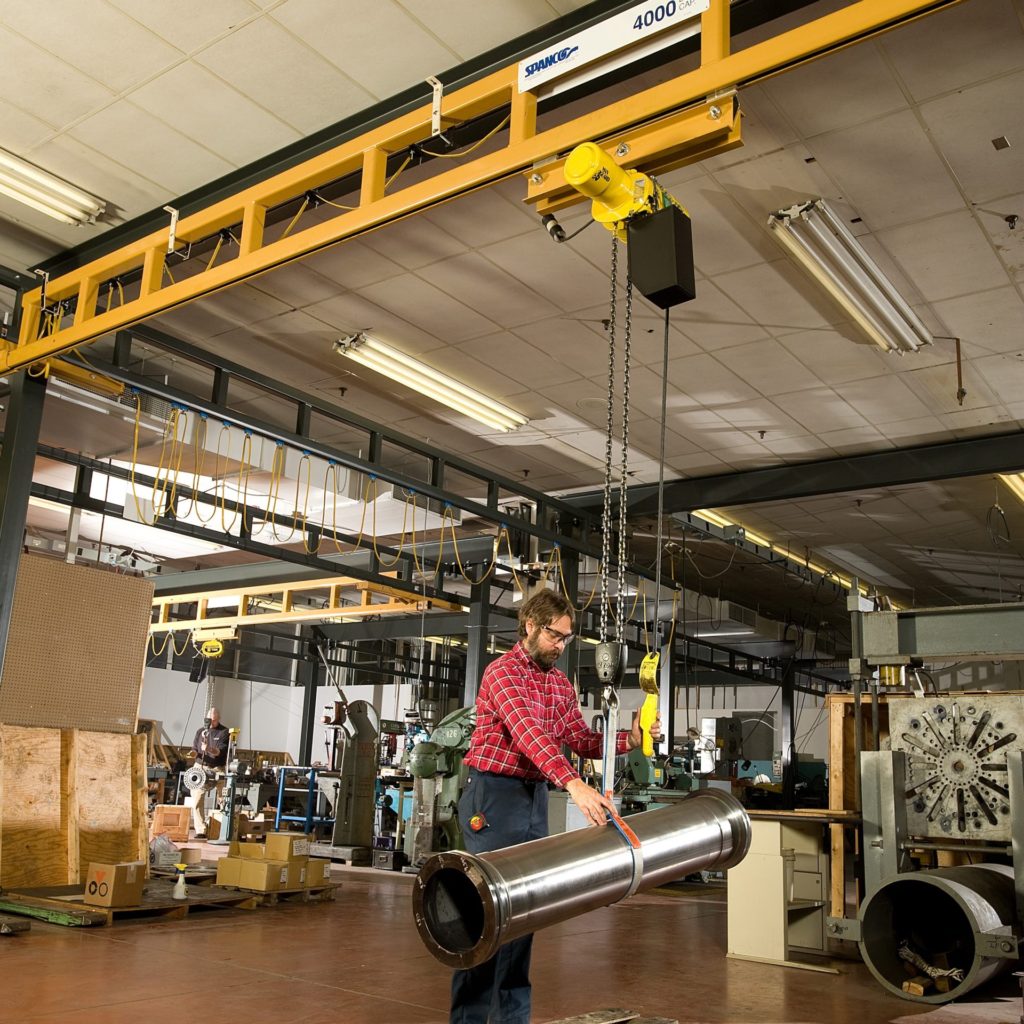
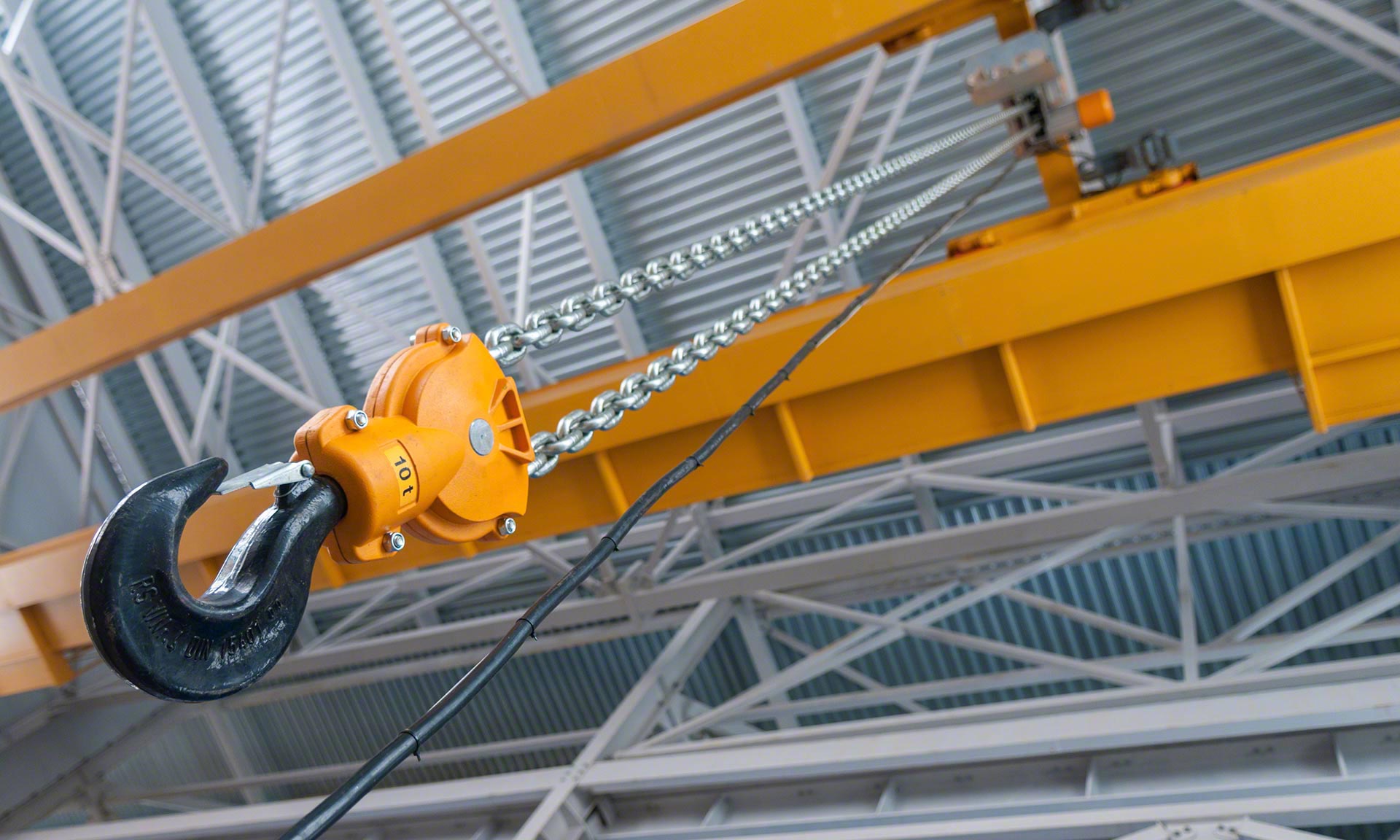
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for overhead Crane
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, sourcing overhead cranes that meet specific operational needs poses a significant challenge for businesses across the globe. As companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam) strive to enhance their productivity and safety standards, understanding the complexities of overhead crane systems is crucial. This guide delves into the diverse types of overhead cranes available, their various applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
By exploring the intricacies of overhead crane components, operational efficiencies, and technological advancements, this comprehensive resource equips international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. From evaluating cost structures to understanding supplier vetting processes, we aim to empower businesses to navigate the global market effectively.
Whether you are looking for lightweight solutions for small workshops or robust systems for heavy industrial applications, this guide serves as your roadmap to selecting the right overhead crane tailored to your operational requirements. With a focus on safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, we provide actionable insights that will help you maximize your investment in overhead crane technology, ensuring that your business remains competitive in an ever-evolving market.
Understanding overhead Crane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overhead Bridge Crane | Horizontal bridge with a hoist that travels along a runway | Manufacturing, Warehousing | Pros: High lifting capacity, efficient space utilization. Cons: Requires overhead space, installation complexity. |
| Gantry Crane | A crane that runs on legs instead of overhead rails | Outdoor applications, shipping yards | Pros: Flexible positioning, no need for overhead support. Cons: Limited to outdoor use, may require more space. |
