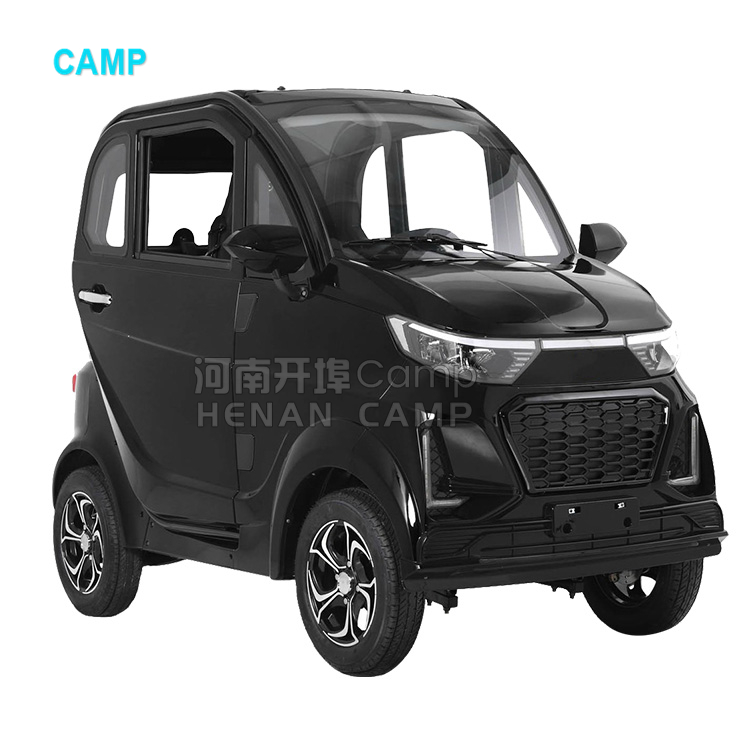
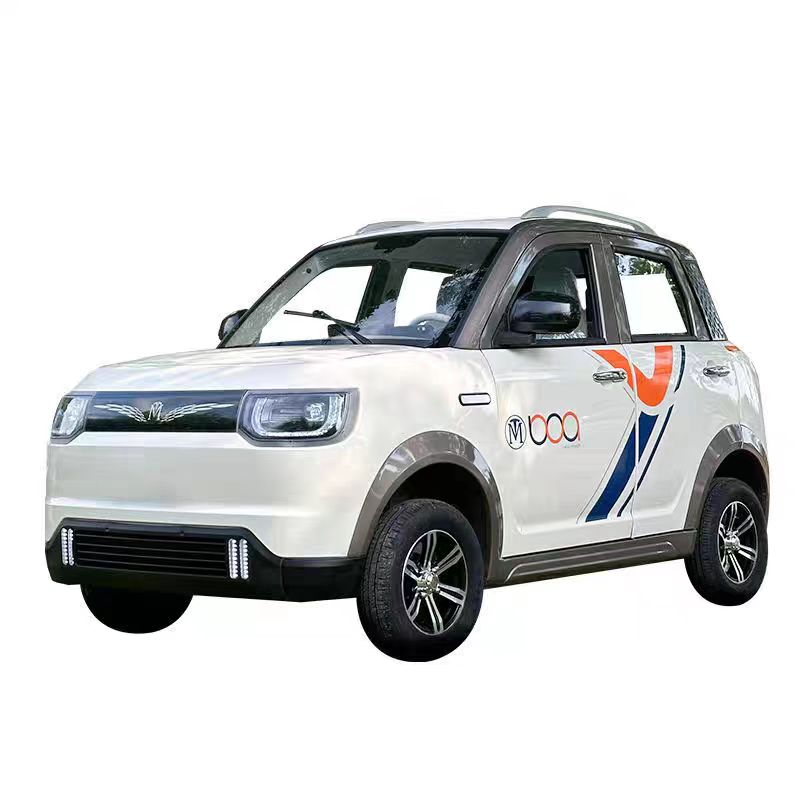
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cheap electric car high speed without license
In today’s fast-evolving automotive landscape, sourcing cheap electric cars that offer high speed without the need for a license presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As urbanization accelerates and the demand for sustainable transport solutions increases, businesses are seeking cost-effective alternatives that cater to diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide aims to empower decision-makers by providing a comprehensive overview of the types of license-free electric vehicles available, their applications, and the factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
With the rise of electric quadricycles, often referred to as voiturettes, these vehicles are gaining traction among consumers looking for safer and more efficient transportation options. This guide will delve into the various models, highlighting their specifications such as range, acceleration, and charging capabilities, while also addressing the cost implications of each option. Furthermore, we will explore the regulatory landscape across different regions, equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate compliance and ensure successful procurement.
