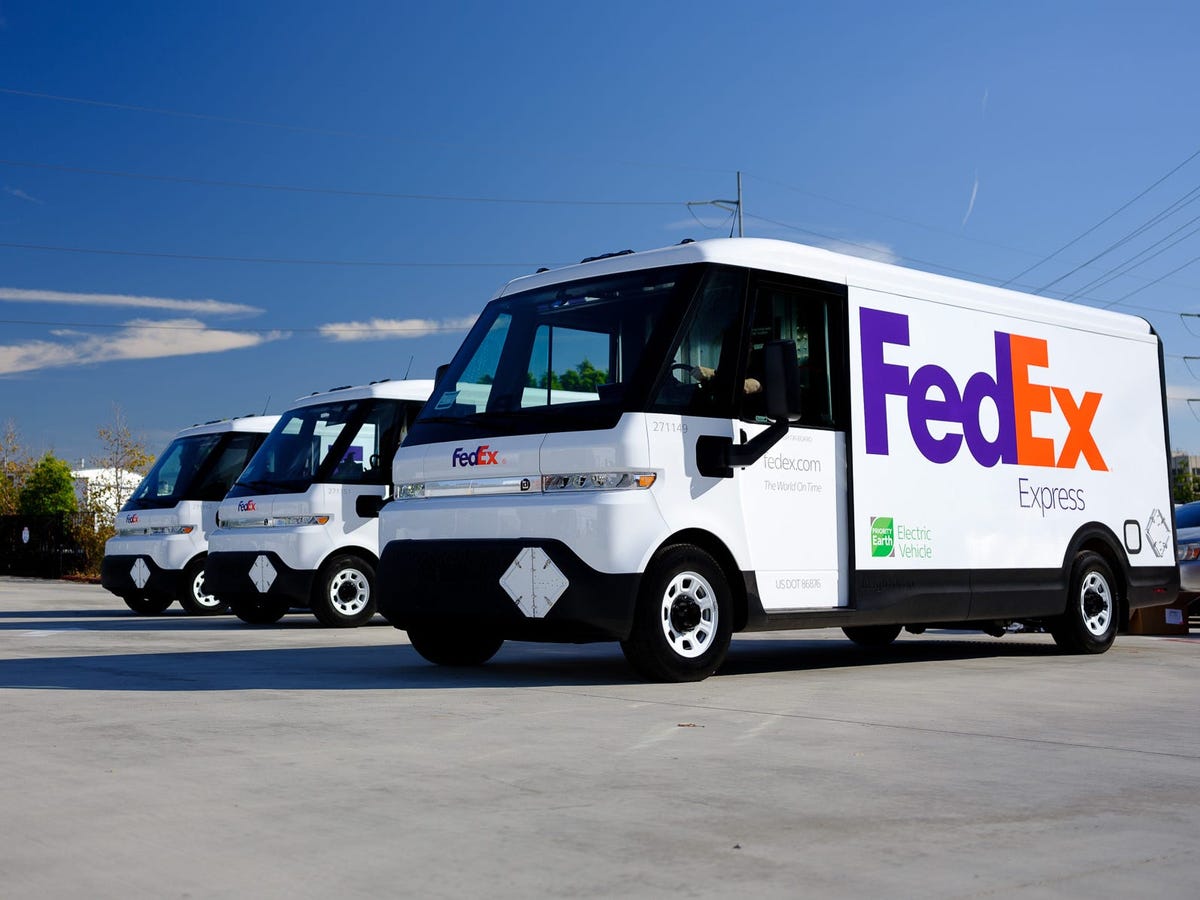
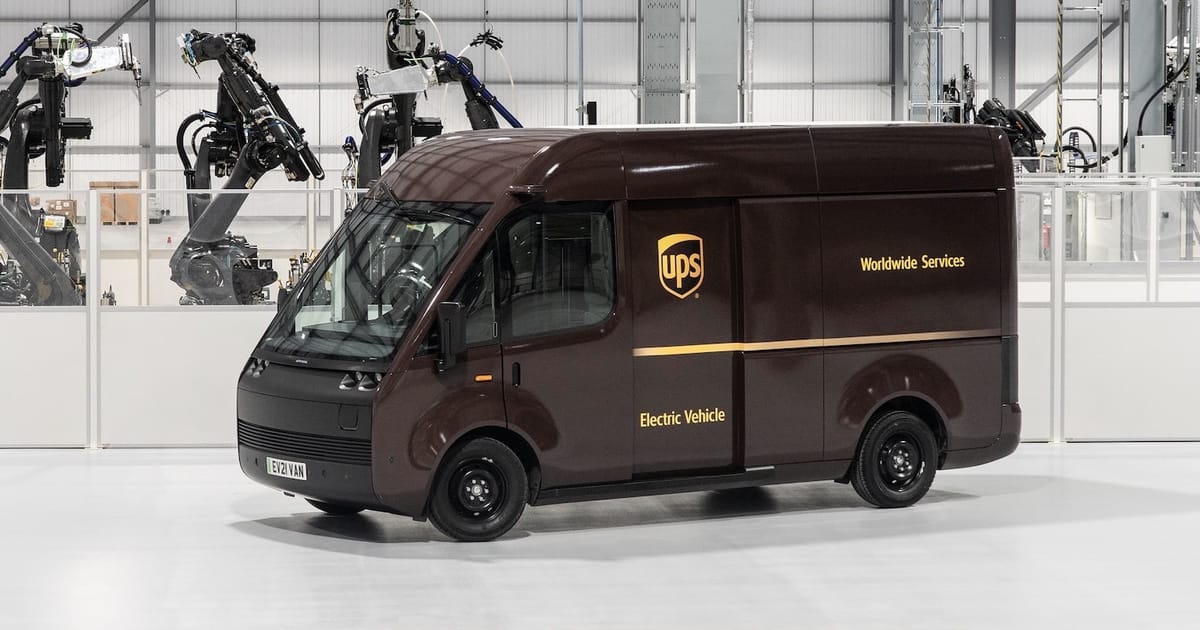
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric vans and trucks
In an era marked by the urgent need for sustainable transportation solutions, sourcing electric vans and trucks has emerged as a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. Companies across diverse sectors are increasingly recognizing the necessity of integrating electric vehicles (EVs) into their fleets to reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. This guide serves as an essential resource for navigating the complex global market of electric vans and trucks, offering insights into various types, applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
From compact delivery vans suited for urban logistics in bustling cities like Lagos to robust trucks designed for long-haul transport across the vast landscapes of Brazil, this guide covers a wide array of electric vehicles tailored to meet the unique demands of businesses operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. It delves into critical aspects such as cost analysis, charging infrastructure, maintenance requirements, and the latest technological advancements that enhance vehicle performance and driver safety.
By empowering B2B buyers with comprehensive knowledge and actionable insights, this guide enables informed purchasing decisions that align with sustainability goals and operational efficiency. Whether you are a fleet manager in Nigeria or a logistics director in Germany, understanding the intricacies of the electric van and truck market is key to optimizing your fleet strategy and achieving long-term success.
Understanding electric vans and trucks Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Cargo Vans | Large cargo space, high payload capacity, versatile configurations | Delivery services, logistics | Pros: Good range, customizable. Cons: Limited charging infrastructure in some regions. |
| Electric Minivans | Family-friendly design, multiple seating configurations | Shuttle services, employee transport | Pros: Comfort and space. Cons: Less cargo capacity compared to cargo vans. |
| Electric Step Vans | High floor space, easy access for loading/unloading | Urban deliveries, food services | Pros: Efficient for frequent stops. Cons: May have limited range under heavy loads. |
| Electric Box Trucks | Enclosed cargo area, robust design for heavier loads | Freight transport, moving services | Pros: Secure cargo, good range. Cons: Larger footprint may limit accessibility. |
