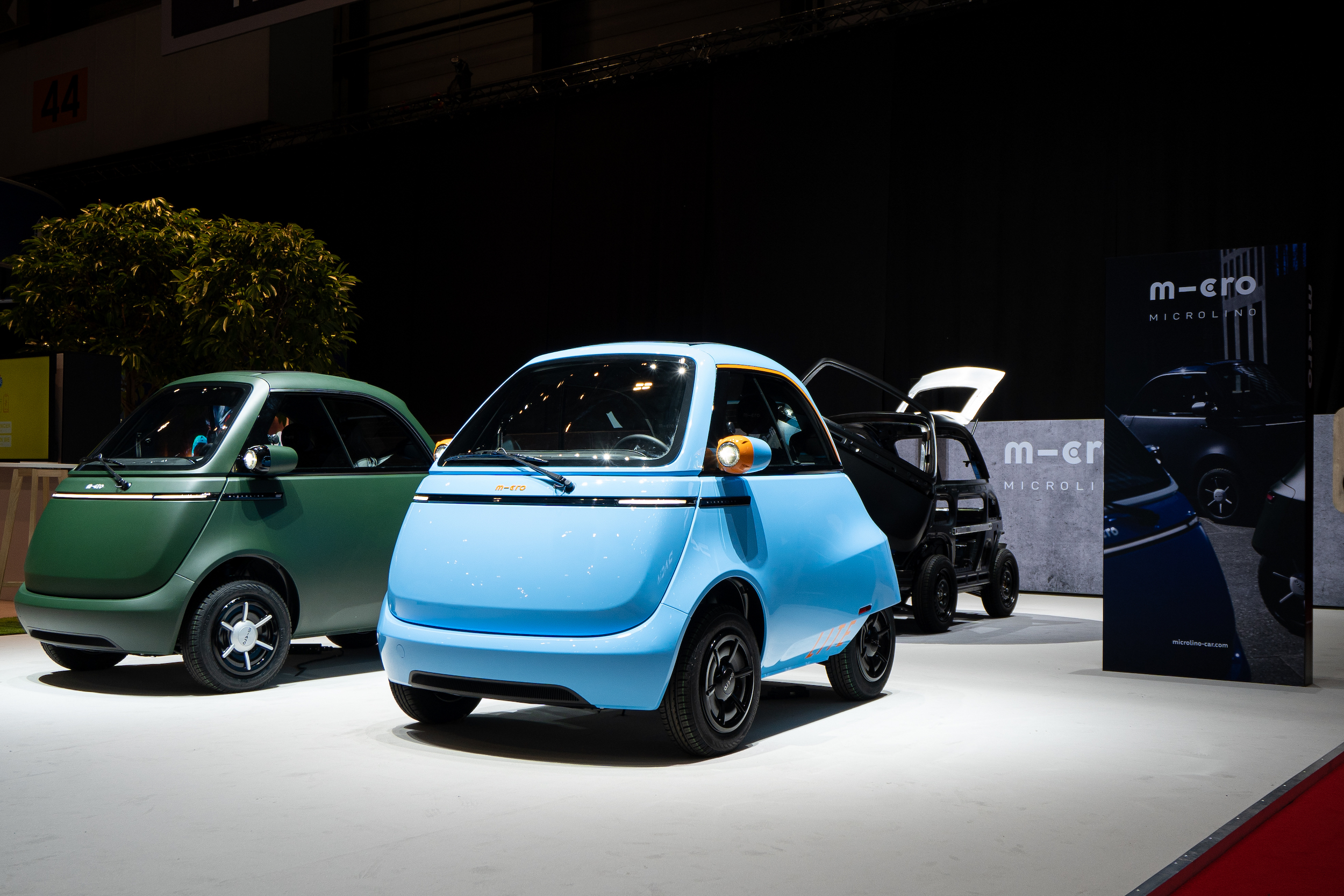
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mini electric car no licence mobility cars
As urban areas worldwide grapple with the dual challenges of rising congestion and environmental sustainability, sourcing mini electric car no licence mobility cars has emerged as a strategic solution for B2B buyers. These innovative vehicles, designed for efficient urban transport without the need for a driving license, present a lucrative opportunity for businesses seeking to enhance their mobility offerings while addressing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener alternatives.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of mini electric cars available in the market, their various applications, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers. We explore critical factors such as cost, maintenance, and the implications of adopting these vehicles in different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions that align with both corporate sustainability goals and market needs.
Whether you are considering integrating these vehicles into a fleet for urban mobility services, exploring options for shared mobility platforms, or looking to cater to a growing consumer base, this resource provides the knowledge necessary to navigate the evolving landscape of mini electric car no licence mobility cars effectively. Embrace the future of urban transport and position your business at the forefront of this transformative market.