By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers will be better positioned to make informed purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to enhanced fleet capabilities and customer satisfaction. Whether you are in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or any other market, understanding the intricacies of the license-free electric vehicle sector will enable you to capitalize on emerging opportunities and drive your business forward.
Understanding cheap electric car high speed without license Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Quadricycles | Limited weight (up to 425 kg), compact design | Urban mobility, delivery services | Pros: Low cost, easy to maneuver; Cons: Limited range and speed compared to full-sized vehicles. |
| Electric Microcars | Small footprint, capable of higher speeds (up to 45 km/h) | Short-distance commuting, rentals | Pros: Increased speed, minimal maintenance; Cons: May require local regulations awareness. |
| Electric Cargo Vehicles | Designed for transporting goods, larger storage | Last-mile delivery, logistics | Pros: Efficient for urban deliveries; Cons: Higher initial investment compared to standard quadricycles. |
| Electric Scooters | Two-wheeled, lightweight, and portable | Short trips, tourism | Pros: Very affordable, easy to park; Cons: Less stable than four-wheeled options. |
| Electric Bicycles | Pedal-assist technology, higher speed capability | Personal transport, rentals | Pros: Eco-friendly, good for fitness; Cons: Requires maintenance, limited cargo capacity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Light Quadricycles?
Light quadricycles are compact vehicles designed for urban environments, with a maximum unladen weight of 425 kg. They typically feature a top speed of around 45 km/h, making them suitable for short commutes and local deliveries. B2B buyers in sectors like urban mobility or delivery services may find these vehicles appealing due to their low operating costs and ease of maneuverability. However, potential buyers should consider the limitations in range and speed, which may not meet the needs of longer-distance transportation.
How Do Electric Microcars Differ From Other Options?
Electric microcars are small, four-wheeled vehicles that can reach speeds up to 45 km/h, providing a balance between speed and compactness. They are ideal for short-distance commuting and rental applications, especially in densely populated urban areas. B2B buyers should evaluate the regulatory landscape in their region, as some areas may have specific licensing requirements or restrictions. While they offer improved speed and comfort over light quadricycles, the initial investment might be higher.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Electric cargo vehicles are specifically designed for transporting goods, featuring larger storage capacities and optimized designs for urban deliveries. These vehicles are increasingly popular among logistics companies seeking eco-friendly alternatives for last-mile delivery. B2B buyers should consider the potential for reduced operational costs and compliance with environmental regulations. However, the higher initial investment compared to standard quadricycles could be a deterrent for smaller businesses.
How Do Electric Scooters Fit into the Market?
Electric scooters are lightweight, two-wheeled vehicles that offer an affordable and portable transportation option. They are particularly suited for short trips and tourism-related services, making them attractive for B2B applications in the leisure and hospitality sectors. Buyers should weigh the benefits of affordability and ease of parking against the stability concerns associated with two-wheeled vehicles, especially in varied urban terrains.
Why Consider Electric Bicycles for B2B Applications?
Electric bicycles combine traditional cycling with pedal-assist technology, allowing for higher speeds and longer distances. They are an excellent option for personal transport and rental services, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. B2B buyers should consider the balance between the eco-friendliness of electric bicycles and the ongoing maintenance requirements. While they offer health benefits and lower operating costs, the limited cargo capacity may not suit all business needs.
Key Industrial Applications of cheap electric car high speed without license
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cheap electric car high speed without license | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-mile delivery services | Reduces transportation costs and increases efficiency | Vehicle range, charging infrastructure, and maintenance support |
| Tourism and Leisure | Rental services for tourists | Provides an eco-friendly transport option for tourists | Fleet management, insurance requirements, and local regulations |
| Education | Campus transportation for students | Enhances student mobility and reduces congestion | Vehicle capacity, safety features, and maintenance agreements |
| Logistics | Short-distance goods transport | Streamlines logistics operations and reduces costs | Load capacity, charging time, and reliability of service |
| Healthcare | Patient transport in urban settings | Improves access to healthcare services | Comfort, accessibility features, and operational costs |
How Can Cheap Electric Cars Without a License Enhance Urban Mobility Solutions?
In urban mobility, cheap electric cars without a license can significantly improve last-mile delivery services. These vehicles offer a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to streamline their delivery processes. With their compact size and ability to navigate congested city streets, they reduce transportation costs while enhancing delivery efficiency. International buyers should consider the vehicle’s range and charging infrastructure to ensure operational reliability in various urban environments.
