Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for eec l7c electric car
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, sourcing EEC L7c electric cars presents both an opportunity and a challenge for international B2B buyers. As demand for sustainable transportation solutions rises, understanding the nuances of electric vehicle specifications, certifications, and market dynamics becomes crucial. This guide delves into the intricacies of the EEC L7c electric car, offering insights into various types, applications, and the essential criteria for selecting reliable suppliers.
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in sourcing these vehicles. From ensuring compliance with local regulations to assessing total cost of ownership, this comprehensive resource equips businesses with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Key topics include evaluating supplier credibility, understanding pricing structures, and navigating logistical considerations for efficient delivery.
By providing actionable insights and expert analysis, this guide aims to empower B2B buyers to confidently engage in the global market for EEC L7c electric cars, ultimately facilitating a smoother transition to electric mobility solutions. Whether you are in Nigeria, Vietnam, or any other emerging market, our aim is to help you optimize your procurement strategies and achieve sustainable growth in the electric vehicle sector.
Understanding eec l7c electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEC L7e Electric Passenger Car | Compact design, max speed of 90 km/h, spacious interior, low maintenance | Urban commuting, short-distance travel | Pros: Affordable, reliable, low ownership cost. Cons: Limited speed and range for long trips. |
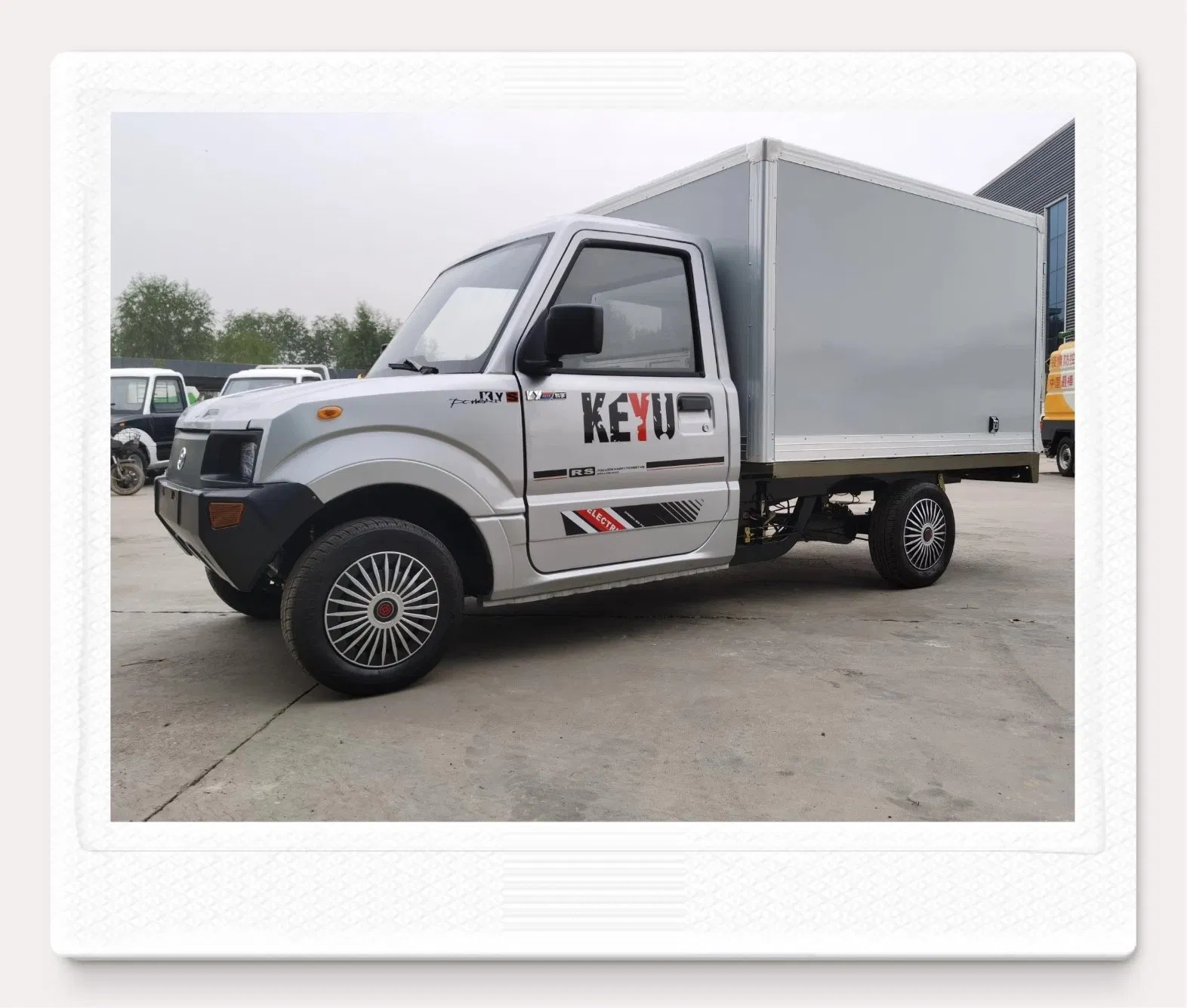
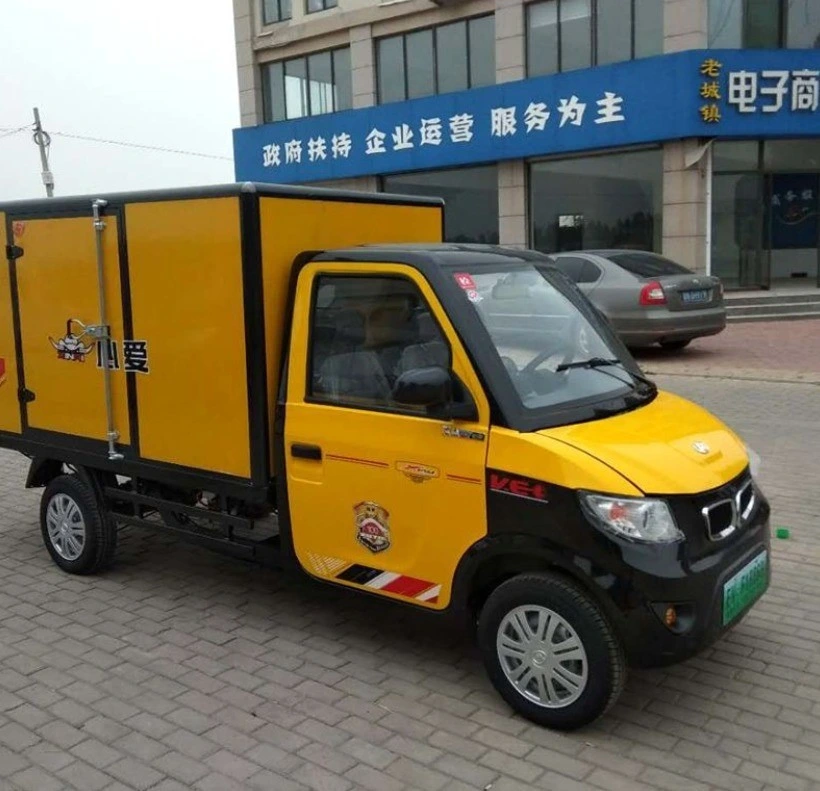
| EEC L7e Mini Delivery Van | Designed for last-mile delivery, cargo capacity, efficient battery system | E-commerce logistics, small business deliveries | Pros: High maneuverability, efficient for urban areas. Cons: Limited cargo space compared to larger vans. |
| EEC L7e Electric Pickup Truck | Versatile cargo space, rugged design, suitable for various terrains | Construction sites, agricultural use | Pros: Durable, higher payload capacity. Cons: Higher initial cost, may require special licensing in some areas. |
| EEC L7e Electric Cabin Car | Enclosed design, suitable for disabled users, low-speed operation | Mobility solutions, community transport | Pros: Accessible, easy to drive. Cons: Limited speed may not suit all users. |