Understanding mini electric car no licence mobility cars Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| L6 Electric Quadricycles | Limited to 45 km/h, no driver’s license required, compact design | Urban mobility solutions, rental services, ride-sharing platforms | Pros: Affordable, easy to park, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| L7 Electric Quadricycles | Capable of speeds up to 70 km/h, seats up to four passengers | Family transport, delivery services, mobility-as-a-service | Pros: Greater passenger capacity, suitable for families. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Solar-Assisted Mini Cars | Integrated solar panels for charging, lightweight construction | Sustainable transport initiatives, eco-friendly fleets | Pros: Low operational costs, zero emissions. Cons: Dependent on sunlight for optimal performance. |
| Compact Delivery Vehicles | Designed for urban logistics, optimized for cargo space | Last-mile delivery, urban freight solutions | Pros: Efficient for short deliveries, reduced congestion. Cons: Limited cargo capacity compared to larger vans. |
| Mobility Scooters | Three or four wheels, designed for the elderly or disabled | Assisted living facilities, personal mobility aids | Pros: Accessible for those with mobility challenges. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to cars. |
What are the Key Characteristics of L6 Electric Quadricycles?
L6 electric quadricycles are compact vehicles designed for urban environments, capable of reaching speeds up to 45 km/h. They do not require a driver’s license in many regions, making them accessible to a broader demographic, including younger drivers. Their small size allows for efficient parking and maneuvering in congested city streets. B2B buyers can leverage these vehicles for rental services or ride-sharing platforms, appealing to consumers seeking affordable and eco-friendly transportation options.
How do L7 Electric Quadricycles Differ from L6 Models?
L7 electric quadricycles offer increased speed and capacity, accommodating up to four passengers and reaching speeds of 70 km/h. This makes them suitable for family transport or small group outings, providing a viable alternative to traditional cars. For businesses, these vehicles are ideal for mobility-as-a-service applications, where demand for shared transport solutions is growing. B2B buyers should consider the higher upfront costs against the potential for increased usage and revenue generation.
What Benefits do Solar-Assisted Mini Cars Provide?
Solar-assisted mini cars are equipped with integrated solar panels that charge the vehicle’s batteries, significantly reducing operational costs and environmental impact. These vehicles are particularly advantageous for businesses focused on sustainability, as they can operate with minimal reliance on grid electricity. However, their efficiency is contingent on sunlight availability, which may limit performance in less sunny regions. B2B buyers should evaluate their operational environments to maximize the benefits of these innovative vehicles.
Why are Compact Delivery Vehicles Important for Urban Logistics?
Compact delivery vehicles are specifically designed for urban logistics, providing efficient solutions for last-mile delivery challenges. Their small footprint allows them to navigate narrow streets and congested areas, reducing delivery times and enhancing service reliability. Companies in the e-commerce and logistics sectors can benefit from integrating these vehicles into their fleets to optimize operations. However, buyers should consider the limited cargo capacity when assessing suitability for larger deliveries.
How do Mobility Scooters Enhance Accessibility?
Mobility scooters are designed for individuals with mobility challenges, featuring three or four wheels for stability and ease of use. They are particularly valuable for assisted living facilities and personal mobility applications, providing users with independence and access to their communities. B2B buyers in healthcare and social services sectors should prioritize these vehicles to enhance mobility solutions for their clients. However, the limited speed and range compared to other vehicle types may constrain their application in broader transport networks.
Key Industrial Applications of mini electric car no licence mobility cars
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mini electric car no licence mobility cars | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility Services | Integration into ride-sharing platforms and urban mobility services | Reduces congestion and enhances service efficiency, attracting more users | Ensure compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Guest transportation within resorts or urban areas | Offers a unique, eco-friendly transport option that enhances guest experience | Focus on durability, ease of use, and aesthetic appeal for branding |
| Logistics and Last-Mile Delivery | Use for last-mile delivery in urban settings | Cost-effective and agile solution for navigating congested areas | Consider battery range and charging options to meet delivery demands |
| Educational Institutions | Student transport within campuses and nearby areas | Provides a safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly transport solution | Assess capacity, safety features, and ease of operation for students |
| Healthcare Services | Transport for patients and medical staff in urban areas | Improves access to healthcare services while reducing emissions | Evaluate range, safety, and comfort features for medical transport needs |
How are mini electric car no licence mobility cars transforming urban mobility services?
Mini electric cars without a license are increasingly being integrated into urban mobility services, such as ride-sharing platforms. These vehicles provide a solution to urban congestion, offering an efficient way for users to navigate busy city streets without the need for a traditional driver’s license. For B2B buyers in this sector, it’s crucial to ensure that the vehicles comply with local regulations and safety standards to avoid operational disruptions. Additionally, the compact design allows for easy maneuverability and parking, enhancing the overall service experience.
What benefits do mini electric cars offer to the tourism and hospitality industry?
