overloading, which can lead to safety issues and increased wear on the vehicle.
-
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR): GVWR is the maximum weight that a vehicle is rated to safely carry, including its own weight and the weight of the cargo. This specification helps buyers determine if a truck is suitable for specific loads while complying with legal weight limits on roads.
-
Engine Specifications: Key details include engine type (gasoline or diesel), horsepower, and torque ratings. A powerful engine is crucial for performance, especially for businesses requiring frequent hauling or navigating hilly terrain. This information aids buyers in evaluating fuel efficiency and operational costs.
-
Transmission Type: This includes automatic or manual transmissions. Automatic transmissions generally provide easier handling, especially in urban settings with frequent stops. Understanding the transmission type can influence operational efficiency and driver comfort.
-
Chassis Configuration: This encompasses the truck’s frame style, such as cab-and-chassis, box truck, or flatbed. The configuration affects the truck’s versatility and suitability for specific business operations, such as deliveries, moving, or hauling equipment.
-
Mileage: The total distance the truck has traveled is a critical factor affecting its remaining lifespan and maintenance needs. Lower mileage typically indicates less wear and tear, which can be a significant consideration for cost-conscious buyers.
Which Trade Terminology Should You Know When Buying Used Cargo Trucks?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly enhance communication between buyers and sellers, facilitating smoother transactions and negotiations.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be sold directly to the end user or through other distributors. Understanding OEM parts is vital for ensuring that any replacements or repairs maintain the vehicle’s integrity and reliability.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): In the context of buying multiple vehicles, MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers should be aware of MOQ requirements to ensure they can meet suppliers’ conditions, especially when purchasing fleet vehicles.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): This is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers. An RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different sellers, helping them secure the best deal for their budget and needs.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases.
-
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership): TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs. Understanding TCO helps businesses budget effectively and choose vehicles that align with their financial goals.
-
VIN (Vehicle Identification Number): A unique code used to identify individual motor vehicles. The VIN provides vital information about a vehicle’s history, including past ownership, accidents, and service records. Buyers should always check the VIN for transparency and to avoid purchasing vehicles with hidden issues.
By grasping these technical properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing used cargo trucks, ensuring they select vehicles that meet their operational needs and financial constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the used Cargo Truck Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Dynamics Affecting the Used Cargo Truck Market?
The used cargo truck market is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by various global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for logistics and delivery services, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As e-commerce continues to expand, businesses are seeking affordable and reliable transportation solutions, leading to a surge in demand for used cargo trucks.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Digital platforms for buying and selling used trucks are becoming increasingly prevalent, enabling international buyers to access a broader range of inventory from various regions. These platforms often provide detailed vehicle histories, inspection reports, and virtual tours, making it easier for buyers to make informed decisions without the need for physical inspections. Moreover, the integration of AI and machine learning in pricing strategies helps sellers set competitive prices, which can benefit buyers looking for value.
Market dynamics are heavily influenced by fluctuating fuel prices and regulatory changes aimed at reducing emissions. For instance, many countries are implementing stricter emissions standards, prompting businesses to invest in more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly used cargo trucks. This shift not only aligns with corporate sustainability goals but also enhances operational efficiency, further driving demand in the market.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Used Cargo Trucks?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the sourcing of used cargo trucks, particularly for international B2B buyers. Environmental impact is a growing consideration, as companies are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints. The used cargo truck sector is responding to this by promoting vehicles that meet or exceed environmental standards, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Ethical sourcing practices are also gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains, ensuring that the vehicles have been maintained responsibly and that their components are sourced ethically. Certifications such as ISO 14001, which outlines effective environmental management systems, are becoming essential in verifying a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials and technologies, such as trucks that have been retrofitted for better fuel efficiency or use alternative fuels, is increasingly important. These innovations not only enhance the sustainability profile of fleets but also appeal to consumers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. As more businesses adopt sustainable practices, the demand for used cargo trucks that align with these values is expected to rise.
What Is the Historical Context of the Used Cargo Truck Market?
The used cargo truck market has evolved significantly over the last few decades. Initially dominated by local dealerships and limited inventory, the sector has transformed with the advent of digital marketplaces that connect buyers and sellers globally. The rise of e-commerce in the early 2000s marked a turning point, as it created a pressing need for efficient logistics solutions.
As global trade expanded, so did the diversity of available models and brands, allowing buyers from regions like Africa and South America to source vehicles that meet their specific operational needs. The introduction of rigorous safety and emissions standards has also played a crucial role in shaping the market, encouraging manufacturers to produce more durable and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Today, the used cargo truck market stands as a testament to the adaptability of businesses in responding to changing consumer demands and regulatory landscapes, making it an essential component of global supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of used Cargo Truck
-
How do I ensure the quality of a used cargo truck before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of a used cargo truck, conduct a thorough inspection both physically and through documentation. Check the truck’s service history, mileage, and accident reports. If possible, request a third-party inspection to assess its mechanical condition. Additionally, verify the reputation of the seller and consider purchasing from certified dealers who offer warranties or guarantees. Engaging with a local mechanic can also provide insights into any potential future issues. -
What are the best cargo truck brands for durability and reliability?
When sourcing used cargo trucks, brands known for their durability and reliability include Ford, Chevrolet, Isuzu, and Mercedes-Benz. These manufacturers often produce vehicles that are well-suited for commercial use, with robust engines and strong chassis. Researching specific models within these brands can help identify those that are best rated for longevity and performance. It’s also beneficial to check user reviews and industry ratings to gauge overall satisfaction. -
How can I vet suppliers of used cargo trucks for international purchases?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by checking their business credentials and reviews from previous customers. Look for certifications or memberships in industry associations, which can indicate legitimacy. Ask for references and contact previous buyers to inquire about their experiences. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s location if feasible or utilizing video calls to inspect the inventory. Trustworthy suppliers will be transparent about their practices and ready to provide necessary documentation. -
What customization options are available for used cargo trucks?