| Jib Crane | Fixed arm that pivots to lift and move loads | Assembly lines, workshops | Pros: Compact design, easy to maneuver. Cons: Limited lifting height and capacity. |
| Chain Hoist Crane | Utilizes a chain mechanism for lifting, typically lighter loads | Smaller industrial settings, maintenance tasks | Pros: Cost-effective, simple operation. Cons: Lower lifting capacity, less versatile. |
| Rope Hoist Crane | Lifts loads using a rope, often with higher capacity | Heavy-duty applications, construction sites | Pros: High lifting capacity, adaptable to various setups. Cons: Requires more maintenance, can be expensive. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Overhead Bridge Cranes?
Overhead bridge cranes are characterized by their horizontal bridge that spans the width of a workspace, supported by end trucks that run along fixed runways. This design allows for efficient multi-directional movement of heavy loads, making them ideal for manufacturing and warehousing environments. Buyers should consider the installation requirements and overhead space availability, as these cranes necessitate significant vertical clearance.
How Do Gantry Cranes Differ from Other Types?
Gantry cranes are distinguished by their ability to operate on legs rather than relying on overhead tracks. This feature allows them to be used in outdoor settings, such as shipping yards and construction sites, where overhead infrastructure may not be feasible. While they offer flexibility in positioning and ease of transport, potential buyers should assess the space requirements and the crane’s limitations concerning indoor use.
Why Choose Jib Cranes for Specific Applications?
Jib cranes are designed with a rotating arm that allows for lifting and moving loads within a limited area. Their compact design makes them suitable for assembly lines and workshops where space is at a premium. When considering a jib crane, buyers should evaluate their specific lifting needs and the limitations in height and capacity, ensuring that the crane fits their operational requirements.