In the tourism and hospitality sector, mini electric cars serve as an innovative transport solution for guests within resorts or urban areas. They provide a unique, eco-friendly alternative to traditional transport options, enhancing the guest experience while aligning with sustainability goals. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing vehicles that are durable, easy to use, and visually appealing to align with branding strategies. The ability to customize these vehicles can further enhance their attractiveness to guests.
How can mini electric cars improve last-mile delivery logistics?
For logistics companies, mini electric cars represent a cost-effective solution for last-mile delivery in urban environments. Their compact size allows for easy navigation through congested streets, reducing delivery times and improving overall efficiency. When sourcing these vehicles, buyers should consider the battery range and charging options to ensure they can meet the demands of frequent deliveries. Additionally, energy efficiency can lead to lower operational costs, making them an attractive option for businesses focused on sustainability.
Why are mini electric cars ideal for educational institutions?
Educational institutions can leverage mini electric cars for student transportation within campuses and nearby areas. These vehicles provide a safe and efficient means of transport, significantly reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional buses or cars. When sourcing for this application, it’s essential to assess the vehicle’s capacity, safety features, and ease of operation, ensuring they meet the specific needs of students and staff alike.
How do mini electric cars enhance healthcare service accessibility?
In the healthcare sector, mini electric cars can be utilized for transporting patients and medical staff in urban settings. They improve access to healthcare services while minimizing environmental impact. B2B buyers must evaluate factors such as range, safety, and comfort features to ensure these vehicles are suitable for medical transport. The ability to navigate tight spaces and park easily can also enhance operational efficiency in busy urban healthcare environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mini electric car no licence mobility cars’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Challenges for License-Free Mobility Cars
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties in understanding and complying with the various regulations surrounding mini electric cars, particularly those that do not require a driver’s license. Different countries, especially in Africa, South America, and Europe, have distinct legal frameworks governing the use of these vehicles. This can lead to confusion regarding vehicle specifications, safety requirements, and operational limits, potentially resulting in costly compliance issues or the inability to market the vehicles effectively.
The Solution: To mitigate regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on the local regulations governing mini electric cars in their target markets. Collaborating with legal experts or consultants who specialize in automotive regulations can provide clarity. Additionally, sourcing vehicles designed to meet specific regional standards, such as EU L6 and L7 classifications, can simplify compliance. Buyers should also consider engaging with local authorities early in the procurement process to ensure that their vehicles align with local laws. Regular updates on regulatory changes through industry associations can further enhance compliance and operational readiness.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure Limitations
The Problem: One of the significant pain points for businesses looking to invest in mini electric cars is range anxiety, particularly in regions where charging infrastructure is still developing. Buyers may worry that the limited range of these vehicles could hinder their operations or the satisfaction of end-users, especially in urban areas where traffic congestion can further restrict mobility.
The Solution: To overcome range anxiety, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing mini electric cars equipped with efficient energy management systems and swappable battery technology. Vehicles that can charge via solar panels, like the Squad Solar City Car, can provide a sustainable solution for daily urban mobility without the dependence on extensive charging stations. Additionally, buyers should assess the local charging infrastructure and collaborate with local businesses or governments to enhance charging accessibility. Offering incentives for users to charge vehicles during off-peak hours or developing partnerships with charging service providers can also alleviate concerns regarding range limitations.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety and Durability in Urban Environments
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern for B2B buyers investing in mini electric cars, especially in densely populated urban areas where accidents and collisions are more likely to occur. Buyers may worry about the structural integrity and safety features of these vehicles, which can impact their marketability and user trust.
The Solution: To ensure safety and durability, B2B buyers should focus on sourcing mini electric cars that meet high safety standards, including robust crash structures and advanced safety features. Buyers should look for vehicles with full roll cages, seat belts, and stability controls. Conducting thorough due diligence on manufacturers’ safety records and independent crash test ratings can further validate the vehicles’ safety credentials. Additionally, offering training programs for users on safe driving practices can enhance safety awareness and reduce the likelihood of accidents, thus building trust with consumers and end-users.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mini electric car no licence mobility cars
What are the Key Materials Used in Mini Electric Car No Licence Mobility Cars?
The selection of materials for mini electric cars without a license is critical, as it directly influences performance, safety, cost, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, composites, and thermoplastics.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Mini Electric Car No Licence Mobility Cars?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. This material typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and can withstand varying pressure levels, making it suitable for structural components and body panels.
Pros: Aluminum’s light weight contributes to improved energy efficiency and range, essential for electric vehicles. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be recycled, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than that of steel. Additionally, while aluminum is durable, it can be less impact-resistant compared to high-strength steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or salt exposure, such as coastal areas in Africa and South America.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheets is crucial. Buyers should also consider local recycling capabilities and the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific performance requirements.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in These Vehicles?
High-strength steel is another commonly used material, especially for structural components such as frames and safety cages. It offers a high yield strength and can withstand significant impact forces, making it ideal for passenger safety.