| Electric Utility Trucks | Built for specific trades, equipped with tools and equipment | Construction, maintenance services | Pros: Tailored for specific tasks. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Electric Cargo Vans?
Electric cargo vans are designed for businesses that require ample storage and payload capacity. They often feature customizable configurations, allowing companies to tailor the interior layout to their specific needs. With competitive ranges, many electric cargo vans can efficiently handle urban delivery routes. B2B buyers should consider the availability of charging infrastructure in their operational areas, as this can significantly impact the vehicle’s usability.
How Do Electric Minivans Serve B2B Applications?
Electric minivans combine the functionality of passenger vehicles with the versatility needed for business operations. They typically offer multiple seating configurations, making them suitable for shuttle services or employee transportation. While they provide comfort and a spacious interior, businesses should weigh their lower cargo capacity against the need for passenger comfort. Understanding the specific needs of your workforce can help in deciding whether this type of vehicle is a good fit.
What Makes Electric Step Vans Ideal for Urban Deliveries?
Electric step vans are characterized by their high floor space and easy access for loading and unloading goods. These vehicles excel in urban environments where frequent stops are necessary, making them ideal for delivery services and food distribution. While they can be highly efficient for short-distance deliveries, potential buyers should consider the range limitations, especially when carrying heavier loads. Assessing your delivery routes can help determine if this vehicle type meets your needs.
Why Choose Electric Box Trucks for Freight Transport?
Electric box trucks are designed for heavier loads and secure cargo transport. Their enclosed cargo area protects goods from weather and theft, making them suitable for freight transport and moving services. These trucks generally offer good range and are equipped with advanced safety features. However, their larger size may pose challenges in urban environments. Businesses should evaluate their specific freight requirements and the operational footprint to ensure compatibility.
How Do Electric Utility Trucks Cater to Specific Business Needs?