What Advantages Do Chain Hoist Cranes Offer?
Chain hoist cranes are ideal for lighter lifting tasks and are often employed in smaller industrial environments. Their straightforward operation and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for maintenance and minor lifting applications. Buyers should weigh the lower lifting capacity against their specific needs, ensuring that the crane can handle the required load without compromising efficiency.
When Should You Consider Rope Hoist Cranes?
Rope hoist cranes are known for their ability to lift heavier loads, making them suitable for demanding applications in construction and heavy industry. Their adaptability allows for various configurations, which can be tailored to specific operational setups. However, potential buyers should be aware of the increased maintenance requirements and costs associated with these cranes, ensuring they align with their long-term operational strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of overhead Crane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of overhead Crane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly Line Operations | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs. | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and workflow. |
| Construction | Heavy Material Handling | Enhances safety and productivity on job sites. | Consider load capacity and environmental conditions. |
| Shipbuilding | Loading and Unloading Heavy Components | Streamlines operations and reduces turnaround time. | Look for cranes with corrosion-resistant features. |
| Mining | Transporting Materials in Harsh Environments | Improves operational safety and efficiency. | Evaluate durability and maintenance support in remote locations. |
| Warehousing | Inventory Management and Order Fulfillment | Maximizes storage space and speeds up retrieval processes. | Assess scalability and integration with inventory systems. |
How is Overhead Crane Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, overhead cranes are essential for assembly line operations, allowing for the efficient movement of components between workstations. They reduce the need for manual handling, which minimizes the risk of workplace injuries. Buyers should consider the crane’s lifting capacity and compatibility with existing systems to ensure seamless integration into their production lines. Additionally, features like smart technology can enhance operational efficiency by providing real-time data on usage and maintenance needs.
What Role Do Overhead Cranes Play in Construction?
In construction, overhead cranes facilitate the heavy lifting of materials, such as steel beams and concrete panels, directly on-site. This capability not only enhances safety by minimizing manual handling but also increases productivity by allowing multiple materials to be moved simultaneously. Buyers need to evaluate the crane’s load capacity, mobility, and suitability for outdoor use, especially in regions with varying environmental conditions, such as those found in Africa and the Middle East.
How Are Overhead Cranes Utilized in Shipbuilding?
Overhead cranes are crucial in shipbuilding for loading and unloading heavy components, such as engines and hull sections. Their ability to maneuver in tight spaces significantly reduces turnaround times and improves overall operational efficiency. When sourcing cranes for shipbuilding, buyers should consider features that provide corrosion resistance and durability, especially for operations in coastal environments.
Why Are Overhead Cranes Important in Mining?
In the mining industry, overhead cranes are used to transport materials in harsh environments, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. These cranes can handle heavy loads, making them ideal for moving ore and equipment within mining facilities. Buyers should prioritize cranes that offer high durability and low maintenance requirements, as well as those equipped with safety features to protect workers in remote locations.
How Do Overhead Cranes Enhance Warehousing Operations?
In warehousing, overhead cranes are employed for inventory management and order fulfillment, allowing for the efficient movement of goods within storage facilities. This application maximizes vertical space and speeds up retrieval processes, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in logistics. Buyers should assess the crane’s scalability and its ability to integrate with existing inventory management systems to optimize warehouse operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘overhead Crane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Safety Compliance in Overhead Crane Operations
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with stringent safety regulations surrounding the operation of overhead cranes. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, where compliance standards can vary significantly, ensuring that a crane meets local regulations can be daunting. Buyers may face issues such as inadequate operator training, failure to perform regular inspections, and not implementing safety features. These oversights can lead to accidents, resulting in injuries, equipment damage, and costly legal liabilities.
The Solution: To effectively address safety compliance, buyers should prioritize investing in comprehensive training programs for crane operators. This includes both theoretical instruction on safety standards and practical training on equipment handling. Additionally, selecting cranes equipped with advanced safety features—such as overload protection, emergency stop functions, and condition monitoring systems—can greatly enhance operational safety. Buyers should also establish a regular inspection schedule in partnership with a reliable service provider to ensure that all equipment meets safety standards. Utilizing remote monitoring systems can provide real-time data on crane performance, aiding in timely maintenance and compliance checks.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies in Material Handling Processes
The Problem: Many businesses experience inefficiencies in their material handling processes due to outdated or inadequate overhead crane systems. This can lead to increased operational costs, extended project timelines, and employee frustration. For instance, a manufacturing facility may struggle with slow load handling times, causing bottlenecks in production and ultimately affecting customer satisfaction. Such inefficiencies can stem from poorly configured systems or insufficient lifting capacities.
The Solution: To combat inefficiencies, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of their current material handling processes and identify areas for improvement. This could involve upgrading to modern cranes that feature smart technology and automation capabilities, which can streamline operations and reduce manual handling times. Additionally, collaborating with manufacturers to customize cranes to fit specific operational needs—such as load capacity and workspace constraints—can optimize performance. Implementing an integrated software solution that coordinates crane operations with other logistics systems can also enhance efficiency by providing real-time data on load movements and inventory status.