| EEC L7e Electric Utility Vehicle | Multi-functional, can be customized for various uses, strong chassis | Municipal services, maintenance tasks | Pros: Versatile, robust design. Cons: Potentially higher maintenance costs due to varied use. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of the EEC L7e Electric Passenger Car?
The EEC L7e Electric Passenger Car is tailored for urban environments, offering a compact design that allows for easy maneuverability in city traffic. With a maximum speed of 90 km/h and a spacious interior, it serves as an ideal second vehicle for families or individuals needing reliable transport for short commutes. B2B buyers should consider its low maintenance costs and affordability, making it a cost-effective option for fleet services or rental companies. However, its limited range may restrict its use for longer journeys.
How Does the EEC L7e Mini Delivery Van Serve Businesses?
This vehicle is specifically designed for last-mile delivery, featuring a cargo area that efficiently accommodates packages while maintaining a compact footprint. Its electric powertrain ensures low operational costs, appealing to e-commerce businesses and logistics companies focusing on sustainable practices. B2B buyers should evaluate its maneuverability in urban settings, although its cargo space might be less than that of larger delivery vans, potentially limiting its utility for bulk shipments.
What Makes the EEC L7e Electric Pickup Truck a Viable Option?
The EEC L7e Electric Pickup Truck is distinguished by its rugged build and versatility, making it suitable for various applications such as construction and agriculture. Its larger cargo capacity compared to passenger vehicles allows businesses to transport tools, equipment, or goods efficiently. Buyers should consider the initial investment against the long-term savings in fuel and maintenance. However, its higher price point and possible licensing requirements may pose challenges for some buyers.
Why Choose the EEC L7e Electric Cabin Car for Mobility Solutions?
Designed for accessibility, the EEC L7e Electric Cabin Car features an enclosed structure that provides comfort and safety, particularly for users with disabilities. Its low-speed operation makes it suitable for community transport services and mobility aids. B2B buyers should assess its ease of use and accessibility features, although its limited speed may not meet the needs of all customers, particularly those requiring faster transport options.
What Are the Advantages of the EEC L7e Electric Utility Vehicle?