Customization options for used cargo trucks can vary widely based on the model and supplier. Common modifications include adding shelving, installing lift gates, or adjusting the cargo area layout to fit specific needs. Suppliers may also offer aftermarket accessories such as GPS systems, enhanced safety features, or specialized cargo securing systems. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available options and any potential additional costs associated with customization. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing used cargo trucks?
Minimum order quantities for used cargo trucks can differ significantly among suppliers and depend on their inventory levels. Some may allow single-unit purchases, while others may have a MOQ of two or more trucks to accommodate bulk buyers. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their policies regarding MOQ and any potential discounts for larger orders. It’s advisable to compare multiple suppliers to find the best terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when buying used cargo trucks internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the specifics of the transaction. Common terms include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or financing options through the supplier. Ensure you understand any additional costs such as shipping, customs duties, and taxes. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide you with security, such as using an escrow service for large transactions, which can help mitigate risks. -
How does international logistics work for transporting used cargo trucks?
International logistics for transporting used cargo trucks typically involves several steps, including freight forwarding, customs clearance, and final delivery. After purchasing, the supplier will prepare the truck for shipment, which may include disassembly for easier transport. You will need to arrange for a freight forwarder to handle shipping logistics, including selecting the appropriate shipping method (e.g., container or roll-on/roll-off). Ensure you understand the customs regulations in your destination country to avoid delays. -
What quality assurance practices should be in place when buying used cargo trucks?
Quality assurance practices are crucial when purchasing used cargo trucks. Ensure the supplier provides a detailed inspection report and any certifications regarding the truck’s condition. Look for warranties that cover a period post-purchase. It’s also beneficial to establish a return policy in case the truck does not meet the agreed-upon specifications. Regular communication with the supplier throughout the purchasing process can help ensure transparency and adherence to quality standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Used Cargo Truck Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AutoTrader – Cargo Vans & Commercial Trucks
Domain: autotrader.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Used Cargo Vans and Commercial Trucks for Sale Near Me, Location: 20146, Condition: New (2,138), Used (698), Manufacturer Certified (26), Third-Party Certified (5), Drive Types: Rear Wheel Drive, Front Wheel Drive, Manual, AWD/4WD, Body Styles: Box Truck, Cargo Van, Dump Truck, Flatbed, Service Body, Stake Truck, Tow Truck, Features: Mileage, Fuel Type, Fuel Economy, Exterior Color, Interior Color…
2. Ford – 2019 F-750 26′ Box Truck
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Commercial Vans & Box Trucks for sale on eBay include various listings such as: 2019 Ford F-750 26′ Dry Box Truck Cargo Van 6.7L V8 Diesel A/T Lift Gate for $11,250; 2011 International 4X2 Durastar 4300 Diesel Box Truck w/ Lift Gate for $8,000; 2018 International 4300 18′ Reefer Truck Refrigerated Cargo Van for $24.99; 2020 International MV607 26′ S/A Curtain Side Van Truck Delivery Cargo for $21,…
3. Ryder – Used Commercial Vans
Domain: ryder.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Ryder offers a selection of used commercial vans for sale, including gas cargo vans, diesel sprinter vans, and electric cargo vans. These vehicles are designed for last-mile deliveries and city navigation, featuring a superior turning radius and ample shelving capacity. Ryder provides warranty options, maintenance packages, and flexible financing with low monthly payments. The financing process ca…
4. Nissan NV Passenger 3500 – Used Cargo Van for Sale
Domain: edmunds.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Used Cargo Vans for Sale: 2019 Nissan NV Passenger 3500 SL – $23,995, 141,582 miles, 1 accident, 1 owner, 12 seats, features include back-up camera, Bluetooth, navigation, leather seats, third-row seating. 2023 Chevrolet Express Cargo 2500 – $24,495, 45,490 miles, no accidents, 1 owner, 2 seats, features include back-up camera, tire pressure warning, trip computer, stability control. 2023 Ram ProM…
5. Nissan NV200 – Used Cargo Van for Sale
Domain: cars.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Used Cargo Vans for Sale Near McKinney, TX
1. 2021 Nissan NV200 S
– Mileage: 91,653 mi
– Price: $13,777
– Deal Status: Fair Deal, High Demand
– Dealer: Freeman Buick GMC, Grapevine, TX
2. 2023 Chevrolet Express 2500 Work Van
– Mileage: 17,376 mi
– Price: $30,977
– Estimated Monthly Payment: $572
– Deal Status: Great Deal
– Features: Backup Camera, Stability Control
…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for used Cargo Truck
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Used Cargo Trucks?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of used cargo trucks offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers. By focusing on well-maintained vehicles with verified histories, businesses can enhance operational efficiency while minimizing costs. The diverse range of available models, including box trucks, cargo vans, and flatbeds, allows companies to tailor their fleet to specific logistical needs.
How Can Buyers Leverage Market Trends for Better Deals?
As the demand for used commercial vehicles continues to grow, especially in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are encouraged to act swiftly to secure the best deals. Engaging with reputable suppliers and leveraging online marketplaces can facilitate access to a wider inventory, ensuring competitive pricing and quality assurance.
What Is the Future Outlook for Used Cargo Trucks?
Looking ahead, the market for used cargo trucks is poised for expansion, driven by the rising need for efficient transportation solutions across global markets. Buyers should remain vigilant about market trends and emerging technologies that could influence vehicle performance and sustainability. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing, businesses can position themselves for success in an evolving landscape.
Take the next step in optimizing your logistics operations by exploring the diverse offerings in the used cargo truck market today.