Pros: High-strength steel is cost-effective and provides excellent durability. It also has good weldability, which simplifies manufacturing processes.
Cons: The weight of steel can negatively impact the vehicle’s energy efficiency compared to lighter materials like aluminum.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly effective in regions where road conditions may be poor, providing enhanced safety and structural integrity.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A572 for high-strength steel is essential. Buyers should also evaluate the local availability of steel and the associated costs for manufacturing.
How Do Composites Enhance Performance in Mini Electric Cars?
Composites, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly being used in mini electric cars for body panels and interior components. These materials are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Composites can significantly reduce the vehicle’s weight, enhancing performance and efficiency. They also allow for more complex shapes, which can improve aerodynamics.
Cons: The main limitation is the higher cost associated with composite materials and the complexity involved in their manufacturing and repair.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly advantageous in regions with variable climates, as they can withstand extreme temperatures and moisture without degrading.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific composite materials that meet local regulations and standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
What Advantages Do Thermoplastics Offer for Mini Electric Cars?
Thermoplastics are increasingly used in the automotive sector for components such as dashboards, panels, and other interior features. They are known for their versatility and ease of manufacturing.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. They also provide good impact resistance and can be recycled.
Cons: While thermoplastics offer good performance, they may not match the strength and durability of metals for structural components.
Impact on Application: Their lightweight nature can enhance energy efficiency, particularly in urban environments where mini electric cars are often used.
Considerations for B2B Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific thermoplastics that meet their performance needs.
Summary of Material Selection for Mini Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for mini electric car no licence mobility cars | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, less impact-resistant | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Frames, safety cages | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, can impact energy efficiency | Medium |
| Composites | Body panels, interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior features, non-structural components | Lightweight, easily moldable | Lower strength compared to metals | Medium |
This guide provides international B2B buyers with insights into material selection for mini electric cars, highlighting the importance of balancing performance, cost, and compliance with local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mini electric car no licence mobility cars
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mini Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process of mini electric cars, particularly those designed for no-license mobility, involves several key stages that ensure high-quality production while optimizing costs. Understanding these stages can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where raw materials are sourced based on specific design requirements. Common materials include lightweight metals like aluminum for the chassis, high-density plastics for body panels, and composite materials for interior components. Suppliers often focus on sustainability, utilizing recycled materials to align with global trends toward eco-friendly manufacturing.
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, various forming techniques are employed to shape the components of the vehicle. These techniques can include stamping, extrusion, and injection molding. For instance, aluminum components are often stamped into shape to create the vehicle’s frame, while interior parts might be produced using injection molding for efficient mass production. Utilizing advanced technologies like CNC machining enhances precision and reduces waste, ensuring that components fit together seamlessly during assembly.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage is crucial for ensuring that all components function correctly together. Typically, this process is organized into assembly lines, where skilled workers or robotic systems systematically put together the vehicle’s parts. Quality assurance measures are integrated at this stage, including visual inspections and automated checks to ensure that each component meets the required specifications. Modular designs are often favored, allowing for easier assembly and maintenance, which is particularly appealing to B2B buyers seeking long-term partnerships.
Finishing Touches
Finishing processes, such as painting and surface treatment, not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the vehicles but also contribute to their durability. Techniques like powder coating and electroplating are commonly used to provide a protective layer against corrosion and wear. Additionally, interior finishes, which may include upholstery and dashboard elements, are tailored to enhance comfort and usability, particularly important for urban mobility solutions.
How is Quality Control Implemented in Mini Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for mini electric cars that cater to diverse markets. Adhering to international and industry-specific standards ensures that products are safe, reliable, and meet customer expectations.
What International Standards Apply to Mini Electric Cars?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who comply with international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. This certification ensures that manufacturers have established processes to maintain product quality and continuously improve operations. Additionally, compliance with CE marking (Conformité Européenne) is crucial for vehicles sold in Europe, indicating that they meet safety and environmental standards.
Which QC Checkpoints Are Critical During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the assembly process to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the completed vehicle to verify that it meets all regulatory and customer requirements before delivery.
These checkpoints help minimize defects and enhance the overall reliability of the mini electric cars.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Common testing methods include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all electronic systems, such as motors and battery management systems, operate correctly.
- Crash Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s safety features and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses the vehicle’s performance under various conditions, including temperature extremes and humidity.
These tests provide critical data that can be shared with B2B buyers, reinforcing the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for minimizing risk and ensuring product reliability.
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive way to assess quality control measures. Buyers should:
- Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed QC documentation, including process flows, inspection reports, and certification copies.
- Perform On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to witness the QC process firsthand and evaluate the working conditions and practices.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards.
How Can Buyers Leverage Quality Reports?
Buyers should require regular quality reports that detail production metrics, defect rates, and corrective actions taken for any issues encountered. This transparency builds trust and allows buyers to make informed decisions about future orders.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Markets?