The EEC L7e Electric Utility Vehicle stands out for its multi-functional capabilities, allowing customization for various municipal and maintenance tasks. Its strong chassis provides durability, making it ideal for demanding environments. B2B buyers should weigh its versatility against potential higher maintenance costs, as varied applications can lead to increased wear and tear. However, its robust design and adaptability make it a valuable asset for businesses looking to streamline operations in diverse settings.
Key Industrial Applications of eec l7c electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of eec l7c electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-mile delivery solutions | Reduced operational costs and enhanced delivery efficiency | Battery capacity, range, and charging infrastructure |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Guest transportation in urban or resort areas | Improved guest experience and eco-friendly image | Vehicle comfort, safety features, and aesthetic appeal |
| Retail and E-commerce | Small goods transportation | Streamlined logistics and lower carbon footprint | Load capacity, vehicle size, and maneuverability |
| Municipal Services | Public transport and utility services | Cost-effective and sustainable urban transport solutions | Compliance with local regulations and maintenance support |
| Agricultural Support | Transporting goods and produce within farms | Increased efficiency in farm operations | Durability, battery life, and terrain adaptability |
How Can the EEC L7C Electric Car Benefit Urban Mobility Solutions?
In urban settings, the EEC L7C electric car serves as an ideal vehicle for last-mile delivery services. With its compact design and efficient battery, businesses can reduce operational costs while enhancing delivery speed and efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in densely populated areas where larger vehicles may struggle to navigate. When sourcing, businesses should consider the vehicle’s battery capacity and charging infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted service, especially in regions with limited charging stations.
What Advantages Does the EEC L7C Electric Car Offer to the Tourism and Hospitality Industry?
The tourism and hospitality sector can utilize the EEC L7C electric car for guest transportation, particularly in urban or resort areas. Its eco-friendly design not only enhances the guest experience but also supports the establishment’s sustainability goals. When sourcing, businesses should prioritize features such as vehicle comfort and safety, as well as aesthetic appeal, to ensure a positive impression on guests.
How Can Retail and E-commerce Benefit from the EEC L7C Electric Car?
Retailers and e-commerce businesses can leverage the EEC L7C electric car for small goods transportation. Its compact size allows for efficient navigation in crowded urban environments, streamlining logistics operations. Additionally, using electric vehicles helps companies reduce their carbon footprint, which is increasingly important to consumers. When sourcing, businesses should focus on the vehicle’s load capacity and maneuverability to meet their specific logistics needs.
In What Ways Can Municipal Services Utilize the EEC L7C Electric Car?
Municipal services can adopt the EEC L7C electric car for public transport and utility services, providing cost-effective and sustainable solutions for urban transit. Its low maintenance requirements and reliability make it an attractive option for local governments looking to modernize their fleets. Key sourcing considerations include compliance with local regulations and the availability of maintenance support to ensure continuous operation.
How Is the EEC L7C Electric Car Effective in Supporting Agricultural Operations?
In the agricultural sector, the EEC L7C electric car can facilitate the transportation of goods and produce within farms. Its efficient battery life and ability to navigate various terrains enhance operational efficiency, allowing farmers to move products swiftly and sustainably. When sourcing, buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s durability and adaptability to different farming environments to ensure it meets their operational requirements effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘eec l7c electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range for Urban Deliveries
The Problem: B2B buyers in logistics or delivery services often face the challenge of vehicle range, especially when considering the EEC L7C electric car for urban deliveries. With a maximum range of 150-170 km, businesses worry about the practicality of using this vehicle for daily operations, particularly in cities with heavy traffic or multiple delivery stops. The concern is that the vehicle may not cover the necessary distances within a single charge, leading to delays and potential customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively utilize the EEC L7C electric car for urban deliveries, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their delivery routes and schedules. By strategically planning routes that prioritize short, efficient trips and minimizing long-distance travel, businesses can maximize the vehicle’s range. Additionally, investing in a robust charging infrastructure at strategic locations—such as warehouses or depots—can ensure that vehicles are charged during off-peak hours, allowing for seamless operations. It’s also beneficial to train drivers on eco-driving techniques, which can help extend the vehicle’s battery life and improve overall efficiency.
Scenario 2: Maintenance and Repair Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are hesitant to adopt electric vehicles like the EEC L7C due to concerns about maintenance and repair. Electric vehicles can have different servicing needs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, and buyers worry about the availability of qualified technicians and spare parts in their region. This is especially true in areas where electric vehicle infrastructure is still developing, leading to fears of prolonged downtime and increased operational costs.
The Solution: Buyers should proactively establish relationships with reputable service providers who specialize in electric vehicle maintenance. It is crucial to inquire about the availability of spare parts and the expertise of local technicians in handling electric vehicle systems. Additionally, investing in comprehensive training for in-house mechanics can be beneficial. This not only ensures that the team can perform routine maintenance but also builds internal capabilities to handle more complex repairs. Lastly, consider negotiating service contracts with manufacturers that include maintenance support to alleviate concerns about downtime.
