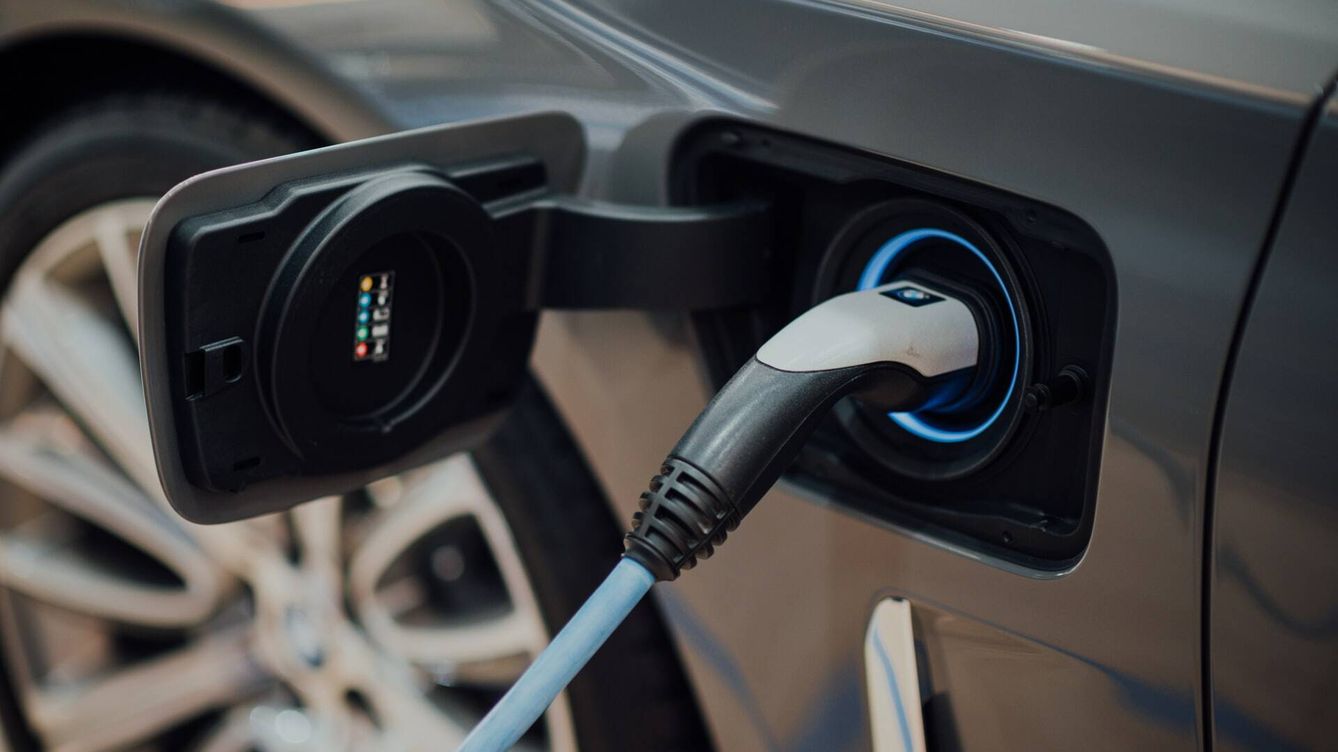
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for coches elctricos
In today’s dynamic landscape, sourcing reliable coches eléctricos (electric cars) presents a multifaceted challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the global demand for sustainable transportation rises, navigating this market requires understanding not only the vehicles themselves but also the diverse applications, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements that come into play. This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for businesses seeking to procure electric vehicles, offering insights into various types of electric cars, from compact urban models to robust SUVs, and highlighting key factors like supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements.
Within these pages, you will discover a wealth of information tailored to empower informed purchasing decisions. We delve into the latest trends in electric vehicle technology, the importance of understanding local infrastructure for charging stations, and the economic implications of transitioning to electric fleets. Additionally, our guide addresses the specific needs and preferences of international buyers, including case studies and best practices from markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of the electric vehicle market, ensuring they make strategic investments that align with their sustainability goals and operational requirements.