Scenario 3: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Overhead cranes, particularly those that operate in harsh environments or are used frequently, can incur high maintenance costs and experience significant downtime. This is a common concern for B2B buyers who require consistent and reliable lifting solutions. Frequent repairs not only affect the budget but also disrupt operations, leading to delays in project timelines and loss of revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance costs and reduce downtime, buyers should consider investing in cranes with durable components designed for their specific operational conditions. Implementing a predictive maintenance strategy, supported by condition monitoring technologies, can help anticipate potential issues before they escalate. This approach allows businesses to schedule maintenance during non-peak hours, minimizing operational disruption. Furthermore, establishing a partnership with a reputable crane service provider can ensure that regular maintenance checks are performed efficiently, and any repairs are executed promptly, thereby extending the lifespan of the crane and optimizing overall performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for overhead Crane
When selecting materials for overhead cranes, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in overhead crane construction: steel, aluminum, polymer composites, and galvanized steel. Each material presents unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel for Overhead Cranes?
Steel is the most widely used material for overhead cranes due to its exceptional strength and durability. It has a high tensile strength, making it capable of supporting heavy loads without deforming. Steel also exhibits excellent temperature resistance, maintaining its structural integrity under extreme conditions. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, particularly in humid or chemically aggressive environments, which necessitates protective coatings or treatments.
Pros and Cons of Steel:
– Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent load-bearing capacity, and availability in various grades.
– Cons: Heavier than alternatives, requires maintenance to prevent rust, and can be more expensive depending on the grade.
Impact on Application:
Steel is suitable for heavy-duty applications in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and shipping. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice for different environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is critical. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that the steel used meets local regulations regarding load capacities and safety standards.
How Does Aluminum Compare for Overhead Cranes?
Aluminum is increasingly popular for overhead cranes, particularly in applications where weight is a concern. It is significantly lighter than steel, which can improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. Aluminum also offers good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor or coastal environments.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
– Pros: Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, and lower energy consumption during operation.
– Cons: Lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit load capacities, and higher cost per pound.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum cranes are ideal for industries requiring frequent relocation or where overhead space is limited, such as in assembly lines or warehouses.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that aluminum components comply with standards like JIS or ASTM. Additionally, understanding the local market’s aluminum availability can influence cost and lead times.
What Role Do Polymer Composites Play in Overhead Cranes?
Polymer composites are emerging as a lightweight alternative for specific crane components. These materials are engineered to provide excellent strength while being resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements, such as thermal stability.
Pros and Cons of Polymer Composites:
– Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and customizable properties.
– Cons: Generally higher cost, potential for lower load-bearing capacity compared to metals, and less widespread acceptance in traditional industries.
Impact on Application:
Polymer composites are suitable for specialized applications, including environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals, where traditional materials may fail.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should assess the availability of polymer composites in their region and ensure that they meet relevant industry standards. Understanding the performance characteristics in local climates is also crucial.
Why Choose Galvanized Steel for Overhead Cranes?
Galvanized steel is steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc to enhance its corrosion resistance. This makes it an excellent choice for cranes operating in harsh environments, such as coastal areas or industries dealing with corrosive substances.
Pros and Cons of Galvanized Steel:
– Pros: Enhanced corrosion resistance, maintains strength similar to regular steel, and relatively low maintenance.
– Cons: Heavier than aluminum, potential for zinc coating to wear off over time, and higher initial costs compared to untreated steel.
Impact on Application:
Galvanized steel is ideal for outdoor cranes or those exposed to moisture and chemicals, ensuring longevity and reliability in challenging conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
It is essential to ensure that galvanized steel meets local standards and regulations, particularly in regions with specific environmental conditions.
Summary of Material Selection for Overhead Cranes
| Material | Typical Use Case for overhead Crane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, portable applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Polymer Composites | Specialized, corrosive environments | Customizable and lightweight | Higher cost, lower load capacity | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Outdoor and harsh environments | Enhanced corrosion resistance | Heavier than aluminum | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to optimize their overhead crane procurement, ensuring they choose materials that align with their operational needs and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for overhead Crane
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Overhead Cranes?
The manufacturing process of overhead cranes involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards for safety, efficiency, and durability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
In this initial phase, manufacturers select high-quality materials, primarily steel, which is crucial for the structural integrity of the crane. The materials are inspected for defects and compliance with international standards. Steel plates and beams are cut to size using advanced cutting techniques such as laser cutting or plasma cutting, which provide precision and reduce waste.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This may include bending, welding, and machining. Advanced techniques like robotic welding can be employed to ensure uniformity and strength in the joints, while CNC machining is used for creating precise components, such as gears and brackets. These processes are vital for creating the framework that will support the crane’s operational capabilities.
Assembly Processes
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete crane. This involves the installation of critical elements such as the hoist, trolley, bridge beams, and end trucks. Each component is meticulously aligned and secured, often using high-torque bolts to ensure stability under heavy loads. Quality checks are integrated at this stage, where each assembly is inspected for proper alignment and functionality.