Scenario 3: Compliance with Local Regulations
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in Africa and South America, regulatory frameworks regarding electric vehicles can be complex and vary significantly. B2B buyers often struggle to navigate these regulations to ensure compliance when importing or utilizing the EEC L7C electric car. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, operational interruptions, or even the inability to register the vehicle for use.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance issues, buyers should engage with local regulatory bodies and industry associations early in the procurement process. Staying informed about the specific requirements for electric vehicles in their region—such as emissions standards, registration processes, and any incentives for electric vehicle usage—can significantly streamline operations. Additionally, consulting with legal experts who specialize in automotive regulations can provide clarity on compliance issues. Buyers should also consider working with manufacturers who have experience navigating these regulations and can provide necessary documentation and certifications for the EEC L7C electric car. By taking a proactive approach to understanding and adhering to regulations, businesses can ensure smoother operations and avoid costly setbacks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for eec l7c electric car
What Are the Key Materials for the EEC L7C Electric Car?
When selecting materials for the EEC L7C electric car, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific needs of international B2B buyers. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in the construction of electric vehicles, particularly the EEC L7C model.
How Does Aluminum Benefit the EEC L7C Electric Car’s Structure?
Aluminum is a popular choice for electric vehicle manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. With a density about one-third that of steel, aluminum significantly reduces the overall weight of the vehicle, enhancing energy efficiency and range. Additionally, it has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for structural components.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and offers good thermal conductivity, which aids in battery cooling. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of the vehicle.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to steel and the complexity involved in manufacturing processes, such as welding and forming.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including battery fluids, making it suitable for electric vehicle applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of the cost implications and potential sourcing challenges. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is also crucial for ensuring quality and safety.
What Role Does Steel Play in the EEC L7C Electric Car?
Steel is widely used in automotive applications due to its strength and affordability. It provides structural integrity and is often used in the chassis and body panels of the EEC L7C electric car.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it an attractive option for manufacturers. It also has excellent tensile strength, which enhances safety features.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact energy efficiency. It is also prone to corrosion unless treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s durability makes it suitable for high-stress areas, but its weight may limit the vehicle’s range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local steel availability and the potential need for protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates.
Why Is Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery Technology Important?
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) is a battery technology commonly used in electric vehicles, including the EEC L7C. This material is known for its safety, thermal stability, and long cycle life.
Pros: LiFePO4 batteries offer excellent thermal stability and a longer lifespan compared to other lithium-ion batteries. They are less prone to overheating, making them safer for electric vehicles.
Cons: The energy density is lower than some other lithium-ion chemistries, which can affect the overall range of the vehicle.
Impact on Application: LiFePO4 is compatible with various charging systems and provides reliable performance for urban commuting.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international battery standards is essential, particularly for markets in Europe and the Middle East, where safety regulations are stringent.
How Does Polycarbonate Enhance the EEC L7C Electric Car’s Design?
Polycarbonate is increasingly used in automotive applications for windows and interior components due to its high impact resistance and lightweight properties.
Pros: Polycarbonate is significantly lighter than glass and offers superior impact resistance, reducing the risk of shattering.
Cons: It can be more expensive than traditional glass and may scratch more easily, requiring protective coatings.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the vehicle while ensuring safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate local regulations regarding material use in vehicle design, as well as the availability of protective coatings to maintain the integrity of polycarbonate.
Summary of Material Selection for EEC L7C Electric Car
| Material | Typical Use Case for eec l7c electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body structure and chassis components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis and body panels | Cost-effective and strong | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | Battery technology | Safe, stable, and long-lasting | Lower energy density compared to alternatives | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Windows and interior components | Lightweight and impact-resistant | More expensive and prone to scratching | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to understand the implications of material choices in the EEC L7C electric car. Understanding these factors can lead to better purchasing decisions and improved product performance in diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for eec l7c electric car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of the EEC L7C Electric Car?
The manufacturing process for the EEC L7C electric car involves several critical stages that ensure the vehicle meets stringent quality and safety standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who are considering procurement.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing involves sourcing high-quality materials. The chassis is typically constructed from auto-grade steel, which is selected for its strength and durability. Batteries, often Lithium Iron Phosphate, are procured from reputable suppliers to ensure performance and safety. Material testing is conducted to verify that they meet specified standards, including corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
Forming and Stamping
Once materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This includes stamping metal sheets into precise shapes for the chassis and body components. Modern CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are utilized to achieve high accuracy and repeatability. This stage is crucial as it forms the foundation of the vehicle’s structure. Quality checks during this phase often include dimensional inspections to ensure that parts fit together correctly.
Welding and Assembly
After forming, components move to the welding stage. Advanced robotic welding techniques are commonly employed to create strong, consistent joints. This is followed by assembly, where various parts, such as the motor, battery, and interior elements, are integrated. During assembly, in-process quality control (IPQC) measures are implemented. These may include torque tests on bolts and connections to ensure they meet specified requirements.