Understanding coches elctricos Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) | Powered solely by electric batteries, high efficiency, zero emissions | Urban delivery fleets, corporate car pools | Pros: Lower operational costs, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited range, longer refueling times. |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) | Combines electric and gasoline power, extended range | Mixed-use fleets, long-distance travel | Pros: Flexibility in fuel options, reduced emissions. Cons: Higher initial costs, complexity in maintenance. |
| Electric SUVs | Larger body, higher seating capacity, advanced safety features | Family transport, corporate events | Pros: Spacious, versatile for various applications. Cons: Typically higher purchase price, reduced range compared to smaller models. |
| Electric City Cars | Compact design, optimized for urban environments | City logistics, short-distance travel | Pros: Excellent maneuverability, lower costs. Cons: Limited cargo space, shorter range. |
| Commercial Electric Vans | Designed for cargo transport, high payload capacity | Delivery services, trade businesses | Pros: Cost-effective for logistics, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited models available, may require charging infrastructure. |
What Are Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are entirely powered by electric batteries, offering high energy efficiency and zero emissions. These vehicles are particularly suitable for urban delivery fleets and corporate car pools, where operational costs can be significantly reduced. B2B buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including charging infrastructure and potential savings on fuel and maintenance, despite the potential challenges of limited range and longer refueling times.
How Do Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) Benefit Businesses?
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) utilize both electric and gasoline power, providing extended range capabilities. They are ideal for mixed-use fleets and long-distance travel, allowing companies to reduce emissions while maintaining flexibility. B2B buyers need to weigh the initial investment against the long-term savings on fuel and emissions, recognizing that the complexity of maintenance may be higher due to the dual powertrains.
What Are the Advantages of Electric SUVs for Corporate Use?
Electric SUVs are characterized by their larger body, higher seating capacity, and advanced safety features. They cater to family transport and corporate events, providing spacious interiors and versatility for various applications. While their purchase price is typically higher, the benefits of reduced operational costs and eco-friendliness make them an attractive option for B2B buyers focusing on corporate responsibility and employee satisfaction.
Why Choose Electric City Cars for Urban Logistics?
Electric City Cars are compact and optimized for urban environments, making them ideal for city logistics and short-distance travel. Their excellent maneuverability and lower costs are appealing to businesses focused on efficiency in densely populated areas. However, B2B buyers should consider the limited cargo space and shorter range, which may not suit all operational needs.
What Should Businesses Consider When Investing in Commercial Electric Vans?
Commercial Electric Vans are specifically designed for cargo transport, featuring high payload capacities. They are perfect for delivery services and trade businesses looking to enhance their eco-friendly initiatives. While these vehicles can be cost-effective for logistics, B2B buyers must assess the availability of models and the need for charging infrastructure to ensure seamless operations.
Key Industrial Applications of coches elctricos
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of coches electricos | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transportation | Electric taxis and ride-sharing services | Reduced operational costs through lower fuel and maintenance expenses | Battery range, charging infrastructure, and vehicle reliability |
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery vehicles | Enhanced efficiency and sustainability in urban logistics | Vehicle size, load capacity, and charging options |
| Public Sector and Municipalities | Electric public transport buses | Decreased emissions and improved air quality | Vehicle durability, total cost of ownership, and government incentives |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Electric shuttle services for hotels and resorts | Improved guest experience and reduced carbon footprint | Range, charging facilities, and fleet management capabilities |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee commuting and service vehicles | Cost savings and enhanced corporate sustainability image | Fleet management software integration and vehicle availability |
How Are Coches Eléctricos Transforming Urban Transportation?
In urban transportation, electric taxis and ride-sharing services are gaining traction as businesses seek to reduce operational costs. These vehicles offer significant savings on fuel and maintenance compared to traditional combustion engines. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to consider battery range and charging infrastructure to ensure seamless operations in urban environments. Additionally, reliability is paramount to maintain service continuity.
What Role Do Coches Eléctricos Play in Logistics and Delivery?
Last-mile delivery vehicles utilizing coches eléctricos are revolutionizing logistics by providing sustainable and efficient solutions for urban deliveries. These electric vehicles help businesses minimize their carbon footprint while enhancing operational efficiency. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, important considerations include vehicle size and load capacity to meet specific delivery requirements, as well as the availability of charging options to facilitate smooth operations.
How Are Coches Eléctricos Benefiting Public Sector Initiatives?
Public transportation systems are increasingly adopting electric buses, contributing to decreased emissions and improved air quality in urban areas. Municipalities stand to benefit from reduced fuel costs and government incentives for electric vehicle purchases. For international buyers, especially in Europe, evaluating vehicle durability and total cost of ownership is essential to ensure the long-term viability of these investments.
In What Ways Are Coches Eléctricos Enhancing Tourism and Hospitality?
Electric shuttle services provided by hotels and resorts are enhancing guest experiences while promoting sustainability. By offering eco-friendly transportation options, businesses can attract environmentally conscious travelers. For B2B buyers in the hospitality sector, key factors include vehicle range, the availability of charging facilities, and fleet management capabilities to ensure efficient service delivery.
How Do Coches Eléctricos Fit into Corporate Fleets?