Electric utility trucks are built for specific trades, often coming equipped with tools and equipment necessary for various maintenance and construction tasks. These vehicles allow businesses to reduce emissions while maintaining productivity. While they offer tailored solutions, they often require a higher initial investment. B2B buyers should consider the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance against the upfront costs when evaluating these vehicles for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of electric vans and trucks
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric vans and trucks | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & Delivery | Last-mile delivery services | Reduced operational costs and lower emissions | Range requirements, charging infrastructure, payload capacity |
| Construction | Material transport and tool delivery | Enhanced efficiency and reduced fuel costs | Vehicle durability, cargo space, and all-weather capabilities |
| Food & Beverage | Distribution of perishable goods | Improved temperature control and reduced carbon footprint | Refrigeration options, range, and local sourcing of parts |
| Public Services | Municipal services (waste collection, maintenance) | Lower emissions and compliance with green initiatives | Fleet size, local service support, and battery life |
| Agriculture | Transport of goods and equipment | Cost-effective logistics and reduced environmental impact | Terrain adaptability, payload capacity, and charging access |
How Are Electric Vans and Trucks Transforming Last-Mile Delivery Services?
In the e-commerce sector, electric vans and trucks are revolutionizing last-mile delivery services. With the growing demand for fast and reliable delivery, businesses are turning to electric vehicles (EVs) to reduce operational costs and carbon emissions. These vehicles are particularly beneficial in urban areas where noise restrictions and environmental regulations are becoming stricter. Buyers should consider range capabilities and the availability of charging infrastructure to ensure that their fleet can meet delivery demands efficiently.
What Role Do Electric Vehicles Play in Construction Material Transport?
In the construction industry, electric vans and trucks are increasingly used for transporting materials and tools to job sites. These vehicles help enhance operational efficiency by reducing fuel costs and offering a cleaner alternative to traditional diesel vehicles. Electric models are designed to handle heavy loads and navigate rough terrains, making them ideal for construction environments. Buyers should focus on vehicle durability, cargo space, and all-weather capabilities to ensure they meet the specific demands of construction projects.
How Can Electric Vans and Trucks Support Food and Beverage Distribution?
Electric vans are crucial in the food and beverage industry, particularly for the distribution of perishable goods. They provide improved temperature control and can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional delivery methods. Businesses can benefit from lower operational costs while meeting the growing consumer demand for sustainable practices. When sourcing, buyers should look for refrigeration options, adequate range, and local sourcing of parts to ensure reliability and compliance with health regulations.
Why Are Electric Vehicles Important for Public Services?
Public service sectors, including waste collection and municipal maintenance, are adopting electric vans and trucks to lower emissions and align with green initiatives. These vehicles support sustainable urban development by minimizing environmental impact while maintaining essential services. Buyers should consider fleet size, local service support, and battery life to ensure that their electric fleet can operate effectively in various public service applications.
What Benefits Do Electric Vans and Trucks Offer to Agriculture?
In agriculture, electric vans and trucks facilitate the transport of goods and equipment, providing cost-effective logistics solutions. By reducing fuel dependency, farmers can lower operational costs and contribute to environmental sustainability. These vehicles must be adaptable to various terrains and have sufficient payload capacities to meet agricultural needs. Buyers should prioritize terrain adaptability, payload capacity, and access to charging stations when considering electric vehicles for agricultural applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric vans and trucks’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range and Charging Infrastructure Concerns
The Problem: For many businesses, especially those operating in remote or underserved regions, the limited range of electric vans and trucks poses a significant challenge. Companies in Africa or South America may find that their operational routes exceed the range of available electric vehicles, leading to concerns about reliability and efficiency. Furthermore, the scarcity of charging stations in these areas exacerbates the issue, making it difficult to plan logistics effectively and risking downtime due to charging needs.
The Solution: To address these range anxiety issues, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of their operational routes and evaluate electric vans that offer extended ranges and robust battery capacities. For example, models like the Ford E-Transit and Ram ProMaster EV provide ranges of around 159 to 174 miles, which may suffice for urban deliveries. Additionally, companies should consider investing in their own charging infrastructure. Partnering with local electricians to install Level 2 or even Level 3 charging stations at depots or warehouses can significantly reduce downtime and enhance fleet reliability. Furthermore, utilizing software tools for route optimization can help ensure that deliveries remain within the operational range, while also maximizing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Scenario 2: High Initial Purchase Costs and Financing Options
The Problem: The upfront costs of acquiring electric vans and trucks can deter many businesses from making the switch from traditional combustion engines. This is particularly relevant for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in regions like the Middle East or Africa, where budget constraints are a common concern. The fear of making a large investment without a clear understanding of long-term savings and incentives can hinder decision-making.