Finishing Processes
The final stages involve painting and finishing. A multi-stage painting process is used to enhance durability and aesthetics. This includes surface preparation, primer application, and top coating. After painting, the vehicles undergo a curing process to ensure the paint adheres properly and withstands environmental factors. Quality checks at this stage might involve visual inspections and adhesion tests to confirm the finish meets standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing of the EEC L7C electric car. B2B buyers should be familiar with the various QC measures that ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
The EEC L7C electric car adheres to several international quality management standards, including ISO 9001, which ensures effective quality management systems. Additionally, compliance with CE (Conformité Européenne) standards is essential for vehicles marketed in Europe, ensuring they meet health, safety, and environmental protection requirements. For electric vehicles, adherence to specific battery safety standards is also critical.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies that raw materials meet specified standards before they enter the production process. Suppliers must provide documentation to prove compliance with material specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout manufacturing, IPQC measures are taken to monitor and control quality during production. This includes regular inspections of welding, assembly, and painting processes to catch any deviations from quality standards early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, each vehicle undergoes a thorough inspection. This includes functional testing of the electrical systems, performance tests, and safety checks. Vehicles are often subjected to dynamic testing to assess their performance under real-world conditions.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Product Quality?
Testing is a vital aspect of quality assurance for the EEC L7C electric car. Various methods are employed to ensure that the vehicle meets safety and performance specifications.
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing all electronic and mechanical systems, including the battery management system, motor performance, and braking efficiency.
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles are subjected to stress tests to simulate long-term use. This may include fatigue testing of structural components and environmental tests to evaluate performance under extreme conditions.
-
Safety Testing: Comprehensive safety tests are conducted, including crash simulations to assess occupant protection. Compliance with relevant safety regulations is verified.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is essential for ensuring product reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Buyers should look for evidence of compliance with international standards and request documentation that demonstrates the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Reviewing Quality Reports
Buyers should request access to quality assurance reports, which detail the outcomes of various testing and inspection processes. These reports should include information on defect rates, corrective actions taken, and overall production quality metrics.
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification. These services can conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing process and product quality, providing unbiased reports to buyers.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing the EEC L7C electric car, international buyers should be aware of the certification nuances that may affect procurement.
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific certification requirements that must be met. For example, vehicles sold in Europe must comply with EU regulations, while those intended for markets in Africa or South America may have different standards.
-
Documentation and Traceability: Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation proving compliance with all relevant standards. This includes certificates of conformity, test reports, and material certifications.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers from different regions must familiarize themselves with local regulations that may impact vehicle certification. This understanding can help prevent compliance issues and ensure smooth market entry.
By understanding the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and certification nuances associated with the EEC L7C electric car, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure reliable products for their markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘eec l7c electric car’
In the growing market for electric vehicles, particularly the EEC L7c electric car, B2B buyers must navigate a series of essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist to streamline your sourcing strategy, ultimately facilitating a smoother transaction and better product alignment with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific technical requirements of the EEC L7c electric car is critical. Consider parameters such as battery capacity, range, and motor power. Clearly defined specifications help ensure that the vehicles will meet your operational needs and comply with local regulations.
Step 2: Identify Your Target Market
Before purchasing, analyze the demographics and requirements of your target market. Are you catering to urban commuters, delivery services, or leisure users? Tailoring your choice of electric car to the preferences and needs of your audience will enhance marketability and customer satisfaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Due diligence in supplier evaluation can significantly impact your purchasing experience. Look for manufacturers with EEC certification and a proven track record in electric vehicle production. Request company profiles, product samples, and references from previous clients to assess reliability and quality.
- Tip: Check for suppliers that offer post-sale support and warranties to safeguard your investment.
Step 4: Review Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the EEC L7c electric car meets the regulatory standards of the regions you plan to operate in. Regulations can vary significantly between countries, particularly regarding safety, emissions, and operational guidelines. Verify that the vehicle complies with local EEC homologation standards.
Step 5: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the electric car, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure. Understanding the long-term financial implications will help in making a more informed decision, especially in markets where operational costs can fluctuate.
- Consider: The availability of local service centers for maintenance and repairs, as well as the cost of spare parts.
Step 6: Negotiate Payment Terms and Delivery Schedule
Clarifying payment terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings later. Standard payment options such as T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) or L/C (Letter of Credit) should be discussed. Also, establish a clear delivery schedule to align with your business operations and avoid potential delays.
Step 7: Conduct a Pilot Test
Before full-scale procurement, consider arranging a pilot test with a small batch of vehicles. This allows you to assess performance, gather feedback, and make any necessary adjustments before committing to a larger order. Engaging potential users in this phase can provide valuable insights into vehicle usability and acceptance.
Following this checklist will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in sourcing the EEC L7c electric car, ensuring that their investment aligns with their operational needs and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for eec l7c electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for EEC L7c Electric Car Sourcing?
When sourcing the EEC L7c electric car, it’s crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. Key elements include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as lithium iron phosphate for batteries, steel for the chassis, and electronic components for the vehicle’s systems, significantly impacts the pricing. High-quality materials can elevate the cost but also enhance the vehicle’s longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be a significant factor in the overall price. Countries with lower labor costs may provide competitive pricing, but this can also affect quality and consistency. Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing complex components like electric motors and battery systems.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, thus lowering the overall price for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production lines can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific vehicle features or modifications will increase the upfront costs but may be necessary for tailored solutions.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the vehicle meets safety and performance standards. This can add to costs but is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring compliance with regulations, especially for international markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight, customs duties, and insurance, play a critical role, particularly for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market competition, demand, and the relationship between the buyer and supplier.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect EEC L7c Electric Car Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of EEC L7c electric cars:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities (Minimum Order Quantity) often leads to discounts. Buyers looking to procure multiple units should negotiate for better pricing based on volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as upgraded battery capacity or unique interior designs, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expenses.