What Benefits Do Cheap Electric Cars Offer in the Tourism and Leisure Sector?
The tourism and leisure sector can leverage cheap electric cars without a license for rental services, providing tourists with an eco-friendly transportation option. This not only enhances the travel experience but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable travel solutions. Businesses in this sector should focus on fleet management capabilities, insurance requirements, and compliance with local regulations to maximize their operational effectiveness.
How Can Educational Institutions Utilize License-Free Electric Cars for Campus Transportation?
In educational settings, cheap electric cars can serve as an effective means of campus transportation for students. These vehicles promote mobility and reduce congestion on campuses, making it easier for students to navigate large grounds. Buyers in this sector should prioritize vehicle capacity, safety features, and maintenance agreements to ensure a reliable transportation solution that meets the needs of students and staff alike.
What Role Do Cheap Electric Cars Play in Streamlining Logistics Operations?
In logistics, cheap electric cars without a license can facilitate short-distance goods transport, enabling businesses to streamline their operations. These vehicles can reduce overall costs associated with logistics while ensuring timely deliveries. Key considerations for international buyers include load capacity, charging time, and the vehicle’s reliability to maintain efficient operations across varying geographical landscapes.
How Can the Healthcare Sector Benefit from Using Electric Cars Without a License?
The healthcare sector can benefit from using cheap electric cars for patient transport in urban settings, improving access to essential healthcare services. These vehicles can navigate through traffic more efficiently, ensuring timely patient transfers. Buyers should consider comfort, accessibility features, and operational costs to ensure that the vehicles meet the specific needs of healthcare providers and patients.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cheap electric car high speed without license’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for License-Free Electric Vehicles
The Problem: For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and the Middle East, understanding the regulatory landscape around license-free electric vehicles can be daunting. Different countries have varying laws regarding vehicle classifications, which can affect the types of vehicles available for purchase and their operational legality. This confusion can lead to costly mistakes, such as investing in a vehicle that ultimately cannot be used legally in the intended market.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific vehicle regulations in their target markets. This involves consulting local government websites, industry reports, and legal experts who specialize in automotive regulations. Additionally, establishing relationships with local vehicle dealers and manufacturers can provide insights into the compliance requirements for license-free electric vehicles. Buyers should also consider investing in vehicles that meet international safety and environmental standards to streamline the approval process across different jurisdictions. Engaging with local associations or chambers of commerce can further assist in understanding the market dynamics and regulatory nuances.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality and Performance in Budget Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that the ‘cheap electric car high speed without license’ they invest in meets their performance expectations. Many low-cost vehicles may compromise on quality, leading to issues such as short battery life, inadequate speed, and poor reliability. This can significantly impact operational efficiency, particularly for businesses relying on these vehicles for logistics or transportation services.
The Solution: To mitigate risks related to quality and performance, buyers should implement a rigorous vetting process before making a purchase. This includes requesting detailed specifications, performance metrics, and independent reviews of the vehicles from other businesses that have previously purchased them. Conducting test drives and inspections can also provide firsthand insight into the vehicle’s capabilities. Furthermore, buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer robust warranties and after-sales support, ensuring that any performance issues can be addressed promptly. Engaging in bulk purchases can also provide leverage for negotiating better terms and securing vehicles that meet higher standards of quality.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Maintenance and Operational Challenges
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the potential for high maintenance costs and operational downtime associated with cheap electric vehicles. Without proper support and service infrastructure, companies may find themselves facing frequent breakdowns, which can disrupt business operations and lead to increased costs.
The Solution: To address maintenance concerns, B2B buyers should evaluate the availability of service centers and spare parts for the vehicles they intend to purchase. Partnering with manufacturers or suppliers who offer comprehensive maintenance packages can alleviate some of these concerns, providing regular servicing and quick access to replacement parts. Additionally, establishing a training program for staff on basic vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting can empower users to handle minor issues on-site, reducing dependency on external service providers. Buyers should also consider investing in fleet management software that allows for real-time monitoring of vehicle performance and maintenance needs, ensuring proactive management of operational challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cheap electric car high speed without license
What Materials Are Optimal for Cheap Electric Cars Without a License?
In the rapidly evolving market for electric vehicles (EVs), particularly for license-free models, selecting the right materials is crucial for performance, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Here, we analyze several common materials used in the manufacturing of these vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Durable
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 600°C and maintains structural integrity under various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances the vehicle’s speed and efficiency. However, it can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various climates, particularly in coastal regions or areas with high humidity, common in parts of Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential when sourcing aluminum components. Buyers should also consider the availability of recycled aluminum, which can reduce costs and environmental impact.