Finishing Touches
The final stage involves surface treatment and finishing. This can include painting, galvanizing, or powder coating, which not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also protects against corrosion and wear. A comprehensive inspection ensures that all surfaces are treated correctly and meet the required specifications for durability.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider for Overhead Cranes?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of overhead cranes, given their significant role in industrial operations. Buyers should be aware of various international and industry-specific standards that govern the quality of these lifting devices.
International Standards
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard indicates that the manufacturer has established a systematic approach to quality assurance throughout the production process. Additionally, ISO 3834 pertains specifically to welding quality, ensuring that welded components meet stringent quality criteria.
Industry-Specific Certifications
For cranes operating in the European market, CE marking is essential. This certification signifies that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are critical for cranes used in oil and gas applications, ensuring that they can withstand harsh operational conditions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Overhead Crane Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential in ensuring that overhead cranes meet the required safety and performance standards. These checkpoints can be categorized into three main stages: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This includes verifying certifications, conducting dimensional checks, and assessing material properties to ensure they conform to specifications. Any substandard materials are rejected, preventing potential issues later in the manufacturing process.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing stages, IPQC focuses on monitoring the production processes. This includes regular inspections of welding quality, dimensional accuracy of machined parts, and assembly tolerances. Using statistical process control (SPC) techniques, manufacturers can identify variations in the process and implement corrective actions promptly.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is conducted once the overhead crane is fully assembled. This final inspection includes load testing to ensure that the crane can safely handle its rated capacity. Additional checks may involve operational tests and safety feature evaluations. Documentation of these tests is crucial for compliance and future reference.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One effective method is to perform supplier audits. This involves visiting the manufacturing facility to review quality control processes, equipment, and employee training practices. Audits provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality and adherence to standards.
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers. These documents should outline the QC processes, test results, and compliance with relevant standards. Transparent suppliers will readily provide this information, demonstrating their commitment to quality.
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the crane’s quality. These independent entities can conduct inspections and testing at various stages of production, providing buyers with additional assurance regarding the product’s quality and safety.
What Are the Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
When sourcing overhead cranes from international manufacturers, buyers must navigate specific quality control nuances. Understanding these factors can help mitigate risks associated with international procurement.
Compliance with Local Regulations
International buyers should ensure that the cranes comply with local regulations and standards in their respective countries. This may require additional certifications or modifications to meet specific safety requirements.
Cultural and Language Barriers
Cultural differences and language barriers can complicate communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear lines of communication and possibly hiring local representatives can help bridge these gaps, ensuring that all parties understand quality requirements.
Logistical Challenges
Transportation of cranes across borders can introduce logistical challenges that may impact quality. Buyers should consider the impact of shipping conditions on the crane’s integrity and ensure that the supplier takes necessary precautions during transport.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for overhead cranes is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable and safe lifting solutions. By considering these factors, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure the longevity and performance of their investment.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘overhead Crane’
In this guide, we aim to provide a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure overhead cranes. This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right crane for your operational needs, ensuring efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your operational requirements is crucial. Start by determining the load capacity, lifting height, and span of the crane you need. Consider the environment in which the crane will operate, including space constraints and any specific industry regulations. This foundational step will guide your discussions with suppliers and ensure you select a crane that meets your unique needs.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Overhead Cranes
Familiarize yourself with the various types of overhead cranes available, such as bridge cranes, gantry cranes, and jib cranes. Each type serves different applications and has distinct features. For instance, gantry cranes are ideal for outdoor use where traditional runways are impractical. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision aligned with your operational context.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay attention to their experience with overhead cranes and customer support capabilities. A reliable supplier should provide transparent information about their products and services, helping you gauge their credibility and expertise.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with international safety standards and regulations relevant to overhead cranes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and compliance with local safety regulations. This step is crucial to mitigate risks associated with equipment failure and ensure safe operations within your facility.
Step 5: Assess Technology and Features
Modern overhead cranes often come equipped with advanced technology designed to enhance safety and productivity. Evaluate features such as remote monitoring, smart controls, and automation capabilities. These technologies can improve operational efficiency and provide real-time data for better decision-making, ultimately leading to cost savings.
Step 6: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotes from your selected suppliers. Ensure that the quotes include not just pricing, but also specifications, warranty terms, and after-sales support. Comparing these elements will help you identify the best value for your investment, considering both upfront costs and long-term operational expenses.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
Finally, consider the installation and training services offered by your supplier. Proper installation is critical to ensure the crane operates safely and efficiently. Additionally, training your staff on the correct usage of the crane will reduce the risk of accidents and enhance productivity. Make sure these services are included in your procurement plan.
By following this checklist, you can make a well-informed decision when sourcing an overhead crane, tailored to your specific operational needs and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for overhead Crane Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Overhead Crane Sourcing?
When sourcing overhead cranes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel and electronic components, significantly influences the final price. Prices can fluctuate based on global market conditions and availability, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less stable.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for both manufacturing and assembly. Labor costs can vary widely by region, with countries in Europe often having higher labor costs compared to those in the Middle East or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, but they can vary significantly depending on the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized crane designs, leading to higher upfront costs. However, investing in the right tooling can enhance production efficiency and quality.