-
Material Choices: Higher-quality materials may lead to increased costs but can improve durability and performance. Buyers should assess the trade-offs when selecting materials.
-
Quality Certifications: Vehicles that meet specific international quality standards may come at a premium. Ensure that the supplier provides relevant certifications, particularly for markets in Europe and North America.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more for their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery can significantly affect the total cost. Buyers should clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in EEC L7c Electric Car Sourcing?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some strategies to optimize sourcing costs:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals and flexibility in future transactions.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, insurance, and depreciation. A slightly higher upfront cost could result in significant savings over the vehicle’s lifespan.
-
Consider Local Regulations: Different regions may have specific requirements for electric vehicles, such as emissions standards and safety certifications. Ensure that the sourced vehicle complies with local regulations to avoid additional costs.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing to ensure that you are getting a fair deal. This can also help in understanding when to negotiate or when to hold off on purchasing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Please note that prices for the EEC L7c electric car can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and specific buyer requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing eec l7c electric car With Other Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles, B2B buyers have a variety of options to consider when selecting a suitable solution for their transportation needs. The EEC L7C electric car stands out for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, but exploring alternatives can provide additional insights for businesses looking to maximize their investment. Below is a comparative analysis of the EEC L7C electric car against two viable alternatives: electric scooters and traditional combustion engine vehicles.
| Comparison Aspect | EEC L7C Electric Car | Electric Scooter | Traditional Combustion Engine Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 90 km/h; Range: 150-170 km | Max speed: 45-60 km/h; Range: 40-100 km | Max speed: 120-200 km/h; Range: 500-800 km |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; Low maintenance | Lower initial cost; Minimal maintenance | Higher initial cost; High fuel and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Minimal infrastructure needed | Requires fuel stations and maintenance facilities |
| Maintenance | Low; battery care and occasional checks | Very low; mainly tire and brake checks | High; regular servicing and parts replacement |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting and short family trips | Individual short trips in urban areas | Long-distance travel and heavy-duty transport |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Electric Scooters as an Alternative?
Electric scooters offer a lightweight, economical solution for individual urban commutes. Their lower initial cost and minimal maintenance make them attractive for cost-conscious buyers. However, they typically have limited range and speed compared to the EEC L7C electric car, making them less suitable for family transport or longer trips. Additionally, the lack of weather protection can be a drawback in less favorable climates.
How Do Traditional Combustion Engine Vehicles Compare?
Traditional combustion engine vehicles excel in performance and range, making them ideal for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications. They are widely available and supported by a robust infrastructure of fuel stations. However, they come with higher initial costs, ongoing fuel expenses, and significant maintenance needs. Furthermore, increasing environmental regulations and the shift towards sustainable solutions may pose long-term viability concerns for combustion engine vehicles.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the appropriate transportation solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including usage patterns, budget constraints, and environmental goals. For businesses focused on urban commuting and short trips, the EEC L7C electric car offers a balanced solution with ample performance and low operational costs. On the other hand, for those needing more flexibility for longer distances, traditional vehicles may be more appropriate. Electric scooters can serve as a supplementary option for individual employees seeking cost-effective transport for short distances. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s operational strategy, budget, and sustainability objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for eec l7c electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the EEC L7C Electric Car?
Understanding the essential technical properties of the EEC L7C electric car is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Battery Capacity and Type
The EEC L7C electric car typically features a Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, with a capacity around 102.4V and 134Ah. This high capacity allows for a substantial driving range of approximately 150 to 170 kilometers on a single charge. In B2B terms, understanding battery specifications is vital for evaluating performance, maintenance needs, and the overall cost of ownership. -
Motor Power
Equipped with a 13kW PMS motor, the EEC L7C achieves a maximum speed of 90 km/h. The motor’s efficiency and power output directly influence the vehicle’s performance in urban settings, making it suitable for short commutes. For businesses, this translates into considerations about operational efficiency and suitability for specific transport needs. -
Curb Weight and Loading Capacity
The curb weight of the EEC L7C is approximately 600 kg, with a loading capacity of 400 kg. These specifications are critical for logistics and operational planning, as they determine how much cargo or additional passengers can be transported without compromising safety or vehicle performance. -
Suspension System
Featuring a front McPherson independent suspension and a rear arm non-independent suspension, the EEC L7C provides a stable and comfortable ride. For buyers, understanding the suspension system is essential for evaluating ride quality, safety features, and the vehicle’s ability to handle various road conditions. -
Safety Features
The EEC L7C includes advanced safety features such as ABS, electronic power brakes, and a robust braking system with front disc and rear drum brakes. Safety specifications are paramount for B2B buyers, as they directly impact insurance costs, liability, and user trust. -
Charging Time
The vehicle requires 6-8 hours for a full charge. This charging duration is a critical factor for businesses that rely on quick turnaround times for their electric fleets. Understanding charging requirements helps in planning operational schedules and minimizing downtime.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing an EEC L7C Electric Car?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common trade terms relevant to the EEC L7C electric car:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can be crucial when sourcing components or negotiating partnerships, ensuring that buyers receive genuine parts and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory management, particularly when considering bulk purchases of vehicles. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for the purchase of specific goods or services. This term is vital for procurement processes, enabling buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B transactions, as they dictate shipping costs, risk, and liability during transportation. -
EEC Homologation
This term refers to the certification process that ensures vehicles meet European standards for safety, emissions, and performance. For buyers, EEC homologation is critical, as it affects vehicle eligibility for sale and use in various markets. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from the initiation of a process until its completion. For electric vehicles, this includes manufacturing and delivery times. Understanding lead times is essential for businesses to effectively plan their operations and customer commitments.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of purchasing the EEC L7C electric car with greater confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the eec l7c electric car Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the EEC L7c Electric Car Sector?