Steel: Strength and Affordability
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for various automotive applications.
Pros & Cons: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s speed and efficiency. Additionally, steel components may require additional treatments to prevent rust and corrosion.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength is advantageous for structural components, but its weight can be a limiting factor in performance-sensitive applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and safety standards, which can vary significantly between regions like Europe and the Middle East.
Composite Materials: Innovative and Versatile
Key Properties: Composites, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to specific performance requirements.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature, which can significantly enhance vehicle performance. However, they are often more expensive than metals and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in body panels and interior components, where weight savings can lead to improved efficiency and speed.
Considerations for International Buyers: The use of composites may require adherence to specific manufacturing standards, and buyers should assess the availability of skilled labor for composite fabrication in their region.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Powering Performance
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rates, making them ideal for electric vehicles.
Pros & Cons: These batteries provide excellent performance and range, essential for high-speed electric cars. However, they can be costly and require careful handling and disposal due to environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: The performance of electric vehicles heavily relies on battery technology, influencing range and charging times, which are critical factors for consumers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety and environmental regulations, such as UN 38.3 for battery transport, is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of local recycling facilities for end-of-life battery management.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for cheap electric car high speed without license | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Structural components | Cost-effective, strong | Heavier, may require rust treatment | Low |
| Composite Materials | Body panels and interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, requires specialized techniques | High |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Power source for electric motors | High energy density, long cycle life | Costly, environmental disposal concerns | High |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers looking to source materials for cheap electric cars without a license. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cheap electric car high speed without license
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cheap Electric Cars Without a License?
The manufacturing process for cheap electric cars, specifically those designed for high-speed operation without requiring a license, involves several critical stages. Each stage is essential to ensure the efficiency, safety, and affordability of the final product.
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting appropriate materials that meet the vehicle’s design specifications while ensuring cost-effectiveness. Common materials include lightweight metals such as aluminum and high-strength steel for the chassis, along with composite materials for body panels to enhance durability and reduce weight.
Sourcing these materials from reputable suppliers is crucial, as it directly impacts both the performance and safety of the vehicle. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international standards for material quality, such as ISO 9001 certification, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems.
2. Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next step involves various forming techniques to shape the components of the vehicle. This can include processes such as stamping, welding, and molding.
- Stamping is commonly used for creating body panels, where sheets of metal are shaped into desired forms using high-pressure machines.
- Welding is essential for joining structural components and ensuring the integrity of the chassis.
- Molding techniques, particularly for plastic components, allow for intricate designs that can be produced at a lower cost.
Utilizing advanced forming technologies can enhance the precision and efficiency of production, reducing waste and lowering costs.
3. Assembly Process
The assembly stage is where the various components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically follows a sequential assembly line model, allowing for a systematic and efficient build.
Key elements of the assembly process include:
- Chassis assembly: The frame of the vehicle is constructed, incorporating the suspension and drivetrain components.
- Electrical system integration: Since these vehicles are electric, integrating the battery systems and wiring harnesses is critical. This includes ensuring the safety and efficiency of the power management systems.
- Interior fitting: Installing seats, dashboard components, and controls are performed in this stage.
Quality control during assembly is paramount. Regular checks should be conducted to ensure that all components meet the required specifications and standards.
4. Finishing Touches
The finishing stage involves applying surface treatments and coatings to enhance the vehicle’s aesthetics and protect it from environmental factors. This can include painting, powder coating, and applying protective films.
Quality assurance during this stage ensures that the vehicle not only looks appealing but also has a durable finish that can withstand various weather conditions.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Cheap Electric Cars Without a License?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, particularly those designed for specific markets that may have varying regulatory requirements.
International Standards for Quality Assurance
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with recognized international quality standards.
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across various industries, including automotive manufacturing. It ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- ISO 26262: Specifically relevant for automotive safety, this standard addresses functional safety in electrical and electronic systems within vehicles.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards) are crucial for products sold in the European market.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Implementing rigorous quality control checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process is essential for maintaining product integrity. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are conducted throughout the assembly process to identify and rectify issues early, minimizing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the vehicle is dispatched, a comprehensive inspection is performed to ensure all specifications are met, and the vehicle is safe for use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers looking to source cheap electric cars without a license should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers.
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide valuable insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should consider:
- On-site audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to observe processes, equipment, and quality control measures firsthand.