Corporate fleets are increasingly integrating coches eléctricos for employee commuting and service vehicles. This shift not only leads to cost savings but also enhances the company’s sustainability image. International buyers should focus on the integration of fleet management software and vehicle availability to optimize operations and maximize return on investment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘coches elctricos’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Limited Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges facing B2B buyers of electric vehicles (EVs) is the lack of a robust charging infrastructure. In regions like Africa and parts of South America, the availability of charging stations can be sparse, making it difficult to integrate electric vehicles into a fleet. This situation can lead to concerns about downtime, operational efficiency, and the overall feasibility of switching to electric options. Fleet managers may worry about the reliability of their vehicles, particularly for long-distance operations or in remote areas where charging options are limited.
The Solution: To mitigate the challenges posed by limited charging infrastructure, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the charging landscape in their operational areas before purchasing electric vehicles. This involves identifying existing charging stations and mapping out potential locations for new installations. Partnering with local governments or private companies to establish a network of charging points can be beneficial. Additionally, investing in fleet management software that tracks vehicle range and charging station availability can streamline operations. Buyers may also consider electric vehicles with longer ranges that can accommodate the current infrastructure limitations, ensuring that their operations remain efficient and uninterrupted.
Scenario 2: Addressing Concerns About Vehicle Range and Performance
The Problem: Another pain point for B2B buyers is the anxiety surrounding the range and performance of electric vehicles, especially when compared to traditional combustion engine vehicles. Many businesses require vehicles that can handle extensive daily routes without frequent recharging. The perception that electric vehicles may not perform well under heavy loads or during long-distance travel can deter businesses from making the switch, even if it would provide long-term cost savings and sustainability benefits.
The Solution: To address range and performance concerns, B2B buyers should focus on selecting electric vehicles that are specifically designed for their operational needs. This includes reviewing the real-world performance data of various models, particularly in the types of driving conditions that will be encountered. Engaging with manufacturers to discuss fleet-specific adaptations—such as enhanced battery packs or optimized load capacities—can also yield beneficial results. Moreover, participating in pilot programs or leasing options allows businesses to test electric vehicles under their typical operating conditions before committing to a purchase, ensuring that the selected vehicles meet performance expectations.
Scenario 3: Managing Initial Investment and Total Cost of Ownership
The Problem: The initial purchase price of electric vehicles can be a significant barrier for many B2B buyers, particularly in industries where margins are tight. Despite the long-term savings associated with lower fuel and maintenance costs, the upfront investment may lead to hesitation. Buyers often find themselves weighing the financial viability of transitioning their fleets against the immediate budget constraints.
The Solution: To overcome the financial hurdles of investing in electric vehicles, B2B buyers should explore various financing options, including government incentives and tax rebates available for electric vehicle purchases. Additionally, forming partnerships with financial institutions that specialize in green financing can provide tailored solutions that ease the upfront burden. Buyers should also conduct a comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis, factoring in long-term savings from reduced fuel costs, lower maintenance expenses, and potential subsidies. Presenting a well-researched business case to stakeholders that highlights both the environmental benefits and financial advantages can facilitate buy-in for the transition to electric vehicles, making it an attractive long-term investment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for coches elctricos
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on a variety of materials to ensure optimal performance, safety, and sustainability. Understanding the properties, advantages, and disadvantages of these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of electric vehicles: aluminum, lithium, carbon fiber, and steel.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Electric Vehicle Performance?
Aluminum is widely used in the construction of electric vehicles due to its lightweight properties and excellent corrosion resistance. This material is crucial for improving energy efficiency, as lighter vehicles require less energy to operate. Aluminum components can withstand temperatures up to 600°C, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances vehicle performance and range. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in battery housings and structural components, where weight reduction is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of varying aluminum standards across regions, such as ASTM in the U.S. and EN in Europe. Compliance with these standards is essential for ensuring safety and performance.
What Role Does Lithium Play in Electric Vehicle Batteries?
Lithium is a key component in lithium-ion batteries, which are the most common type of battery used in electric vehicles. This material offers high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges and quicker charging times. Lithium can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -20°C to 60°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of lithium is its lightweight nature and high electrochemical potential, which significantly enhances battery efficiency. However, lithium mining raises environmental concerns, and the material can be costly, impacting the overall price of EVs.
Impact on Application: Lithium is essential for battery packs, directly influencing the vehicle’s range and charging capabilities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the sourcing of lithium, as ethical and sustainable sourcing practices are increasingly important in many markets. Compliance with international environmental regulations is also a key factor.
How Does Carbon Fiber Enhance Electric Vehicle Design?