-
Quality Control: Implementing stringent quality assurance processes ensures that the cranes meet safety and operational standards, which can add to the overall cost but is essential for reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including transportation and insurance, can be substantial, particularly for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms is vital to navigate these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s reputation, market demand, and the complexity of the crane.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Overhead Crane Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of overhead cranes, which buyers should consider when making purchasing decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess whether these customizations are necessary or if standard models would suffice.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs but ensure better performance and compliance with safety standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and experience can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher quality and reliability but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. For instance, choosing a supplier that offers FOB (Free on Board) shipping can shift some transportation risks and costs to the seller.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Overhead Crane Prices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions, there are several strategies to optimize costs.
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage the competitive landscape by obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers. Use these quotes to negotiate better terms and pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the specific pricing structures and common practices in different regions. For example, in Africa and South America, negotiation may play a more critical role compared to Europe, where prices can be more fixed.
-
Consider Local Regulations: Compliance with local regulations can influence costs. Ensure that the crane meets all safety and operational requirements to avoid additional expenses down the line.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is essential for B2B buyers sourcing overhead cranes. While indicative prices may vary, being informed can lead to better purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing overhead Crane With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Overhead Cranes for Material Handling Solutions
When considering material handling solutions in industrial settings, overhead cranes are a popular choice due to their robust performance and efficiency. However, various alternatives may also meet your operational needs. This section compares overhead cranes with two viable alternatives: Gantry Cranes and Forklifts. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these solutions can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Overhead Crane | Gantry Crane | Forklift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High lifting capacity; ideal for large spaces | Good for outdoor or warehouse applications; flexible movement | Versatile for various loads; limited vertical reach |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; long-term value | Moderate cost; lower than overhead cranes | Lower upfront cost; higher operational costs over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires fixed installation; more complex setup | Easier to set up; can be mobile or fixed | Quick to deploy; minimal setup required |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections needed; complex parts | Easier to maintain; fewer components | Routine maintenance; parts readily available |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty lifting in manufacturing | Outdoor or large warehouse settings | Transporting materials over short distances |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Gantry Cranes?
Gantry cranes are an excellent alternative for facilities with limited overhead space or for outdoor applications. They provide significant lifting capabilities and are often more cost-effective than overhead cranes. Their design allows for mobility, making them ideal for tasks that require movement across a larger area. However, they may not be suitable for environments requiring precise lifting or for heavy loads exceeding their capacity. Additionally, while maintenance is generally simpler than that of overhead cranes, they still require regular checks to ensure safety and functionality.
How Do Forklifts Compare as a Material Handling Solution?
Forklifts are widely recognized for their versatility in various industries. They are less expensive upfront and can quickly maneuver in tight spaces, making them suitable for smaller operations. Forklifts can handle a range of loads and are easily operated by trained personnel. However, their lifting capacity is generally lower than that of overhead and gantry cranes, and they can be less efficient for heavy-duty tasks. Moreover, forklifts require more frequent maintenance and can incur higher operational costs over time, especially in terms of fuel or battery replacement.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
Selecting the best material handling solution depends on various factors, including the nature of your operations, budget constraints, and specific lifting requirements. If your business requires heavy lifting in a confined space, an overhead crane might be the best choice despite its higher initial investment. Conversely, if you need mobility and flexibility, a gantry crane could provide a cost-effective alternative. For more versatile and immediate needs, a forklift may be the most practical option. Ultimately, understanding your operational demands and weighing the pros and cons of each solution will guide you in making the right decision tailored to your business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for overhead Crane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Overhead Cranes?
When considering an overhead crane for your operations, understanding its technical specifications is crucial. Here are some critical properties that impact performance, safety, and efficiency.
1. Load Capacity
The load capacity of an overhead crane refers to the maximum weight it can lift safely. It is typically expressed in tons. This specification is vital for B2B buyers as it directly influences the types of materials that can be handled, ensuring that the crane meets the operational demands without risk of overload, which could lead to equipment failure or safety hazards.
2. Span
Span is the distance between the crane’s end trucks, measured from one side of the runway to the other. This property is essential for determining how much area the crane can cover within a facility. A proper span maximizes workspace efficiency and ensures that the crane can maneuver freely without obstruction, which is particularly important in environments with limited space.
3. Lifting Height
Lifting height indicates how high the crane can raise a load. This specification is crucial for operations that require lifting materials to significant heights, such as in warehouses or manufacturing plants with multi-level storage systems. Understanding the lifting height helps businesses plan their layout and material flow effectively.
4. Hoisting Speed
The hoisting speed is the rate at which the crane can lift and lower loads, usually measured in meters per minute. This property is important for operational efficiency; faster hoisting speeds can reduce cycle times and enhance productivity. B2B buyers should assess their workflow requirements to select a crane with an appropriate hoisting speed.