Navigating the complexities of international markets requires an understanding of local regulations and standards. For example, vehicles sold in Europe must meet stringent EU regulations, while those targeted at African or South American markets may have different requirements. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have experience in these markets and can adapt their QC processes accordingly.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies employed in the production of mini electric cars without a license is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on reliable manufacturing practices, adherence to international standards, and robust quality control measures, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they are investing in high-quality mobility solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mini electric car no licence mobility cars’
In today’s evolving automotive landscape, sourcing mini electric cars that do not require a driver’s license has become an increasingly strategic decision for businesses targeting urban mobility solutions. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help international B2B buyers effectively navigate the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search, clearly outline the technical specifications that your mini electric car needs to meet. Consider factors such as size, range, maximum speed, and passenger capacity, as these will influence usability in specific markets. For instance, vehicles designed to comply with EU L6 and L7 regulations may be more suitable for European markets, while different standards might apply elsewhere.
Step 2: Identify Target Markets and Regulatory Requirements
Understanding the specific markets you intend to operate in is crucial. Research local regulations regarding licensing, safety standards, and environmental impact. For example, some regions may have strict emission regulations or specific requirements for vehicle dimensions and speed limits. This knowledge will inform your supplier selection and help avoid costly compliance issues.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and track records in similar markets. Focus on their experience with mini electric cars, specifically those designed for no-license use, as this will indicate their proficiency in meeting your specifications.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that the supplier adheres to international safety and quality standards.
- Request References: Ask for case studies or testimonials from other businesses that have procured similar vehicles.
Step 4: Assess Product Features and Innovations
When evaluating models, pay close attention to innovative features that enhance usability and sustainability. Look for aspects such as solar charging capabilities, swappable battery systems, and compact designs that facilitate parking in urban settings. These features can significantly improve operational efficiency and user satisfaction.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers and products, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Be clear about your budget constraints and any additional costs that may arise, such as import duties or maintenance agreements. Consider options like leasing or subscription models, which might provide greater flexibility and lower upfront costs.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Test Drives
Before finalizing your purchase, arrange for demonstrations or test drives of the mini electric cars. This hands-on experience will allow you to assess the vehicle’s performance, comfort, and ease of use. It’s also an opportunity to evaluate the supplier’s customer service and support during the procurement process.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Delivery Logistics
After selecting the right vehicle and supplier, ensure that all contractual terms are clearly defined and agreed upon. Pay attention to delivery timelines, warranties, and after-sales support. Additionally, consider logistics for transportation and storage, especially if you are importing vehicles from overseas.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing mini electric cars that cater to the growing demand for no-license mobility solutions, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mini electric car no licence mobility cars Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Mini Electric Cars Without Licenses?
When sourcing mini electric cars that do not require a license, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength plastics are favored for their strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing energy efficiency. Additionally, sourcing eco-friendly materials may attract environmentally conscious consumers but can increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by the complexity of the vehicle’s design and the skill level required for assembly. Automation in manufacturing processes can reduce labor costs, but initial investments in technology may be substantial.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can help lower these overheads.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are essential for the production of vehicle components. Custom tooling for specific designs can lead to higher upfront costs but may yield long-term savings through increased production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Implementing rigorous QC processes is crucial, particularly for vehicles that will be used in urban environments.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the destination, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and local tariffs should be considered to estimate logistics costs accurately.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically build in a profit margin, which can fluctuate based on market demand and competition. Understanding the typical margins in your target market can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions for Mini Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of mini electric cars without licenses, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Larger orders typically reduce the per-unit cost, making it advantageous for buyers to negotiate bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced battery capacity or unique design elements, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both cost and quality. Premium materials may enhance durability and consumer appeal but will also raise production costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles that meet higher safety and environmental standards may command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their market.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established manufacturers may offer better quality assurance but at a premium cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international buyers. Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers concerning shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, impacting the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Mini Electric Car Sourcing?
To optimize sourcing strategies, B2B buyers should consider the following:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your purchasing power, especially for bulk orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, energy consumption, and insurance costs. Energy-efficient vehicles may have higher upfront costs but lower operational expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and regulatory requirements, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These factors can affect pricing strategies and sourcing decisions.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends can provide insights into pricing strategies and help anticipate changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Please note that the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific configurations chosen by the buyer. Always conduct thorough market research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mini electric car no licence mobility cars With Other Solutions
When considering urban mobility solutions, B2B buyers face various options that cater to the growing demand for efficient, sustainable transportation. Among these solutions, mini electric cars that do not require a license have emerged as a popular choice. However, it is essential to compare them against alternative methods to identify the best fit for specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Mini Electric Car No Licence Mobility Cars | E-Scooters | Public Transport |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Top speed of 45-70 km/h; range up to 100 km | Speed up to 25 km/h; range around 30-50 km | Varies by mode; generally efficient |
| Cost | Starting at €6,250; low operating costs | Initial cost around €300-800; low maintenance | Monthly passes range from €30-100 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires minimal infrastructure; easily parked | Requires charging stations; limited by weather | Established networks; may face congestion |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to electric design; battery swaps | Minimal maintenance; battery replacements needed | Routine maintenance by transit authorities |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for short urban commutes; shared mobility | Great for last-mile connectivity; quick trips | Suitable for longer distances and busy routes |
What are the Pros and Cons of E-Scooters as an Alternative Solution?