Carbon fiber is known for its exceptional strength and lightweight properties, making it an ideal material for high-performance electric vehicles. It can withstand high temperatures and offers excellent fatigue resistance, which is vital for vehicle durability.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of carbon fiber is its ability to reduce vehicle weight without compromising strength, leading to improved efficiency. However, it is significantly more expensive than traditional materials and requires specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in high-performance components, such as body panels and chassis, where weight reduction is critical for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the different standards for carbon fiber production and use across regions, such as JIS in Japan and ISO standards globally.
Why Is Steel Still Relevant in Electric Vehicles?
Steel remains a fundamental material in electric vehicle construction, particularly for structural components and safety features. Its high strength and durability make it an ideal choice for crash protection and structural integrity.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of steel include its cost-effectiveness and widespread availability. However, it is heavier than alternatives like aluminum and carbon fiber, which can negatively impact energy efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the frame and body of electric vehicles, providing essential structural support.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the variations in steel grades and standards, such as ASTM and DIN, ensuring compliance with local regulations and safety standards.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection for Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for coches electricos | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Battery housings, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Lithium | Battery packs | High energy density, lightweight | Environmental concerns, high cost | High |
| Carbon Fiber | Body panels, chassis | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very high cost, specialized processes | High |
| Steel | Frame, body | Cost-effective, widely available | Heavier, impacting energy efficiency | Low |
In conclusion, the selection of materials for electric vehicles is critical for performance, cost, and sustainability. International B2B buyers must consider the unique properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, as well as compliance with regional standards and ethical sourcing practices.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for coches elctricos
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for electric vehicles (coches eléctricos) involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, reliable vehicles. These stages are:
-
Material Preparation: This initial phase involves sourcing and preparing the raw materials required for various vehicle components. Key materials include lithium for batteries, aluminum for the chassis, and advanced composites for lightweight structures. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet international standards for quality and safety.
-
Forming: In this stage, raw materials are shaped into components using processes such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. For electric vehicles, battery packs are often formed using advanced techniques to ensure structural integrity and performance efficiency. Manufacturers may use automation and robotics to improve precision and reduce production time.
-
Assembly: The assembly phase is where various components, such as the battery system, electric motors, and body panels, are brought together. This process requires meticulous attention to detail, as any misalignment can affect vehicle performance. Advanced assembly techniques, including modular assembly lines, allow for flexibility and scalability in production.
-
Finishing: The final stage of manufacturing includes painting, quality checks, and the installation of interior features. It is crucial that the finishing process not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetics but also provides durability against environmental factors. Electrocoating and powder coating are popular methods used to ensure long-lasting finishes.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in the Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles?
Several innovative techniques are employed throughout the manufacturing process of electric vehicles:
-
Advanced Welding Technologies: Techniques such as laser welding and robotic welding are commonly used to join components, ensuring strong and reliable connections, especially in battery and chassis assembly.
-
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This technology is increasingly used for producing complex parts and prototypes, enabling manufacturers to reduce waste and improve design flexibility.
-
Battery Manufacturing Techniques: The production of battery cells involves precise layering of materials and controlled environments to ensure performance and safety. Techniques such as dry coating are gaining traction for their efficiency and sustainability.
-
Smart Manufacturing: The integration of IoT and AI in the manufacturing process allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance in electric vehicle manufacturing is governed by various international and industry-specific standards. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO 9001 is often a prerequisite for B2B buyers when selecting suppliers.
-
ISO 26262: Specifically for automotive safety, this standard addresses functional safety in electric and electronic systems. It is critical for ensuring that electric vehicles operate safely under various conditions.
-
CE Marking: For manufacturers targeting the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: While more common in oil and gas, API standards can also apply to components used in electric vehicles, particularly regarding safety and performance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential to maintain high manufacturing standards. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during various stages of the manufacturing process, IPQC checks are vital for identifying defects early. This can include monitoring assembly processes and testing components at critical stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before vehicles leave the production line. This stage involves comprehensive testing of all systems, including electrical, mechanical, and safety features, to ensure the vehicle meets performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control standards:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help verify compliance with international standards and internal quality protocols. This includes reviewing production processes, quality records, and employee training programs.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports, compliance certificates, and any third-party testing results.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer unbiased assessments of a supplier’s quality practices and product reliability, ensuring that they align with the buyer’s expectations.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial:
-
Regional Compliance Requirements: Different regions may have specific compliance requirements that vary from international standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards to ensure that products meet market demands.