The Solution: B2B buyers should explore various financing options available for electric vehicles, including lease agreements, government incentives, and tax rebates that can significantly lower the initial financial burden. Many manufacturers offer tailored financing solutions specifically for fleets, making it easier to manage cash flow. Furthermore, conducting a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis can provide a clearer picture of the long-term savings associated with electric vans, such as reduced fuel and maintenance costs. Engaging with local financial institutions that specialize in green investments can also uncover additional funding avenues. Collaborating with industry partners to share resources and potentially co-invest in electric vehicles can further alleviate financial pressures.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Technical Support Challenges
The Problem: As electric vehicles become more prevalent, many businesses face uncertainty regarding maintenance and support. Companies may worry about finding qualified technicians who are familiar with electric drivetrains and battery systems, particularly in regions where traditional automotive services dominate. This can lead to concerns over the reliability of their fleets and the potential for increased downtime.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance concerns, businesses should prioritize sourcing electric vans from manufacturers that offer robust service packages and comprehensive training for local technicians. Establishing partnerships with certified service centers that specialize in electric vehicles can also ensure that maintenance is handled efficiently and effectively. Additionally, businesses should take advantage of manufacturer warranties and support programs that often accompany the purchase of electric vehicles. These programs can include regular software updates, roadside assistance, and diagnostic tools that help streamline maintenance operations. Investing in training for in-house staff can further enhance the capability to address basic maintenance needs, thereby reducing reliance on external service providers. By proactively addressing maintenance and support, businesses can enhance the longevity and reliability of their electric fleets, leading to greater operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric vans and trucks
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Vans and Trucks?
When selecting materials for electric vans and trucks, it is crucial to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material, especially in the context of international markets. The following analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, steel, composite materials, and plastics. Each material has distinct characteristics that can impact performance, manufacturing, and overall vehicle suitability.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Vans and Trucks?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. Key properties include a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³ and a melting point of around 660°C. This material is particularly advantageous for electric vans and trucks, as it helps reduce overall vehicle weight, improving energy efficiency and range.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, offers high strength-to-weight ratios, and is relatively easy to fabricate. Its resistance to corrosion also minimizes maintenance costs over time.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to steel and its susceptibility to fatigue under cyclic loading. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for structural components, body panels, and chassis, where weight reduction is critical for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and recycling options, as aluminum can be more expensive in areas with limited supply chains.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Construction?
Steel remains a staple material in vehicle manufacturing due to its high strength and affordability. It typically has a density of about 7.85 g/cm³ and can withstand significant mechanical stress, making it ideal for structural applications.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective, readily available, and offers excellent durability and crash resistance. It can also be treated for corrosion resistance.
Cons: The main limitation is its weight, which can negatively impact the efficiency of electric vans and trucks. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion if not adequately treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used for frames, axles, and other structural elements where strength is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards like JIS in Japan or DIN in Europe. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of the Middle East, corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Electric Van and Truck Design?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly being utilized in electric vehicle production due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics. Composites have a density ranging from 1.5 to 2 g/cm³ and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros: Composites offer excellent fatigue resistance and can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility. They also contribute to weight reduction, improving energy efficiency.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high cost of raw materials and manufacturing processes. Additionally, recycling composites can be challenging, which may impact sustainability efforts.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components, where weight savings and aesthetics are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the lifecycle impacts of composites and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. In regions with stringent recycling laws, such as Europe, this may be a significant factor.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer for Electric Vans and Trucks?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics, are increasingly used in electric vehicles due to their versatility and lightweight properties. Common types include polycarbonate and polypropylene, which offer various mechanical properties.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can be easily molded into complex shapes, enhancing design options.
Cons: The main limitation is lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which may affect safety and durability. Plastics can also degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for interior components, dashboards, and non-structural elements where weight savings are beneficial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local safety and environmental standards. In regions like Africa, the availability of certain plastics may vary, affecting sourcing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Vans and Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric vans and trucks | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, chassis | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, fatigue issues | High |
| Steel | Frames, axles | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, corrosion potential | Low |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interiors | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, recycling challenges | High |
| Plastics | Interior components, dashboards | Versatile, lightweight | Lower strength, UV degradation | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, ensuring informed decisions that align with performance requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric vans and trucks
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Vans and Trucks?
The manufacturing of electric vans and trucks involves several intricate stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and performance of the final product.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Electric vans and trucks typically use lightweight materials such as aluminum and advanced composites to enhance efficiency and reduce overall vehicle weight. High-strength steel is often used for the frame to ensure durability and safety. Additionally, battery cells, electric motors, and electronic control systems are sourced from specialized suppliers, emphasizing the importance of quality materials in achieving optimal performance.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Created?
After material preparation, the forming stage begins. This includes processes such as stamping, extrusion, and casting, which shape the components of the vehicle. For example, body panels are often stamped from sheets of aluminum or steel, while components like battery housings may be cast from aluminum for strength and lightweight characteristics. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including additive manufacturing (3D printing), are increasingly being adopted to produce complex parts that traditional methods struggle with.
Assembly: What Techniques Are Employed in the Assembly Process?
The assembly stage is critical, where all the manufactured components come together. Electric vans and trucks generally employ modular assembly techniques, allowing for flexibility and efficiency in production. Automated robotic systems are increasingly utilized for tasks such as welding and painting, which not only speeds up the process but also enhances precision. Importantly, each assembly line is designed to accommodate variations in models and configurations, ensuring that different fleet requirements can be met without significant delays.