E-scooters have gained traction as a convenient urban mobility solution, especially in densely populated areas. They offer a low-cost entry point for users and are easy to deploy with minimal infrastructure. However, their performance is limited by speed and range, making them less suitable for longer commutes. Additionally, e-scooters are affected by weather conditions, and their safety can be a concern in crowded environments. While they are ideal for short trips and last-mile connectivity, they may not replace the functionality of a mini electric car.
How Does Public Transport Compare to Mini Electric Cars?
Public transport provides a reliable and established method for urban mobility, with various options such as buses and trams. It is particularly effective for longer journeys and can significantly reduce traffic congestion. However, it often requires users to adhere to schedules and may involve waiting times, which can be inconvenient. Furthermore, the quality of public transport can vary widely depending on the region, impacting user experience. While public transport can be economical, it may not offer the same level of comfort and flexibility as mini electric cars.
Conclusion: Which Urban Mobility Solution is Right for Your Business?
Choosing the right urban mobility solution involves assessing specific business needs, including budget, operational efficiency, and user demographics. Mini electric cars without licenses provide a versatile and sustainable option for short urban trips, especially for businesses focusing on shared mobility. In contrast, e-scooters may serve as a supplementary solution for last-mile connectivity, while public transport remains a dependable choice for longer routes. Ultimately, B2B buyers should evaluate their unique requirements and consider a multi-modal approach to optimize urban mobility within their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mini electric car no licence mobility cars
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Mini Electric Cars Without Licenses?
When considering mini electric cars designed for urban mobility without the need for a driving license, several technical specifications stand out. Understanding these properties is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to enter this growing market.
-
Vehicle Classification
Mini electric cars typically fall under specific classifications such as L6 and L7 in Europe, or Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) in the US. L6 vehicles can reach speeds of up to 45 km/h and are limited to two occupants, while L7 vehicles can accommodate up to four passengers with a maximum speed of 70 km/h. This classification impacts regulatory compliance and market opportunities, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand local regulations. -
Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity is usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), with common capacities ranging from 1.6 kWh to 10 kWh for mini electric cars. A higher capacity allows for extended range, which is vital for urban users who may rely on these vehicles for daily commuting. B2B buyers should consider battery efficiency and the average daily distance traveled by potential users, which is often around 12 km. -
Construction Materials
The use of lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength composites is common in mini electric cars to enhance energy efficiency and performance. These materials not only reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving range, but also contribute to safety through better crash protection. For B2B buyers, understanding the material properties can inform decisions about durability and maintenance costs. -
Charging Options
Many mini electric cars feature swappable or portable battery systems, allowing users to replace depleted batteries with fully charged ones easily. This innovation enhances convenience and reduces downtime. B2B buyers should assess the charging infrastructure in their target markets, as well as consumer preferences for home charging versus battery swapping. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in urban mobility solutions. Mini electric cars often include roll cages, seat belts, and enhanced visibility features, such as high seating positions. Understanding the safety standards relevant to their market can help B2B buyers ensure compliance and promote these features effectively to end-users.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Mini Electric Car Industry?
Navigating the mini electric car market also involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon that can impact purchasing decisions.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of mini electric cars, OEM partnerships can affect the supply chain and product quality. B2B buyers should seek reliable OEMs for components to ensure product reliability and compliance with regulations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly influences inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQ helps in planning purchases and scaling operations effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to submit price quotes for specific products or services. For B2B buyers in the mini electric car market, issuing RFQs can facilitate competitive pricing and ensure they are getting the best value for their investments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and liability issues, which are essential when dealing with international suppliers. -
MaaS (Mobility as a Service)
MaaS refers to integrated, user-centric mobility services that allow users to plan, book, and pay for various transportation services through a single platform. This concept is increasingly relevant for mini electric cars, particularly in urban settings. B2B buyers should consider how their products fit into the MaaS ecosystem to enhance market appeal.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, positioning themselves strategically in the expanding market for mini electric cars designed for urban mobility without a license.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mini electric car no licence mobility cars Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting Mini Electric Cars Without a License?
The mini electric car sector, particularly for no-license mobility vehicles, is experiencing a surge driven by urbanization, rising environmental concerns, and a shift towards sustainable transportation. As cities grapple with congestion and pollution, mini electric cars present an attractive solution, especially in developing regions like Africa and South America, where traditional vehicle ownership may be economically unfeasible for a large segment of the population. For international B2B buyers, this presents a unique opportunity to tap into a burgeoning market.