-
Language and Cultural Barriers: Communication with suppliers across different regions can pose challenges. It’s essential to establish clear channels for discussing quality expectations and addressing any issues that arise.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality control extends beyond manufacturing; it also includes the logistics and transportation of vehicles. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers have robust processes in place to maintain quality during transit.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric vehicles, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers committed to quality and safety.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘coches elctricos’
The following guide serves as a practical roadmap for B2B buyers looking to procure electric vehicles (coches eléctricos). As the demand for sustainable transportation options rises globally, understanding the nuances of sourcing electric vehicles is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before entering the market, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your electric vehicle fleet. This includes factors such as battery capacity, range, charging speed, and vehicle type (e.g., compact, SUV, or commercial). Defining these specifications ensures that you select vehicles that align with your operational needs and usage patterns, particularly in urban versus long-distance travel scenarios.
Step 2: Research Local Incentives and Regulations
Understanding the local incentives and regulations surrounding electric vehicles is vital for cost savings and compliance. Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, and grants for purchasing electric vehicles, which can significantly reduce upfront costs. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding emissions, charging infrastructure, and vehicle registration, as these can impact your procurement strategy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs effectively. Look for established manufacturers with a strong reputation in the electric vehicle market. Request comprehensive company profiles, case studies, and references from other B2B buyers, particularly those in your industry or region. This due diligence helps mitigate risks associated with quality and service.
Step 4: Assess Vehicle Performance and Reliability
Evaluate the performance metrics of the electric vehicles you are considering. This includes looking at real-world range, charging times, and overall reliability. Request performance reports or customer testimonials to understand how these vehicles perform under various conditions, especially in urban settings where stop-and-go traffic can affect battery life.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Warranties
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with industry standards and regulations. Certifications from recognized organizations indicate that the vehicles meet safety and performance standards. Additionally, inquire about warranty offerings and after-sales support, as these can be crucial for minimizing maintenance costs and ensuring long-term satisfaction.
Step 6: Plan for Charging Infrastructure
Consider the charging infrastructure required to support your electric vehicle fleet. Assess the availability of charging stations in your operational area and determine whether you need to invest in private charging solutions. Efficient planning for charging facilities will ensure that your vehicles remain operational without unnecessary downtime.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure favorable terms and pricing. Discuss bulk purchase discounts, financing options, and any additional services such as maintenance packages. Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings and better overall value for your investment in electric vehicles.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for electric vehicles, ensuring they make informed, strategic decisions that align with their business objectives and sustainability goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for coches elctricos Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing Electric Vehicles?
When sourcing electric vehicles (coches eléctricos), it is crucial to understand the various cost components that influence pricing. The primary elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, particularly batteries, which can account for a significant portion of the total vehicle cost. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are essential components, and their prices can fluctuate based on global supply and demand.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for assembly and quality assurance. Labor costs vary by region, with countries in Europe typically having higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for electric vehicle production can be substantial, especially for custom designs. This includes the cost of molds and specialized machinery necessary for assembly.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards is essential. Investment in QC processes can affect the overall cost but is crucial for maintaining quality and brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the distance and method of transport. Incoterms play a vital role in determining who bears these costs, impacting the final price to the buyer.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the margins applied can help in negotiating better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Electric Vehicles?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electric vehicles, particularly for B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing models, where costs decrease with higher order quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific configurations can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these customizations are necessary for their market.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can increase the price but may be necessary for compliance with local regulations, especially in markets like Europe.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better warranties and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in contracts is critical. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the overall cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Electric Vehicles Internationally?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to optimize sourcing costs:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation skills can lead to better pricing. Buyers should be prepared with market data and competitor pricing to leverage during discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis, considering not just the purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and resale value. This approach helps in evaluating the long-term financial impact of sourcing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different markets may have varying pricing structures due to tariffs, taxes, or incentives for electric vehicles. Researching these factors can reveal additional savings opportunities.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and favorable contract terms.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Being aware of trends in electric vehicle technology and pricing can help buyers anticipate changes and make informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
The prices mentioned throughout this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market dynamics, currency fluctuations, and other external factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers for the most accurate pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing coches elctricos With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to ‘Coches Eléctricos’
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, ‘coches eléctricos’ (electric vehicles) represent a growing segment aimed at reducing emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. However, B2B buyers should consider various alternatives that may better align with their operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental goals. Below, we compare ‘coches eléctricos’ with two viable alternatives: hybrid vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cochés Eléctricos | Hybrid Vehicles | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in urban settings; limited range for long-distance travel | Good range; efficient fuel consumption; relies on gasoline and electric power | High efficiency; fast refueling; long range |