- Supplier self-assessments: Requesting suppliers to provide self-assessment reports detailing their quality management systems and practices.
Requesting Documentation and Reports
Buyers should also request documentation related to quality control processes, including:
- Quality assurance reports: These documents outline the results of quality checks and any corrective actions taken.
- Certificates of compliance: Validating that suppliers meet necessary industry standards and regulations.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further enhance the verification process. These independent entities can conduct comprehensive inspections and audits, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in different markets is crucial.
Navigating Regulatory Differences
Buyers must be aware of the varying regulatory environments in their regions. For instance, vehicles sold in Europe must comply with stringent CE marking requirements, while regulations in other regions may differ.
Cultural and Operational Differences
Cultural differences can also impact quality assurance practices. B2B buyers should consider the operational capabilities of suppliers in different regions, including their familiarity with international standards and customer expectations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for cheap electric cars without a license is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key manufacturing stages, adhering to international quality standards, and implementing rigorous verification processes, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that deliver safe, efficient, and cost-effective vehicles. This not only enhances business operations but also contributes to the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions across global markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cheap electric car high speed without license’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving market for electric vehicles, sourcing a cheap, high-speed electric car that does not require a license can be a strategic advantage for B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured approach to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring you select vehicles that meet your operational needs while adhering to local regulations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential to align your procurement with business needs. Consider factors such as maximum speed, battery range, and vehicle dimensions. This will help in identifying models that not only meet performance criteria but also comply with regional licensing laws.
- Speed Requirements: Determine the necessary speed capabilities for your target market.
- Range Considerations: Assess how far the vehicle needs to travel on a single charge to optimize logistics.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Understanding the legal framework surrounding license-free vehicles is critical. Regulations can vary significantly between regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Ensure that the vehicles you are considering meet the local standards for quadricycles or light electric vehicles.
- Check Weight Limits: Most jurisdictions have strict weight restrictions for vehicles that do not require a license.
- Safety Standards: Verify that the vehicles adhere to safety regulations applicable in your target markets.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request comprehensive company profiles, including their experience in the electric vehicle sector, and ask for case studies or references from similar businesses.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering quality vehicles.
- Customer Reviews: Analyze feedback from other B2B buyers to gauge satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: Analyze Cost Structures
Cost considerations go beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, charging infrastructure, and insurance (if applicable). This will give you a clearer picture of the long-term financial implications.
- Hidden Costs: Look for potential expenses related to servicing and parts.
- Financing Options: Explore leasing versus buying to determine what aligns best with your financial strategy.
Step 5: Request Prototypes or Demos
Before finalizing a purchase, request prototypes or arrange for demonstrations. This hands-on experience will allow you to assess the vehicle’s performance and suitability for your specific applications.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate acceleration, braking, and overall handling.
- User Experience: Gather feedback from potential users within your organization to ensure the vehicle meets their needs.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers and vehicles, it’s time to negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes discussing payment terms, warranties, and after-sales support.
- Warranties and Support: Ensure you understand what is covered and the duration of the warranty.
- Flexibility in Terms: Look for suppliers willing to accommodate your operational timelines and payment preferences.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Plan for Integration
After agreeing on terms, finalize the purchase and develop a plan for integrating the new vehicles into your operations. This includes training staff on usage and maintenance.
- Training Programs: Ensure that your team is well-versed in operating and maintaining the vehicles.
- Logistics Planning: Prepare for the logistics of deploying the vehicles, including charging infrastructure if necessary.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for cheap, high-speed electric cars that do not require a license, ensuring a strategic fit for their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cheap electric car high speed without license Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Cheap Electric Cars Without a License?
When analyzing the cost structure for cheap electric cars that do not require a license, several cost components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials involved in the production of electric cars include batteries, electric motors, chassis, and body components. Battery costs, in particular, can fluctuate significantly based on lithium and cobalt prices. Buyers should consider sourcing materials from regions with stable pricing or long-term contracts to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can significantly impact the overall pricing. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in South America or parts of Africa, may offer competitive pricing for manufacturing. However, skilled labor is essential for quality assembly, particularly in electric vehicle production, which may necessitate higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes, such as automation, can help reduce these costs over time.
-
Tooling: Investment in tooling is crucial for the production of electric cars, especially for unique designs or specifications. High-quality tooling ensures consistency and reduces waste, which can lead to cost savings in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards is vital. Implementing stringent QC processes may incur additional costs upfront but can prevent expensive recalls and repairs later.