The EEC L7c electric car market is witnessing significant growth driven by the global shift towards sustainable transportation. Key factors influencing this trend include rising fuel prices, stringent emissions regulations, and growing consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are increasingly seeking electric vehicles that not only meet regulatory standards but also offer cost-effective solutions for urban commuting and last-mile delivery.
Emerging technologies such as advanced battery systems and smart connectivity features are reshaping the electric vehicle landscape. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into electric cars enhances fleet management and operational efficiency, making these vehicles attractive for businesses focused on logistics and transportation. Furthermore, the rise of electric mini delivery vans and compact passenger cars aligns with the urbanization trend, as cities look for efficient ways to manage traffic congestion and pollution.
B2B buyers should also consider the importance of local partnerships and supply chain resilience. Sourcing electric vehicles from manufacturers with established networks in target regions can mitigate risks related to shipping delays and tariffs, particularly in markets with fluctuating trade policies.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence B2B Decisions in the EEC L7c Electric Car Market?
The environmental impact of sourcing practices is increasingly critical for B2B buyers in the electric car sector. As companies strive to meet sustainability goals, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers who adhere to environmentally responsible practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring minimal waste during production.
In the context of EEC L7c electric cars, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to EU regulations ensure that vehicles are produced with sustainability in mind. Moreover, sourcing from suppliers that utilize green materials and renewable energy sources can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Engaging in ethical sourcing also means assessing the social impact of the supply chain. Companies should consider labor practices, community engagement, and the overall well-being of workers involved in the manufacturing process. This holistic approach not only contributes to environmental stewardship but also supports the long-term viability of the supply chain, fostering loyalty among customers who value corporate responsibility.
What is the Brief History and Evolution of the EEC L7c Electric Car Sector?
The EEC L7c electric car segment has evolved significantly over the past decade, driven by advancements in battery technology and growing regulatory support for electric vehicles. Initially, electric vehicles were viewed as niche products, but increasing concerns over climate change and urban air quality have propelled them into the mainstream.
The introduction of the L7c classification within the European Economic Community (EEC) allowed for the development of compact, low-speed electric vehicles that cater to urban commuting needs. This regulation has paved the way for manufacturers to innovate and produce versatile electric cars suited for various applications, from family transportation to last-mile delivery solutions.
As the market continues to mature, the focus is shifting towards integrating smarter technologies, improving vehicle performance, and enhancing user experience, ensuring that the EEC L7c electric car remains a competitive option for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of eec l7c electric car
-
How do I ensure the quality of the EEC L7C electric car before purchasing?
To ensure quality, consider conducting a thorough supplier vetting process. Request product samples and certifications, such as EEC homologation. Establish communication with the manufacturer to discuss their quality assurance protocols, testing standards, and production capabilities. It’s also beneficial to visit the manufacturing facility if possible, or arrange for third-party inspections to verify the vehicle’s compliance with international quality standards. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing EEC L7C electric cars?
Most suppliers offer flexible payment terms, commonly including T/T (telegraphic transfer) and L/C (letter of credit). T/T is often preferred for its simplicity, requiring a deposit upfront, with the balance due before shipment. L/C provides more security, as it guarantees payment upon meeting specific conditions. Discuss payment options with the supplier to choose terms that align with your financial strategy and risk tolerance. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for the EEC L7C electric car?
The MOQ can vary by supplier but generally ranges from 1 to 5 units for initial orders. For larger orders, you may negotiate better pricing or terms. Consider your market demand and storage capabilities when determining the quantity. Some suppliers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time buyers or bulk orders, so it’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with them. -
How can I customize the EEC L7C electric car to meet my needs?
Customization options typically include color choices, interior features, and additional technology integrations like GPS or enhanced multimedia systems. Engage with the supplier to discuss your specific requirements and explore available modifications. It’s important to understand the implications of customization on pricing and lead times, as these factors can impact your order’s delivery schedule. -
What logistics options are available for shipping the EEC L7C electric car internationally?