Finishing: How Is the Vehicle Prepared for Delivery?
The final stage, finishing, includes painting, quality checks, and pre-delivery inspections. This stage is crucial, as it prepares the vehicle for its operational environment. Electrostatic painting techniques are often used to ensure a durable and attractive finish. The vehicles are then subjected to a series of quality control checks to ensure that they meet both safety and performance standards before being delivered to clients.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Electric Van and Truck Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the manufacturing of electric vans and trucks. It ensures that every vehicle meets international standards and is free from defects, which is particularly important for B2B buyers who depend on reliability.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental to the quality management systems in place at manufacturing facilities. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that organizations have established procedures for managing quality throughout the manufacturing process. Other relevant standards may include CE marking for products sold in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC checks are conducted to monitor ongoing operations. This includes regular inspections and tests on assembled components to catch any deviations early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the vehicle is fully assembled, FQC involves comprehensive testing, including functional tests of electrical systems, battery performance, and safety features.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Common testing methods for electric vans and trucks include:
- Functional Testing: Evaluating the operational capabilities of electric systems and components.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting vehicles to stress tests that simulate real-world conditions to assess their longevity and reliability.
- Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with crash safety standards and electrical safety regulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial to ensuring that they receive reliable products. Here are several actionable steps:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Audits?
Buyers should perform regular audits of their suppliers. This can include:
- On-Site Audits: Visiting manufacturing facilities to assess their processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
- Document Review: Examining quality assurance documentation, including ISO certifications and test reports.
- Supplier Performance Evaluation: Using metrics such as defect rates and delivery times to evaluate supplier reliability.
How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process. These inspectors can conduct thorough evaluations at different checkpoints, offering detailed reports on quality compliance and potential areas for improvement.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware of?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various nuances in quality assurance:
-
Regulatory Differences: Different countries have varying regulations regarding vehicle safety and emissions standards. Understanding these local requirements is essential for compliance.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: Buyers should consider the stability and reliability of the supply chain, especially in regions where logistics can be challenging. This includes evaluating suppliers’ capabilities to deliver consistent quality over time.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication and understanding of quality expectations. Cultural differences may influence negotiation styles and expectations regarding quality.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electric vans and trucks are complex yet critical for ensuring the delivery of high-quality vehicles. B2B buyers must engage in thorough due diligence to verify supplier capabilities and maintain standards that align with their operational needs. By understanding these processes and quality measures, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their fleet’s performance and sustainability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric vans and trucks’
Introduction
When sourcing electric vans and trucks, a systematic approach is essential to ensure that your investment aligns with your business needs and sustainability goals. This checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through the critical steps necessary for procuring electric commercial vehicles, helping you to make informed decisions that will enhance your fleet’s efficiency and environmental impact.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s crucial to determine the specific requirements for your fleet. Consider factors such as payload capacity, range, and charging options.
– Payload Capacity: Ensure the vehicle can handle the weight of your typical cargo.
– Range Requirements: Assess the distance your vehicles need to travel on a single charge to avoid operational disruptions.
2. Research Available Models
Explore the current market offerings for electric vans and trucks that meet your defined specifications. Focus on reputable models that have been tested and rated by automotive experts.
– Performance Metrics: Look for vehicles that excel in range, comfort, and cargo space.
– Brand Reputation: Consider manufacturers known for reliability and after-sales support, such as Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and Rivian.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your business needs. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and references from previous clients.
– Supplier Experience: Choose suppliers with a proven track record in the electric vehicle market.
– Client References: Ask for case studies or testimonials from companies in similar industries or regions to gauge satisfaction levels.
4. Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Calculate the total cost of ownership, which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, charging infrastructure, and potential tax incentives.
– Operational Costs: Evaluate fuel savings and maintenance costs compared to traditional vehicles.
– Incentives: Research local and national tax credits or subsidies available for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly reduce upfront costs.
5. Verify Charging Infrastructure Compatibility
Ensure that the electric vans or trucks you are considering are compatible with your existing or planned charging infrastructure.
– Charging Levels: Understand the differences between Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging options, and choose a vehicle that aligns with your charging capabilities.
– Installation Needs: Assess whether you will need to upgrade your facilities to accommodate new charging stations.
6. Test Drive and Evaluate Performance
Before making a final decision, arrange for test drives of shortlisted models. This hands-on experience will help you assess performance, comfort, and usability.
– Driver Feedback: Gather input from your drivers regarding the vehicle’s handling and comfort during the test drive.
– Real-World Performance: Pay attention to how the vehicle performs under conditions similar to your operational needs.
7. Finalize Purchase and Review Contracts Carefully
Once you’ve selected a supplier and model, review all purchase agreements and service contracts meticulously.
– Warranty Details: Ensure you understand the warranty coverage and what it includes.
– Service Agreements: Look for comprehensive service and maintenance agreements to minimize downtime and ensure long-term support.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vans and trucks effectively, ensuring a successful and sustainable fleet transition.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric vans and trucks Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Vans and Trucks?