-
Logistics: Transportation of components and finished vehicles adds to overall costs. International buyers should consider the logistics involved in shipping, including tariffs, duties, and shipping times, which can vary widely based on Incoterms.
-
Margin: Finally, the profit margin is influenced by the competitive landscape and the perceived value of the vehicle. Manufacturers may adjust margins based on market demand, ensuring they remain competitive while achieving profitability.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cars Without a License?
Several factors influence pricing, which international B2B buyers should consider when sourcing electric cars.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Manufacturers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs), and exceeding these can yield lower per-unit prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses associated with custom features that may not be essential.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can elevate costs but can also enhance vehicle performance and safety. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certified vehicles against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more due to their brand’s perceived value, while newer entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for calculating total costs. Different Incoterms can affect who bears the risk and costs during transportation, influencing the final price.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in the B2B Electric Vehicle Market?
When negotiating prices for electric cars without a license, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms and pricing. Suppliers may have flexibility in pricing, especially for large orders or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential resale value. A lower initial purchase price may lead to higher TCO if the vehicle is not energy-efficient or reliable.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, electric vehicle incentives in Europe may not be available in Africa or South America, influencing overall pricing strategies.
-
Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers. Long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing, more favorable terms, and priority in production schedules.
Conclusion
The market for cheap electric cars without a license is evolving, offering significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. Understanding the cost structure, pricing influencers, and strategic negotiation techniques will help buyers make informed decisions while maximizing their investment in this emerging sector.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cheap electric car high speed without license With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cheap Electric Cars Without a License
As the demand for efficient and cost-effective transportation solutions grows, many businesses are exploring alternatives to cheap electric cars that do not require a license. This analysis compares the ‘cheap electric car high speed without license’ against other viable transportation methods, such as electric bicycles and small electric scooters. By understanding the pros and cons of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Cheap Electric Car High Speed Without License | Electric Bicycle | Small Electric Scooter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Speed up to 45 km/h, suitable for urban areas | Speed up to 30-40 km/h | Speed up to 25-30 km/h |
| Cost | Approximately $10,000 – $15,000 | Ranges from $500 to $3,000 | Ranges from $300 to $1,500 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Minimal setup; can charge at home | Minimal setup; can charge at home |
| Maintenance | Moderate; battery and mechanical upkeep needed | Low; regular tire and brake checks | Low; regular tire and battery checks |
| Best Use Case | Short to medium urban commutes | Commuting in urban or suburban areas | Short-distance travel and urban mobility |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
Electric Bicycle
Electric bicycles are a popular alternative for individuals seeking a blend of performance and affordability. They offer a decent speed range and can be used for commuting in urban areas. The initial investment is significantly lower than that of a cheap electric car, making them accessible for small businesses or startups. However, they require regular maintenance, including tire checks and battery management, which could be a drawback for some users.
Small Electric Scooter
Small electric scooters are another viable option for license-free transport. They are generally the most cost-effective solution, with lower purchase prices and minimal maintenance requirements. Scooters are lightweight and easy to maneuver in crowded urban environments. However, their speed and range limitations may restrict their use for longer commutes, making them less suitable for businesses needing reliable transport over longer distances.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Transportation Solution
When choosing between a cheap electric car without a license and its alternatives, businesses should evaluate their specific transportation needs, budget, and operational context. For companies focusing on short-distance urban commuting, electric bicycles or scooters may provide adequate solutions at a lower cost and with fewer maintenance burdens. Conversely, if speed and comfort for medium-distance travel are priorities, investing in a cheap electric car might be more beneficial. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower B2B buyers to select the most appropriate solution for their requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cheap electric car high speed without license
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cheap Electric Cars Without a License?
When considering cheap electric cars designed for high-speed travel without the need for a driving license, several technical specifications become crucial for B2B buyers. Understanding these specifications can guide purchasing decisions and ensure compliance with regional regulations.