| Cost | Generally higher upfront costs; potential savings on fuel and maintenance | Mid-range pricing; lower than electric vehicles; fuel costs vary | High initial investment; potential savings on fuel and incentives |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; may have limited availability in some regions | Easier to integrate with existing fueling stations | Requires hydrogen refueling stations; limited infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; requires both electric and combustion system upkeep | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts compared to traditional vehicles |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for urban environments and short commutes | Versatile; suitable for mixed driving conditions and longer trips | Best for fleets needing long range and quick refueling |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hybrid Vehicles: Balancing Efficiency and Range
Hybrid vehicles combine traditional internal combustion engines with electric motors, providing a balanced solution for businesses that require flexibility. They excel in both urban and highway settings, offering good fuel economy and reduced emissions compared to conventional vehicles. However, they still depend on gasoline, which can undermine their environmental benefits. Additionally, while the upfront costs are generally lower than electric vehicles, hybrid systems may require more maintenance due to their dual powertrains.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: The Future of Clean Transport
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent a cutting-edge alternative, generating electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. They offer several advantages, including quick refueling times and a long driving range comparable to traditional vehicles. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still limited, especially in developing regions, which can pose a significant challenge for widespread adoption. The high initial investment may also deter some buyers, despite potential savings on fuel in the long run.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating alternatives to ‘coches eléctricos’, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific operational requirements, budget considerations, and environmental objectives. Electric vehicles are particularly well-suited for urban use and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint, while hybrid vehicles provide flexibility for varied driving conditions. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may be ideal for fleets requiring quick refueling and long ranges but necessitate infrastructure investment. By weighing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business strategies and sustainability goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for coches elctricos
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars (Coches Eléctricos)?
Understanding the essential technical properties of electric cars is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– Definition: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), this indicates the total amount of energy the battery can store.
– Importance: A higher battery capacity allows for longer driving ranges, which is vital for businesses looking to optimize fleet operations and reduce downtime. For instance, a vehicle with a 60 kWh battery may offer a range of 300-400 km, making it suitable for urban logistics. -
Range (km)
– Definition: This is the distance an electric vehicle (EV) can travel on a single charge, typically quoted in kilometers.
– Importance: Understanding range is essential for B2B buyers to assess the vehicle’s practicality for specific applications, such as urban deliveries or long-haul transport. A range of over 300 km is often considered adequate for most commercial uses. -
Charging Time (hours)
– Definition: The time required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery, which can vary based on the charger type (e.g., Level 1, Level 2, or DC Fast Charging).
– Importance: Quick charging solutions can minimize downtime, enhancing operational efficiency. Businesses should consider investing in fast-charging infrastructure to support their fleets. -
Power Output (kW)
– Definition: This measures the maximum power that the electric motor can deliver, typically expressed in kilowatts (kW).
– Importance: Higher power output translates to better acceleration and handling, essential for businesses requiring agile vehicles for urban environments or logistics. -
Regenerative Braking Efficiency
– Definition: This technology allows the vehicle to recover energy during braking, extending the range and improving overall efficiency.
– Importance: For companies focused on sustainability, vehicles with efficient regenerative braking systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs. -
Vehicle Weight (kg)
– Definition: The total mass of the vehicle, which affects performance and energy efficiency.
– Importance: Lighter vehicles generally offer better efficiency and handling. Understanding weight helps businesses select vehicles that meet both performance and regulatory requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the electric vehicle market. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: B2B buyers often work directly with OEMs to ensure they receive quality components that meet their specifications, impacting the overall performance of electric vehicles. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively, ensuring they meet supply chain requirements without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing information for specified products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is critical for procurement processes, allowing businesses to compare prices and terms from different suppliers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of pre-defined international rules published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Knowledge of Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations, which is essential for international trade in electric vehicles. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: A financial estimate that helps buyers assess the direct and indirect costs of owning a vehicle over its entire lifecycle.
– Importance: Understanding TCO allows businesses to evaluate the long-term financial implications of electric vehicle investments, factoring in maintenance, fuel costs, and potential resale value. -
EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
– Definition: The equipment used to deliver electrical energy for the recharging of electric vehicles.
– Importance: B2B buyers must consider the compatibility and availability of EVSE when deploying electric vehicle fleets to ensure efficient operations and customer satisfaction.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs and market opportunities in the growing electric vehicle sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the coches elctricos Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Coches Eléctricos Sector?
The coches eléctricos market is experiencing significant growth globally, driven by increasing environmental concerns, government incentives, and advancements in battery technology. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a growing demand for sustainable transport solutions, spurred by urbanization and the need for cleaner air. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Emerging technologies such as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems and smart charging solutions are reshaping the market landscape. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) but also create new business opportunities in energy management and infrastructure development. Additionally, the rise of shared mobility services is influencing sourcing strategies, as companies look to integrate electric fleets into their operations to meet consumer demands for sustainability.