Understanding the cost structure of electric vans and trucks is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) involves high-quality materials, particularly for the battery packs. Lithium-ion batteries, which are a significant part of the overall cost, can fluctuate based on market demand and raw material prices.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the assembly of electric vans and trucks. Training and expertise in EV technology add to labor costs, particularly in regions where such skills are scarce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs related to the factory’s operation, including utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. EV manufacturers often invest heavily in advanced manufacturing techniques to streamline production, which can affect pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for electric vehicle production can be substantial. Custom molds and assembly fixtures are essential for producing parts that meet strict quality and safety standards.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the safety and reliability of electric vans and trucks necessitates rigorous QC processes. This includes testing battery performance, vehicle safety features, and software systems, which can further increase costs.
-
Logistics: The distribution of electric vans and trucks involves transportation costs that can vary significantly based on distance and shipping methods. International buyers should account for these logistics costs when sourcing vehicles from different regions.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market conditions. This margin can vary based on the manufacturer’s brand reputation and perceived value in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Van and Truck Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric vans and trucks, particularly for B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better rates for larger orders, which is crucial for fleet operators.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customizing vehicles to meet specific business needs can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and compliance with international safety and environmental standards can increase the price but may offer better performance and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more due to brand strength, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly impact the final price. Buyers should be aware of shipping responsibilities and costs associated with different Incoterms to avoid unforeseen expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Electric Vehicle Procurement?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage suppliers in open discussions about pricing. Leveraging competitive offers from multiple manufacturers can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also long-term costs such as maintenance, energy consumption, and potential tax incentives. Electric vehicles often have lower operating costs compared to traditional vehicles.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes can significantly affect the final price. Buyers should factor in these elements when budgeting for electric vans and trucks.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of developments in the EV market, including changes in technology and material costs, can help buyers anticipate price changes and make strategic purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, price influencers, and effective purchasing strategies is vital for B2B buyers in the electric van and truck market. By focusing on these elements, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. As always, prices can vary widely based on many factors, so it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and maintain flexibility in negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric vans and trucks With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Electric Vans and Trucks
As businesses seek to optimize logistics and reduce operational costs, the demand for efficient transportation solutions has surged. While electric vans and trucks present a sustainable and innovative option, various alternatives exist that may cater to specific business needs. This analysis will compare electric vans and trucks against two viable alternatives: conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and hybrid vehicles. Each solution offers unique advantages and limitations, making it crucial for B2B buyers to consider their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Vans and Trucks | Conventional ICE Vehicles | Hybrid Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, instant acceleration; limited range for some models | Good range and fuel efficiency; performance varies by engine size | Balanced performance; better fuel efficiency than ICE |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operating costs over time due to fuel savings | Lower upfront costs; fluctuating fuel prices can increase long-term costs | Moderate initial cost; savings on fuel but higher maintenance than EVs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; longer setup time | Established fueling infrastructure; easy integration into existing fleets | Minimal change to existing infrastructure needed |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts | Regular maintenance required; parts wear out faster | Moderate maintenance; more complex than EVs but simpler than ICE |
| Best Use Case | Urban deliveries, short to medium-range transport | Long-distance transport, diverse applications | Mixed-use scenarios, urban and suburban deliveries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Conventional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
Conventional ICE vehicles are a time-tested solution for businesses needing reliable transportation. They typically have lower upfront costs compared to electric vehicles, making them an attractive option for companies with tight budgets. The established infrastructure for fuel availability simplifies operations, especially in areas where charging stations are scarce. However, ICE vehicles face rising fuel costs and increasing regulatory pressure to reduce emissions, which may impact long-term viability.
Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles combine a traditional combustion engine with an electric powertrain, offering a compromise between fuel efficiency and convenience. They provide better fuel economy than conventional vehicles, making them suitable for businesses looking to lower fuel expenses. Additionally, hybrids can operate on gasoline when electric power runs low, which enhances their range and usability. However, the complexity of the hybrid system can lead to higher maintenance costs compared to fully electric options. This solution is ideal for companies that need flexibility across varying distances and conditions without a complete overhaul of their current infrastructure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate transportation solution requires a thorough understanding of your business’s specific needs, operational context, and budget. Electric vans and trucks shine in urban environments where sustainability and low operating costs are prioritized. On the other hand, conventional ICE vehicles may still be the best choice for businesses that require long-distance travel and have budget constraints. Hybrid vehicles offer a middle ground, providing flexibility for mixed-use applications. Ultimately, B2B buyers should weigh the pros and cons of each alternative against their operational goals to make an informed decision that aligns with their sustainability and efficiency objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric vans and trucks
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Vans and Trucks?
When considering electric vans and trucks, several critical specifications determine their performance, suitability, and overall value to a business. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the battery can store. A higher capacity generally leads to a longer driving range, which is crucial for businesses that rely on transportation. For example, a vehicle with a 100 kWh battery can typically achieve a range of 300 miles, depending on driving conditions and load. This property directly impacts operational efficiency, as longer ranges reduce the frequency of charging stops.