-
Maximum Speed (km/h)
The maximum speed of these electric vehicles typically ranges from 45 km/h to 90 km/h, depending on local laws. It is critical for businesses to consider the speed limits in their target markets, as exceeding these limits can require additional licensing or insurance. -
Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity directly impacts the vehicle’s range and performance. For license-free electric cars, a battery capacity between 5 kWh and 15 kWh is common, allowing for a range of approximately 50 to 150 kilometers on a single charge. Understanding battery specifications is vital for businesses to estimate operational costs and customer satisfaction regarding range anxiety. -
Charging Time (hours)
The time required to charge the vehicle’s battery can vary significantly, typically ranging from 3 to 8 hours for a full charge using standard home chargers. Fast charging capabilities can reduce this time to as little as 30 minutes. For B2B buyers, knowing the charging options available can influence the vehicle’s practicality for end-users, especially in markets where charging infrastructure is still developing. -
Weight Limit (kg)
Most electric cars without a license must adhere to specific weight limits, often capped at 425 kg for light quadricycles. This specification is essential for ensuring compliance with regional regulations and can influence the design and materials used in manufacturing. -
Material Composition
The use of lightweight materials, such as aluminum or high-strength composites, is becoming increasingly prevalent in the design of electric vehicles. These materials contribute to better energy efficiency and performance. Buyers should evaluate the material specifications to ensure durability and long-term cost-effectiveness.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Electric Vehicle Industry?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is crucial for B2B transactions in the electric vehicle sector, particularly for license-free models.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, OEMs are essential for sourcing quality components such as batteries, electric motors, and control systems. Building relationships with reputable OEMs can enhance product quality and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for businesses as it impacts inventory management and cost calculations. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their market demand to avoid excess inventory or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products. For B2B buyers of electric cars, issuing an RFQ can help gather competitive pricing and terms, ensuring better procurement decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and risk management in the procurement of electric vehicles. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time taken from the placement of an order to the delivery of the product. For electric vehicles, lead time can vary based on manufacturing schedules and supply chain dynamics. Understanding lead times helps businesses plan their inventory and sales strategies effectively.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing cheap electric cars designed for high-speed travel without a license.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cheap electric car high speed without license Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Cheap Electric Cars Without License?
The market for cheap electric cars that do not require a license is experiencing a notable transformation driven by multiple global factors. Increasing urbanization, coupled with rising fuel prices and a growing emphasis on sustainable transportation, has led consumers to seek alternative modes of mobility. This trend is particularly evident in developing regions like Africa and South America, where public transportation systems may be limited, and the cost of traditional vehicles remains prohibitive. In Europe and the Middle East, younger demographics, including teenagers and young adults, are gravitating towards license-free electric vehicles (often referred to as voiturettes), viewing them as a practical and safe alternative to scooters and traditional cars.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends within this sector. Innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, enhance vehicle performance and reduce costs, making electric cars more accessible. Additionally, digital platforms are streamlining the sourcing process for B2B buyers, allowing them to compare models, pricing, and specifications easily. International buyers can now leverage online marketplaces and direct-to-consumer sales models to obtain competitive pricing and access to a wider array of products.
Market dynamics are further influenced by regulatory frameworks. Various countries are implementing policies that encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and relaxed licensing requirements for low-speed vehicles. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam should stay informed on local regulations, as these can significantly affect market entry strategies and product viability.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Purchasing Decisions for Electric Cars Without License?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of purchasing decisions in the B2B space, particularly in sectors like electric vehicles. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, vehicle performance, and end-of-life recyclability are critical considerations for buyers. As consumers increasingly prioritize eco-friendly products, B2B buyers must assess the sustainability practices of manufacturers. This includes evaluating the sourcing of materials, energy consumption during production, and the overall lifecycle emissions of the vehicles.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly for international buyers. Companies are encouraged to work with manufacturers that adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a company’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. By prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate transparency and responsibility in their operations, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for socially responsible products.
Furthermore, the use of recycled materials in vehicle manufacturing is gaining traction, contributing to a circular economy. Buyers should seek manufacturers that utilize sustainable materials in their electric cars to align with global sustainability goals and consumer preferences.
How Has the Cheap Electric Car Without License Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of cheap electric cars without a license is marked by significant advancements in technology, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. Initially, these vehicles were viewed as niche products, primarily catering to specific demographics such as young drivers or those seeking an alternative to traditional cars. However, as urban populations grew and environmental concerns intensified, the demand for practical, cost-effective, and eco-friendly transportation options surged.
In the past decade, improvements in battery technology have enabled manufacturers to produce more efficient and affordable electric vehicles. This has resulted in a wider variety of models available to consumers, transforming perceptions and expanding market reach. Regulatory changes in various regions, including relaxed licensing laws and increased incentives for electric vehicle purchases, have further propelled the growth of this segment.