5. Control System
The control system encompasses how the crane is operated, including manual and automated options. Advanced control systems often feature wireless controls, programmable settings, and smart technology that enhance safety and efficiency. Choosing the right control system can significantly impact operator comfort and operational safety.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in Overhead Crane Procurement?
Navigating the procurement of overhead cranes involves understanding specific industry terms that can affect purchasing decisions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to the company that manufactures the crane or its components. Understanding whether you are purchasing from an OEM or a reseller is crucial, as OEMs often provide better warranties, support, and parts availability. This knowledge can influence long-term maintenance and operational costs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For overhead cranes, knowing the MOQ can help businesses budget effectively and avoid excess inventory. This is particularly important for companies that may not require multiple units at once but want to ensure they receive the best pricing.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that businesses send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific product or service. For overhead cranes, an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive pricing and specifications, enabling informed decision-making based on budget and requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transit, which can significantly impact overall project costs.
5. Load Testing
Load testing involves assessing the crane’s performance by lifting a specified weight to ensure it operates safely within its rated capacity. This term is important for buyers to understand, as it is a critical step in the installation and commissioning process, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and operational standards.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terminologies, you can make informed decisions when sourcing overhead cranes, ensuring that they meet your operational needs while enhancing safety and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the overhead Crane Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Overhead Crane Market?
The global overhead crane market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several factors. The increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes and material handling is one of the primary catalysts. Industries such as construction, automotive, and shipbuilding are increasingly adopting overhead cranes for their ability to enhance operational efficiency and safety. Additionally, the rise in infrastructural development across emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East is propelling the demand for overhead cranes. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam are investing heavily in industrial projects, which further fuels this growth.
Furthermore, technological advancements are shaping the B2B landscape, with smart features and IoT capabilities becoming standard in overhead crane systems. These innovations not only improve safety and productivity but also provide real-time data analytics, enhancing operational decision-making. International buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer tailored solutions that integrate advanced technology, which can lead to more efficient material handling processes.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Be Integrated into Overhead Crane Procurement?
As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, B2B buyers in the overhead crane sector are increasingly prioritizing ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is a significant concern. Buyers should seek suppliers committed to minimizing their ecological footprint by utilizing renewable energy sources and implementing efficient waste management systems.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a focal point for businesses, as consumers and stakeholders demand transparency. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to sustainable sourcing practices are essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled steel and eco-friendly lubricants, should be considered in procurement decisions. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements while contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
What is the Evolution of Overhead Crane Technology and Its Impact on B2B Buyers?
The evolution of overhead crane technology has significantly influenced the B2B landscape. Initially, overhead cranes were simple mechanical devices primarily used for lifting heavy loads in industrial settings. However, advancements in materials, controls, and automation have transformed them into sophisticated machines capable of performing complex tasks with enhanced precision and safety.
The introduction of electric hoists, advanced control systems, and smart technologies has improved the efficiency and reliability of overhead cranes. Modern cranes are now equipped with features like remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and advanced safety protocols, making them indispensable for industries looking to optimize their operations. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial; it allows them to make informed purchasing decisions and select equipment that not only meets their current needs but also aligns with future technological trends and operational demands.
By focusing on these key areas, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the overhead crane market effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment and partners to drive their business success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of overhead Crane
-
How do I choose the right overhead crane for my facility?
Selecting the right overhead crane involves assessing your specific lifting needs, including load capacity, span, and the type of materials you’ll be handling. Consider the operational environment—factors like space constraints, ceiling height, and the frequency of use are critical. Evaluate the various types available, such as bridge, gantry, and jib cranes, and consult with suppliers about customization options. Finally, review your budget, including initial costs and ongoing maintenance, to find a solution that balances performance and cost-effectiveness. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of overhead cranes?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, experience, and track record in delivering cranes that meet safety standards. Request references and case studies from previous clients to gauge satisfaction. Assess their technical expertise, including knowledge of local regulations and certification requirements. Additionally, consider their capacity for customization, availability of spare parts, and after-sales services like maintenance and training, which are essential for long-term operational efficiency. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering an overhead crane?
Lead times for overhead cranes can vary based on several factors, including the type of crane, customization requirements, and supplier location. Standard models may have a lead time of 6 to 12 weeks, while custom solutions could take longer, ranging from 12 to 24 weeks. It’s important to communicate your project timeline with suppliers upfront to ensure they can meet your deadlines. Additionally, consider potential delays related to shipping and customs, especially for international orders. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing overhead cranes?
Payment terms for overhead cranes typically vary by supplier and project size. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (often 20-50%), with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timeline, and ensure that all terms are clearly documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
Can I customize an overhead crane to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for overhead cranes to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations can include modifications to lifting capacity, span, and travel speed, as well as the addition of smart technology features for enhanced safety and efficiency. Discuss your unique needs with potential suppliers and request detailed proposals that outline the specifications, costs, and lead times associated with custom solutions. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for when sourcing overhead cranes?
When sourcing overhead cranes, ensure that suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Ask about their manufacturing processes, quality control procedures, and testing protocols to verify the crane’s performance and safety. Additionally, inquire about warranties and service agreements, as these are indicators of the supplier’s confidence in their product’s quality and reliability. A robust QA process can help mitigate risks associated with crane operation. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing overhead cranes?