2. Payload Capacity (lbs or kg)
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight a van or truck can carry, including cargo and passengers. This specification is vital for businesses in logistics, delivery, and construction, as it dictates how much product can be transported per trip. Understanding payload capacity helps in optimizing fleet operations and ensuring compliance with local weight regulations.
3. Charging Time (hours)
Charging time is the duration required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery. This varies significantly based on the type of charger used (Level 1, Level 2, or DC fast charging). For instance, a DC fast charger can charge an electric van to 80% in about 30 minutes, while a Level 1 charger might take 12 hours for a full charge. Shorter charging times enhance vehicle availability and can improve overall fleet productivity.
4. Driving Range (miles)
The driving range is the distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge. This specification is critical for route planning and operational efficiency. Electric vans and trucks vary widely in range, with some models offering over 300 miles per charge, making them suitable for long-haul deliveries, while others may be better suited for urban operations with shorter distances.
5. Torque (lb-ft or Nm)
Torque is a measure of rotational force and is crucial for vehicle acceleration and load handling. Electric motors typically provide maximum torque instantly, which can lead to better performance, especially when starting from a stop or carrying heavy loads. Understanding torque specifications helps businesses select vehicles that can efficiently handle their operational demands.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations in the electric vehicle market. Here are several essential terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vans and trucks, OEMs are responsible for the design and manufacturing of the vehicles, ensuring that they meet specific standards and regulations. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers assess the reliability and quality of vehicles.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for fleet buyers, as it can affect inventory management and purchasing costs. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategies effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers often use RFQs to compare offers from different vendors and negotiate better terms. Understanding how to create and respond to RFQs can streamline the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with purchasing and operating a vehicle over its entire lifespan, including acquisition, maintenance, fuel, insurance, and depreciation. For B2B buyers, understanding TCO is essential for evaluating the financial viability of electric vans and trucks compared to traditional options.
In conclusion, grasping these technical properties and trade terms is vital for B2B buyers looking to invest in electric vans and trucks. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures that businesses can optimize their operations and enhance their bottom line.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric vans and trucks Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Electric Vans and Trucks?
The electric vans and trucks market is witnessing transformative growth driven by global sustainability initiatives, regulatory pressures, and advancements in technology. As governments push for reduced carbon emissions, businesses are increasingly adopting electric vehicles (EVs) to align with these mandates and enhance their brand reputation. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this shift presents a unique opportunity to invest in modern, efficient fleets that comply with emerging environmental regulations.
Emerging technologies are significantly influencing sourcing strategies. Innovations in battery technology are enhancing the performance and range of electric vans, addressing previous concerns regarding operational efficiency. For instance, models like the 2025 Ford E-Transit and the Mercedes-Benz eSprinter offer impressive ranges, making them suitable for urban logistics and delivery services. Additionally, the integration of advanced telematics and fleet management software allows businesses to optimize routes, track vehicle performance, and reduce operational costs.
Moreover, the market is witnessing a rise in collaborations between manufacturers and tech companies to develop smart charging solutions and infrastructure. As electric vans become more prevalent, investing in robust charging networks is essential for maintaining operational uptime, especially in regions where charging infrastructure is still developing.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Electric Vans and Trucks Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric vans and trucks sector, as businesses recognize the importance of reducing their environmental impact. The transition to electric vehicles not only lowers greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes energy efficiency. B2B buyers are increasingly evaluating suppliers based on their commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction, with companies prioritizing suppliers who adhere to responsible labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for sustainable building practices are becoming essential criteria in the procurement process. By choosing suppliers that prioritize these standards, businesses can enhance their corporate social responsibility profile, which is increasingly important to consumers and stakeholders.
Furthermore, the lifecycle impact of electric vans must be considered. From sourcing raw materials for batteries to end-of-life recycling, a comprehensive understanding of the supply chain is critical. B2B buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers that not only provide ‘green’ vehicles but also engage in transparent practices regarding material sourcing and waste management.
What Has Been the Evolution of Electric Vans and Trucks in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of electric vans and trucks can be traced back to the early 20th century, when electric vehicles were common before the rise of internal combustion engines. However, the recent resurgence of interest in EVs has been propelled by technological advancements, rising fuel costs, and growing environmental awareness.
In the last decade, electric vans have transitioned from niche products to mainstream commercial solutions, with major automotive manufacturers entering the market to meet demand. The introduction of models such as the Ram ProMaster EV and Rivian’s electric vans illustrates the commitment of established brands to innovate and cater to the needs of businesses seeking efficient, sustainable transport options.
As the market continues to mature, international B2B buyers must remain vigilant about evolving trends and technologies that can influence their fleet strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric vans and trucks
-
How do I choose the right electric van or truck for my business needs?