Today, the market for cheap electric cars without a license is not only thriving but is also on the cusp of becoming a mainstream transportation solution, particularly in urban environments across diverse markets. As this sector continues to evolve, B2B buyers must remain agile, adapting to technological advancements and shifting market demands to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cheap electric car high speed without license
-
1. How do I choose the right supplier for cheap electric cars without a license?
To select a reliable supplier for electric cars without a license, consider factors such as the supplier’s reputation, experience in the industry, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with international safety standards. Request samples or references from previous clients to assess product quality. Additionally, evaluate their capacity for customization and after-sales support, which are crucial for long-term partnerships. -
2. What are the key specifications to look for in a high-speed electric car without a license?
When sourcing high-speed electric cars, focus on specifications such as maximum speed, range per charge, battery capacity, and charging time. Consider the vehicle’s weight and dimensions, which may impact its usability in different markets. Safety features, including braking systems and stability controls, are also essential. Lastly, ensure the vehicle meets local regulations regarding electric cars without licenses. -
3. What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric cars without a license?
MOQs for electric cars can vary significantly based on the supplier and the model. Generally, larger manufacturers may require higher MOQs, ranging from 50 to 100 units, while smaller or niche suppliers might offer lower MOQs, starting at 10 to 20 units. It’s advisable to negotiate terms, especially if you’re exploring different models or require customization. -
4. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric cars internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include a deposit of 30% to 50% upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit to facilitate transactions. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and consider using escrow services for added protection. -
5. How can I customize electric cars to meet my specific market needs?
Customization options depend on the supplier’s capabilities. Common modifications include branding, color choices, and specific features such as enhanced battery capacity or additional safety systems. Discuss your requirements early in the negotiation process to understand the supplier’s flexibility and any associated costs or lead times for modifications. -
6. What are the logistics considerations for importing electric cars without a license?
Logistics for importing electric cars involve several steps, including shipping, customs clearance, and local transportation. Choose a freight forwarder experienced in handling vehicles and understand the import regulations specific to your country. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance, is prepared to avoid delays at customs. -
7. How do I ensure quality assurance for electric cars sourced from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, establish a robust quality assurance (QA) process that includes pre-shipment inspections and adherence to international standards. Request detailed specifications and testing reports from the supplier. Consider hiring third-party inspection services to evaluate the vehicles before shipment. Additionally, negotiate warranties and after-sales support to protect your investment. -
8. What are the best markets for selling cheap electric cars without a license?
Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe present significant opportunities for selling electric cars without licenses. Urban areas with high population density and limited public transport options are particularly promising. Conduct market research to identify local demand, regulatory environments, and competition to tailor your sales strategy effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Cheap Electric Car High Speed Without License Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Eli – Electric Micro Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Eli launches its electric micro ‘car’ in the US for $11,900.
2. Gemcar – Street-Legal Electric Carts
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Street-Legal Electric Carts are designed for on-road driving, with a speed of up to 25 mph (40 km/h). They can accommodate up to 6 forward-facing passengers and feature high-back upholstered seats with bolster support. These carts are street-legal in nearly all U.S. states and include an occupant protection system (OPS) certified to SAE J2358 standards. Optional full doors can create a fully enclo…
3. Cars.com – Electric Vehicle Overview
Domain: cars.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: [{“model”:”Nissan Leaf”,”starting_price”:”$29,280″,”EPA_estimated_range”:”149-212 miles”},{“model”:”Fiat 500e”,”starting_price”:”$32,495″,”EPA_estimated_range”:”141-149 miles”},{“model”:”Hyundai Kona Electric”,”starting_price”:”$34,470″,”EPA_estimated_range”:”200-261 miles”},{“model”:”Chevrolet Equinox EV”,”starting_price”:”$34,995″,”EPA_estimated_range”:”307-319 miles”},{“model”:”Toyota bZ4X”,”st…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cheap electric car high speed without license
As the demand for affordable, high-speed electric vehicles without licensing requirements grows, strategic sourcing becomes crucial for B2B buyers in emerging markets. By leveraging insights into the evolving landscape of quadricycles and electric mobility, businesses can tap into a diverse range of options that meet consumer needs while minimizing costs. The shift toward these vehicles is driven by their accessibility, safety, and environmental benefits, making them particularly appealing in regions where traditional transportation is less viable.
Furthermore, international buyers should focus on building relationships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation, sustainability, and compliance with local regulations. This will ensure a competitive edge in markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where demand for license-free electric cars is surging.
In conclusion, as the landscape of transportation continues to evolve, the opportunity to invest in and promote cheap electric cars without a license is ripe for exploration. B2B buyers are encouraged to act decisively, leveraging strategic sourcing to not only meet current demand but also anticipate future trends. Engage with industry leaders, explore partnerships, and position your business at the forefront of this electrifying transformation.