International buyers must also navigate the complexities of local regulations and incentives that vary significantly across regions. For instance, while Europe offers robust subsidies for EV purchases, the incentives in South America and Africa may still be in the nascent stages. Understanding these regional differences is vital for B2B buyers seeking to capitalize on the electric vehicle trend.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence B2B Decisions in the Coches Eléctricos Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of business strategy in the coches eléctricos sector. As consumers and governments increasingly prioritize environmental responsibility, B2B buyers are compelled to consider the ecological impact of their sourcing decisions. This includes evaluating the lifecycle of electric vehicles, from production to disposal, and ensuring that suppliers adhere to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly regarding the materials used in electric vehicle production. The demand for lithium, cobalt, and nickel—key components in batteries—raises concerns about mining practices and their environmental consequences. Buyers should seek suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and have certifications that prove their commitment to ethical sourcing.
Moreover, utilizing green certifications and materials can enhance a company’s brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also position themselves as leaders in the transition to a greener economy.
How Has the Coches Eléctricos Sector Evolved Over Time?
The coches eléctricos sector has evolved significantly over the past two decades, transitioning from niche products to mainstream vehicles. Early electric cars struggled with limited range and high costs, but technological advancements in battery efficiency and charging infrastructure have led to widespread adoption.
Government policies and consumer awareness have further accelerated this evolution. Initiatives promoting renewable energy and reducing carbon emissions have made electric vehicles more attractive for both personal and commercial use. As manufacturers continue to innovate, the future of coches eléctricos appears bright, offering numerous opportunities for B2B buyers to engage in sustainable and profitable practices within this dynamic market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of coches elctricos
-
How do I solve the issue of limited charging infrastructure for electric vehicles?
To address the challenge of limited charging infrastructure, B2B buyers should consider partnering with local governments and private entities to establish charging stations. Investing in charging networks can enhance the usability of electric vehicles in target markets. Additionally, exploring options for fast-charging technology and mobile charging solutions can help alleviate range anxiety for users. Engaging with electric utility companies may also provide incentives or support for developing necessary infrastructure. -
What is the best electric vehicle for urban delivery in South America?
The ideal electric vehicle for urban delivery in South America would be compact, with a sufficient range of around 200-300 km to accommodate daily routes without frequent recharging. Vehicles like the BYD Dolphin and Peugeot e-208 are excellent options due to their size, agility in city traffic, and competitive pricing. Additionally, assess local regulations and incentives that may favor specific models, ensuring compliance with urban transport policies. -
How can I ensure the quality of electric vehicles when sourcing internationally?
To guarantee the quality of electric vehicles, it’s crucial to conduct thorough supplier vetting. This includes reviewing certifications, quality control processes, and production capabilities. Requesting samples and conducting factory visits can provide insights into manufacturing practices. Additionally, consider third-party quality assurance services to perform inspections before shipment. Establishing clear quality standards in contracts can help mitigate risks related to defects or non-compliance. -
What are typical payment terms for purchasing electric vehicles from manufacturers?
Payment terms for electric vehicles can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the region. Generally, terms may range from 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon delivery, to more extended terms like 60-90 days post-delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and consider options like letters of credit for additional security. Always clarify the implications of late payments to avoid penalties or loss of favorable terms. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) when sourcing electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric vehicles can differ based on the manufacturer and model. Typically, MOQs range from 10 to 50 units, especially for lesser-known brands. For established manufacturers, the MOQ might be lower due to existing production capacity. It’s essential to discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are a new buyer or entering a new market. -
How do I manage logistics for shipping electric vehicles internationally?
Managing logistics for international shipping of electric vehicles involves several critical steps. First, select a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling automotive shipments. Ensure that the vehicles are properly packaged and comply with international shipping regulations. Understand customs requirements for each destination country to avoid delays. Finally, factor in lead times for production and shipping to align with your inventory needs and customer expectations. -
What customization options are available when ordering electric vehicles?
Customization options for electric vehicles often include modifications to battery capacity, interior features, and exterior finishes. Some manufacturers may offer software updates or enhancements for fleet management. Discussing customization options early in the procurement process is vital, as lead times may vary. Ensure that any customizations comply with local regulations and consider how they affect warranty and service agreements. -
What incentives should I consider when purchasing electric vehicles for fleet use?