Key trends include the growing acceptance of Mobility as a Service (MaaS), where these vehicles are increasingly integrated into shared mobility solutions. As urban planners and governments prioritize public transport and shared mobility, B2B buyers can capitalize on partnerships with ride-sharing platforms or local governments. Additionally, advancements in battery technology, such as swappable batteries, are enhancing the appeal of these vehicles by addressing range anxiety and charging infrastructure challenges.
In Europe, favorable regulations around low-speed vehicles (LSVs) and urban micro-mobility are encouraging the adoption of mini electric cars, while in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, the affordability and ease of use of these vehicles cater to a significant market gap. Buyers should remain vigilant about regulatory changes and evolving consumer preferences to effectively navigate this dynamic landscape.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Mini Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of business strategies in the automotive sector, and mini electric cars without licenses are no exception. As B2B buyers consider sourcing options, they should prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. This not only mitigates environmental impact but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible products.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are committed to fair labor practices and transparent sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as benchmarks for assessing supplier sustainability.
Investing in sustainable technologies, such as solar charging capabilities seen in models like the Squad Solar City Car, adds value by reducing operational costs and appealing to eco-conscious consumers. Additionally, ethical sourcing can enhance brand reputation, making companies more attractive to both consumers and business partners in an increasingly competitive market.
How Has the Mini Electric Car Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of mini electric cars without licenses can be traced back to the early 2000s when the concept of quadricycles began gaining traction in Europe. Initially viewed as niche products, these vehicles have transformed into viable alternatives to traditional cars, particularly in urban settings. The rise of electric mobility, combined with regulatory support for low-speed vehicles, has accelerated this transformation.
As urban congestion became a pressing issue, cities began to adopt policies that favored smaller, more efficient vehicles. The introduction of car-sharing services further legitimized the use of mini electric cars, leading to their increased acceptance among younger consumers and those seeking convenient mobility solutions without the burden of full vehicle ownership.
Today, the sector stands at a pivotal juncture, characterized by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer expectations, making it a promising area for B2B investment and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mini electric car no licence mobility cars
-
How do I select a reliable supplier for mini electric cars without a license?
When sourcing mini electric cars, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Start by reviewing their company history, certifications, and compliance with international regulations. Request references from other B2B clients and assess their customer service responsiveness. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or trade shows to connect with verified suppliers and seek out those with a proven track record in your specific market region. -
What features should I consider when choosing a mini electric car for urban mobility?
Key features to consider include battery life, charging options, and safety features. Look for vehicles that offer swappable batteries for convenience and minimal downtime. Evaluate the design for urban maneuverability, such as compact dimensions and efficient parking capabilities. Additionally, consider the environmental impact, including energy efficiency and sustainability practices of the manufacturer. Comfort features, like seating capacity and storage space, also play a crucial role in user satisfaction. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for mini electric cars?
Minimum order quantities vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs for mini electric cars can range from 10 to 100 units. Suppliers may offer better pricing and terms for larger orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms upfront, considering your market demand and potential for resale. If your needs are smaller, inquire if the supplier allows for sample orders or pilot programs to assess product performance before committing to larger quantities. -
What are the payment terms commonly used in international transactions for electric vehicles?
Payment terms for international transactions typically involve a mix of advance payments and balance upon delivery. Commonly, suppliers may request a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the remaining balance payable before shipping or upon delivery. Ensure you understand the payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letters of credit) and consider using escrow services for added security. Always clarify the currency used for transactions to avoid exchange rate issues. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for mini electric cars sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a clear QA process with your supplier, including specifications for materials, manufacturing processes, and performance standards. Request detailed documentation of certifications and compliance with local regulations. Conduct pre-shipment inspections through third-party inspection services to verify that products meet your standards. Consider implementing a trial period for initial orders to assess product performance in real-world conditions before scaling your purchases. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mini electric cars?
Logistics for importing mini electric cars involve several key factors, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose between container shipping or roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) options based on cost and time. Ensure your supplier provides all necessary shipping documents, including the bill of lading and compliance certificates. Familiarize yourself with import tariffs and duties applicable in your target market to budget accurately. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process. -
Are there specific regulations to consider when importing mini electric cars into different regions?
Yes, regulations vary by region, impacting vehicle specifications, emissions standards, and safety features. In Europe, for instance, vehicles must comply with EU L6 and L7 regulations, while other regions may have different standards. Conduct research on local automotive regulations in your target market, focusing on licensing, insurance, and registration requirements. Collaborate with local experts or legal advisors to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively and ensure compliance. -
What customization options are typically available for mini electric cars?