Importing overhead cranes involves several logistics considerations, including customs regulations, shipping methods, and handling requirements. Ensure that your supplier can assist with compliance documentation, such as import permits and customs declarations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in heavy machinery logistics to handle the transportation. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs inspections and plan for on-site installation logistics, including crane assembly and operator training. -
What are the maintenance requirements for overhead cranes?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of overhead cranes. Typical maintenance tasks include routine inspections, lubrication of moving parts, and checking electrical systems and safety devices. Develop a maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry best practices. Additionally, consider training your staff or hiring professional services for maintenance to ensure compliance with safety regulations and prolong the crane’s lifespan.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Overhead Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Amquip Inc – Overhead Crane
Domain: amquipinc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: An overhead crane is a lifting device designed to move, assemble, position, and handle heavy objects. It operates by moving loads horizontally across the ceiling of a facility. Key components include:
– **Bridge Beam**: The main horizontal beam that the trolley moves across, typically made of steel.
– **Girders**: Support the bridge beam and connect it to the end trucks, available in various shape…
2. Konecranes – Overhead Cranes & Smart Lifting Solutions
Domain: konecranes.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Reliable overhead cranes for safe and efficient lifting, including Konecranes C-series electric chain hoist cranes, rope hoist cranes, gantry cranes, portable cranes, wall-mounted console cranes, built-up cranes, and custom cranes. Features include smart technology such as remote operating stations and crane advisor tools. Specialized cranes for hazardous environments include EX electric wire rope…
3. Munck Cranes – Overhead Crane Types
Domain: munckcranes.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Overhead Cranes: 1. Top Running Overhead Crane – travels on rails mounted to runway beams supported by columns. 2. Under Running Overhead Crane – travels on the bottom flange of a runway beam supported by the roof structure. 3. Single Girder Bridge Crane – consists of a single bridge girder, two end trucks, and a trolley hoist. 4. Double Girder Bridge Crane – consists of two bridge girder…
4. Crane Depot – Overhead Bridge Cranes
Domain: cranedepot.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Overhead Bridge Cranes for Sale – Overhead Crane Systems. Types include single girder and double girder configurations. Single girder is less expensive and simpler, while double girder is for heavy-duty lifting. Capacities range from 1 Ton to over 25 Tons. Custom built options available. Products include: 1 Ton Advantage Single Girder Under Running Push Bridge Crane, 2 Ton Advantage Single Girder …
5. PWI Works – Overhead Crane Types
Domain: pwiworks.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: The article discusses four types of overhead cranes: Gantry Cranes, Jib Cranes, Bridge Cranes, and Monorail Cranes.
1. **Gantry Cranes**:
– Built on a movable framework (gantry).
– Sizes range from small (for garage use) to large (for shipping/container yards).
– Smaller models cost around $4,000 and can lift several thousand pounds.
– Larger models can cost up to $40 million (e….
6. Hoists Direct – Comprehensive Crane Solutions
Domain: hoistsdirect.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Cranes available include freestanding jib cranes, wall mounted jib cranes, davit cranes, pneumatic cranes, portable cranes, gantry cranes, bridge cranes, truck mounted cranes, and tripod cranes. Custom engineering options for single girder and double girder overhead cranes are available. Popular models include 5 ton to 10 ton custom overhead traveling cranes from manufacturers such as Wallace Cran…
7. Dearborn Crane – Overhead, Gantry & Jib Cranes
Domain: dearborncrane.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Dearborn Crane offers a variety of cranes and hoists, including: Overhead Cranes (Top Running and Under Running Bridge Cranes), Gantry Cranes (Pre-Engineered and Custom Design), Jib Cranes (Floor Mounted, Wall Mounted, and Special Application), and Crane Kits & Hoists (Electric Chain Hoists, Electric Wire Rope Hoists, and Air Operated Hoists). They also provide crane parts for all major manufactur…
8. Reid Lifting – Gantry and Overhead Cranes
Domain: us.reidlifting.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Gantry cranes and overhead cranes are both lifting devices used for lifting and lowering operations, which can be manually or electrically operated. Overhead cranes, also known as bridge cranes, are mounted to the interior structure of a building and are permanent installations, suitable for extremely heavy objects. Gantry cranes are self-sufficient, supported by their own A frames, and can be use…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for overhead Crane
In summary, strategic sourcing for overhead cranes is pivotal in enhancing operational efficiency and safety across various industries. By understanding the diverse types of overhead cranes available, businesses can tailor their investments to meet specific lifting and handling needs. Key considerations include evaluating the crane’s design, capacity, and technological features, such as smart monitoring systems, which contribute to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of choosing reliable suppliers cannot be overstated. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers ensures access to high-quality equipment and comprehensive support services, including installation, maintenance, and training.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for advanced lifting solutions will only grow. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves to leverage new technologies and innovations in overhead crane systems, driving both safety and efficiency in their operations. Now is the time to evaluate your crane needs and engage with leading suppliers to secure the optimal solutions for your business’s future.