When purchasing electric vehicles for fleet use, it’s essential to explore available incentives such as tax credits, government subsidies, and grants. Many countries offer financial incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, which can significantly reduce the overall cost. Additionally, inquire about potential partnerships with local governments for charging infrastructure support. Staying informed about evolving policies can help you maximize savings and enhance the sustainability of your fleet.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Coches Elctricos Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Citroën – ë-C3 eléctrico
Domain: quecochemecompro.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Coches eléctricos 2025: guía de compra
1. **Citroën ë-C3 eléctrico**
– Precio: 12.490 €
– Ahorra: 10.627 €
2. **BYD Dolphin**
– Precio: 21.990 €
– Ahorra: 14.700 €
– Valoración: 5,5/10
– Garantía: 6 años
– Lo mejor: Relación calidad-precio, tecnología, calidades interiores
– Lo mejorable: Versiones de acceso con poca potencia
3. **Cupra Born**
– Precio: 28.650 €
– …
2. GreenCars – Información sobre Vehículos Eléctricos y Híbridos
Domain: greencars.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GreenCars ofrece información sobre vehículos eléctricos (EV), híbridos enchufables y híbridos, destacando sus beneficios como el ahorro de combustible, reducción de mantenimiento y tecnología moderna. Los vehículos eléctricos funcionan con baterías, proporcionando una experiencia de conducción más limpia y eficiente. GreenCars también proporciona herramientas como guías de compra, consejos para ma…
3. Opel – Astra 33,800€ 156CV 419km
Domain: caranddriver.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 1. Opel Astra – 33,800 euros, 156 CV, 419 km autonomía.
2. Leapmotor C10 – 33,800 euros, 218 CV, 420 km autonomía.
3. Citroën ë-Berlingo – 33,298 euros, 136 CV, 345 km autonomía, batería LFP de 50 kWh.
4. Fiat 600 – 33,273 euros, 156 CV, batería de 54 kWh, más de 400 km autonomía.
5. Ford E-Tourneo – 32,912 euros, autonomía cerca de 300 km.
6. Opel Combo – 32,725 euros, 136 CV, 344 km autonomía.
7…
4. Renault – RENAULT 5 y RENAULT 4 Eléctricos
Domain: renault.es
Introduction: RENAULT 5: desde 23.971 €, eléctrico, motorizaciones de 95CV, 120CV, 150CV, etiqueta 0, acceso libre a zonas de bajas emisiones, sistema multimedia openR con Google. RENAULT 4: desde 28.771 €, eléctrico, motorizaciones de 120CV y 150CV, mayor altura libre al suelo de 18,1 cm, umbral de carga de 60 cm, sistema openR link con Google. MEGANE: desde 35.251 €, eléctrico, autonomía de hasta 470 km, pote…
5. Volvo – Gama de Coches Eléctricos
Domain: volvocars.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Gama de coches eléctricos de Volvo incluye sedanes, familiares y SUV diseñados para el lujo, la seguridad y la innovación. El EX90, SUV de 7 plazas, tiene la mayor autonomía eléctrica con hasta 600 km. Los coches eléctricos utilizan una batería para almacenar energía y no requieren combustible. Se recomienda el uso de una wallbox de Volvo para carga en casa, que permite una carga más rápida y efic…
6. Ford – Coches Eléctricos y Híbridos
Domain: ford.es
Introduction: Coches eléctricos: vehículos eléctricos (VE) disponibles incluyen: 1. Vehículos 100% eléctricos 2. Vehículos híbridos enchufables 3. Vehículos híbridos 4. Mild Hybrid. Se ofrecen opciones de financiación para particulares y empresas. Información sobre carga en casa y carga pública, así como detalles sobre autonomía. Promociones y ofertas disponibles.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for coches elctricos
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers in the Electric Vehicle Market?
In conclusion, the landscape of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly evolving, presenting significant opportunities for strategic sourcing. B2B buyers must focus on the growing diversity of electric models, particularly those designed for urban environments, which excel in performance and cost-effectiveness. The shift towards sustainable transportation is not merely a trend but a necessity, driven by regulatory changes and rising consumer demand.
Investing in electric vehicles can yield substantial long-term savings, both in operational costs and environmental impact. However, buyers should remain vigilant about the challenges associated with charging infrastructure and vehicle range limitations, especially in regions with developing networks. Engaging with manufacturers that prioritize technological innovation and robust after-sales support will be crucial.
How Can B2B Buyers Prepare for the Future of Electric Vehicles?
As we look to the future, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must seize the moment to integrate electric vehicles into their fleets. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can enhance their competitive edge while contributing to a greener planet.
Now is the time to act—explore partnerships with leading EV manufacturers, assess local market incentives, and align your procurement strategies to embrace the electric vehicle revolution. Together, we can drive sustainable growth in the automotive sector.