Customization options often include vehicle color, interior features, and additional functionalities like enhanced battery capacity or solar charging capabilities. Some suppliers may offer bespoke modifications tailored to your specific market needs, such as branding opportunities or storage solutions. Discuss your requirements with the manufacturer during the sourcing process to understand the scope of customization available and any additional costs associated with these modifications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Mini Electric Car No Licence Mobility Cars Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Citroën – Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
Domain: citroen.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Citroën Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
– Price: From £7,695 OTR
– Electric Range: 46 miles (WMTC)
– Top Speed: 28 mph
– Charging Time: 4 hours from 0% to 100%
– Dimensions: 2.41m long, 1.39m wide, 1.52m high
– Turning Circle: 7.2m
– Seating: 2 adjustable seats
– Interior Storage: 63L to 200L (if passenger seat used for storage)
– Warranty: 2-year manufacturer warranty, 3-year battery warranty, 3-ye…
2. Nissan – Silence Microcar
Domain: silence-mobility.nissan.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Key Features: 100% electric microcar, available in L6e and L7e models, with options for 1 or 2 removable batteries. Charging Options: Unique removable plug-in batteries, public battery stations (coming soon), standard mains charging (7-9 hours for a full charge). Dimensions: Width of two Silence scooters, 2.28m long, one of the largest boot capacities of any microcar. Interior Features: Climate co…
3. Mobilize – Duo Electric Micro-City Car
Domain: mobilize.co.uk
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Mobilize Duo is a 100% electric micro-city car designed for urban mobility. Key features include:
– Driving range: Up to 100 miles
– Max speed: 50 mph
– Dimensions: 1.30 m width
– Seating: 2 seats with scissor doors for easy access
– Comfort features: Heated seats, air conditioning
– Connectivity: Bluetooth, USB-C socket, My Duo app for vehicle management
– Safety: Equipped with a driver’s airbag,…
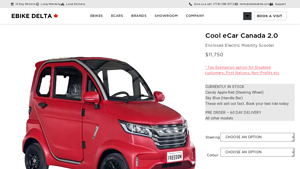
4. Cool eCar Canada 2.0 – Premium Electric Vehicle
Domain: ebikedelta.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Cool eCar Canada 2.0
Price: $11,750
Tax Exemption: Available for disabled customers, First Nations, Non-Profits
Current Stock Colors: Candy Apple Red (Steering Wheel), Sky Blue (Handle Bar)
Delivery: Pre-order with 60-day delivery for other models
Warranty: 1 Year all-inclusive warranty
Returns: 14 Day Returns policy
Range: 85 km per charge (estimate)
Motor Power: 2000 W
Battery: Lit…
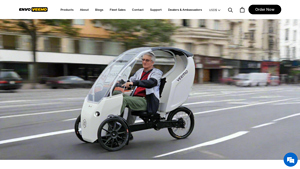
5. Veemo – Enclosed Electric Vehicle
Domain: veemo.ca
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Veemo is a pedal-assisted enclosed electric vehicle designed for urban living. It is a three-wheeled electric vehicle that offers weather protection, cargo space for daily errands, and is compact enough to navigate dense urban streets. Veemo is classified as an e-bike in many regions, meaning no driver’s license, insurance, or registration is required. It features an enclosed cabin for protection …
6. Eli – $11,900 Electric Micro Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Eli launches its $11,900 electric micro ‘car’ in the US.
7. Facebook – Mini Cars as Mobility Scooters
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: mini cars considered mobility scooters
8. Riedis – Electric Mini Car J4 EEC & Three-Wheel Cargo Scooter NC05
Domain: riedis-electric.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Electric mini car J4 EEC: Nominal power of the engine/motors (W): 1000W, Design speed (km/h): 45km/h, Wheel size (inch): 19inch, Range (km): 50km, Battery capacity (Ah): 65Ah, Weight (kg): 302kg, Price: €5,249.00 (with tax). Electric three-wheel cargo scooter NC05: Nominal power of the engine/motors (W): 1000W, Design speed (km/h): 45km/h, Wheel size (inch): 16inch, Range (km): 56km, Battery capac…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mini electric car no licence mobility cars
In the evolving landscape of urban mobility, mini electric cars designed for no-license use are emerging as vital solutions for addressing congestion and environmental concerns. These vehicles, such as the Squad Solar City Car, offer a compelling combination of affordability, convenience, and sustainability, making them attractive options for B2B buyers in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Strategic sourcing of these mobility solutions not only aligns with global trends towards greener transportation but also capitalizes on the growing demand for accessible urban mobility alternatives. As populations swell in urban areas and traditional transportation methods become increasingly untenable, investing in mini electric vehicles can enhance service offerings and meet regulatory requirements in various regions.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should consider the potential for integrating these vehicles into existing transportation frameworks, particularly through Mobility as a Service (MaaS) platforms. By prioritizing strategic sourcing in this niche market, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of the mobility revolution, ultimately contributing to smarter, cleaner cities. Now is the time to explore partnerships and investments in mini electric cars to drive sustainable urban mobility solutions.