International shipping options usually include container shipping, RoRo (Roll-on/Roll-off), or flat rack shipping, depending on your destination and budget. Ensure the supplier has experience in exporting vehicles and can provide assistance with customs clearance and documentation. It’s crucial to discuss shipping timelines, insurance, and potential tariffs or duties to avoid unexpected costs. -
How do I assess the reliability of a supplier for the EEC L7C electric car?
To assess supplier reliability, check their experience in the electric vehicle market, read customer reviews, and verify their certifications. Request references from previous B2B clients and inquire about their delivery timelines and after-sales service. Additionally, engaging in direct communication can provide insight into their responsiveness and professionalism, which are key indicators of a reliable supplier. -
What are the key safety features of the EEC L7C electric car?
The EEC L7C electric car is designed with multiple safety features, including a robust braking system, a strong chassis for impact protection, and advanced lighting systems for visibility. It also includes features like anti-lock braking systems (ABS), seat belts, and a stable suspension system to enhance safety during operation. Reviewing the vehicle’s safety certifications can provide additional assurance of its reliability. -
What are the maintenance requirements for the EEC L7C electric car?
Maintenance for the EEC L7C is relatively low compared to traditional vehicles, primarily involving regular checks on the battery system, brakes, and tires. Schedule periodic inspections to ensure all components function correctly and to identify any wear and tear early. Consult with the supplier for specific maintenance guidelines and recommended service intervals to keep the vehicle in optimal condition and prolong its lifespan.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Eec L7C Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
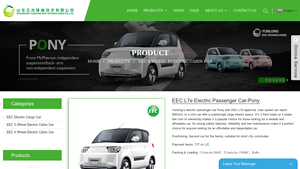
1. Yunlong – EEC L7e Electric Passenger Car-Pony
Domain: bev-cars.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “EEC L7e Electric Passenger Car-Pony”, “Manufacturer”: “Yunlong”, “Max Speed”: “90 km/h”, “Endurance Mileage”: “150 km”, “Battery”: {“Type”: “Lithium Iron Phosphate”, “Voltage”: “102.4V”, “Capacity”: “134Ah”}, “Motor”: {“Power”: “13Kw PMS Motor”}, “Brake System”: “Front disc and rear drum with hydraulic system”, “LED Lights”: “Full light control system with LED headlights”, “Dashb…
2. Cieauto – Lixiang Auto Mega Electric MPV
Domain: cieauto.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: 33 new Electric Vehicles for sale, driving ranges from 0 to 50 kilometres, mostly Chinese brands, CLTC mileage standard. Popular models include ZEEKR 007 series, 001 series, Avatr11, BYD series. Key products: Lixiang Auto Mega Electric Large Size MPV Ultra Version Car – From $73,239.00; 2025 BYD Han New Energy Electric Vehicle – From $22,378.00; 2025 AITO M9 Ultra Electric Car Hybrid – From $67,00…
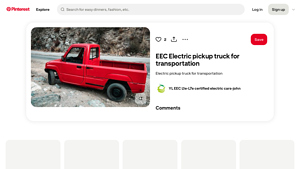
3. EEC – Electric Pickup Truck
Domain: es.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: EEC Electric Pickup Truck for Transportation
4. EEC – Electric Car
5. Dongfeng – M5 EV
Domain: forthingmotor.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer: Dongfeng
Model: M5 EV
Type: Electric MPV
Seating Capacity: 7/9 seats
Battery Capacity: 68 kWh
Cruising Range: 401 km
Charging Time: Fast charge 0.58 hours / Slow charge 13 hours
Fast Charge Capacity: 80%
Maximum Power: 90 kW (122 Ps)
Maximum Torque: 300 Nm
Gearbox: Electric vehicle single speed gearbox
Dimensions (L x W x H): 5135 x 1720 x 1990 mm
Body Structure: 4 Door MPV
Top Speed…
6. Easirent – Electric Vehicle Rentals
Domain: us.easirent.com
Introduction: Easirent offers electric vehicle rentals including the Kia e-Niro SUV and Tesla Model 3. These vehicles provide a quiet, smooth, and eco-friendly driving experience. Renting an EV is cost-effective, as it eliminates fuel costs and may offer incentives like reduced charging rates and free parking. The Kia e-Niro features a tech-savvy infotainment system compatible with Apple CarPlay and Android Aut…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for eec l7c electric car
In summary, the EEC L7c electric car presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Its impressive specifications—including a maximum speed of 90 km/h, an endurance range of 150 km, and robust safety features—position it as an ideal solution for urban commuting and last-mile logistics. The vehicle’s low cost of ownership and maintenance further enhance its appeal, making it a strategic choice for fleet managers and businesses seeking sustainable transport options.
Strategic sourcing is essential in capitalizing on these advantages. By engaging with trusted manufacturers who adhere to EEC standards, buyers can ensure product reliability, compliance, and quality assurance. Emphasizing long-term partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, enhanced service support, and innovation in product development.
Looking ahead, the market for electric vehicles is expected to expand rapidly. Now is the time for international buyers to explore the EEC L7c electric car as a viable addition to their fleets. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your business’s sustainability profile and meet the evolving demands of eco-conscious consumers. Reach out to manufacturers today to begin your journey towards greener transportation solutions.