Selecting the right electric van or truck depends on various factors including your operational requirements, budget, and range needs. Assess the payload capacity, cargo space, and driving range of the vehicle. Consider the specific use case—whether for urban deliveries, long-haul transportation, or service jobs. Additionally, evaluate the availability of charging infrastructure in your region and any potential government incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Consulting with suppliers and conducting a cost-benefit analysis can further aid in making an informed decision. -
What are the key features to look for in electric vans and trucks?
When sourcing electric vans and trucks, prioritize features such as battery capacity, range, payload capacity, and charging options. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) enhance safety and efficiency, while connectivity features support fleet management. Ensure the vehicle offers a comfortable driving experience for operators, as this impacts productivity. Additionally, consider the warranty and service options provided by the manufacturer to ensure long-term support and maintenance for your fleet. -
What is the average lead time for ordering electric vans and trucks?
Lead times for electric vans and trucks can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, model, and customization options. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few months to over a year for delivery. Factors influencing lead times include production schedules, supply chain constraints, and regional demand. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers for the most accurate timelines and to factor in potential delays when planning your fleet acquisition. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric vans and trucks?
Minimum order quantities for electric vans and trucks often depend on the manufacturer and specific model. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, while others might require bulk orders to meet production efficiencies. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about any flexibility in MOQs and consider pooling orders with other businesses in your region to meet the minimum requirements. This can enhance your bargaining position and potentially reduce costs. -
How can I verify the credibility of a supplier for electric vans and trucks?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, conduct thorough research that includes checking their reputation, financial stability, and client testimonials. Review their history in the electric vehicle market and any partnerships with reputable manufacturers. Request references from other B2B buyers who have previously purchased from them. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or attending trade shows to engage with their team and assess their operations firsthand. -
What payment terms are typical for international purchases of electric vans and trucks?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely depending on the supplier, but common arrangements include deposits followed by progress payments or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or leasing agreements to ease the initial financial burden. It’s crucial to negotiate clear terms that include currency, payment methods, and timelines. Ensure that any agreed terms are documented to protect both parties in the transaction. -
How do I handle logistics for importing electric vans and trucks?
Handling logistics for importing electric vans and trucks involves several steps, including selecting a reliable freight forwarder, understanding customs regulations, and planning for transportation from the port to your location. Work closely with your supplier to ensure all necessary documentation is prepared, such as bills of lading and import permits. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and taxes that may apply to electric vehicle imports in your region. -
What kind of after-sales support can I expect for electric vans and trucks?
After-sales support for electric vans and trucks typically includes warranty coverage, maintenance services, and access to spare parts. Many manufacturers offer comprehensive service packages that can include remote diagnostics and software updates. It’s important to clarify the details of the warranty and what is covered, including battery performance. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate ongoing support and ensure that any issues are resolved efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Vans And Trucks Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rivian – Commercial Electric Vans
Domain: rivian.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rivian Fleet offers electric work and commercial vans starting at $79,900. The Rivian Commercial Van is designed for sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and safety, featuring 360-degree cameras and patented energy-saving microclimate seats. Operational GHG emissions can be reduced by 50% or more compared to internal combustion vehicles. Dimensions include a length of 248.5 in, height of 114.7 in, …
2. Mike Albert – Electric Cargo Vans and Trucks
Domain: mikealbert.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Electric cargo vans and pickup trucks expected to hit the market in 2024 include: 1. Ford E-Transit: Range: 126 miles, Payload: 3,800 pounds, Cargo volume: Up to 536.4 cubic feet, Cost: $55,000+ (with $7,500 tax credit), Launch: In production now. 2. BrightDrop Zevo 600: Range: 250 miles, Payload: 2,200 pounds, Cargo volume: Up to 614.7 cubic feet, Cost: Must request info, Launch: In production no…
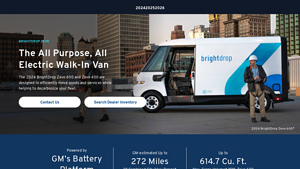
3. BrightDrop – Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Product Name: BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
Type: All Electric Walk-In Van
Purpose: Designed for efficient goods and services movement, helping to decarbonize fleets.
Power Source: Powered by GM’s Battery Platform
Estimated Range: Up to 272 miles (combined city/highway)
Max Cargo Volume:
– Zevo 600: 614.7 cu. ft.
– Zevo 400: 412.1 cu. ft.
Lease Offer: $599 per month for 36 months, $2,999 due a…
4. Mullen Commercial – Class 1 Urban Delivery Cargo Van
Domain: mullencommercial.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: {“vehicles”: [{“model”: “Class 1 Urban Delivery Cargo Van”, “max_payload”: “1,683 lbs.”, “cargo_volume”: “157 cu.ft.”, “range”: “110 miles”, “note”: “Range can vary depending on conditions such as climate, driving behavior, road conditions, etc. *Pre-production model shown”}, {“model”: “Class 3 Urban Utility Low Cab Forward”, “max_payload”: “5,316 lbs.”, “gvwr”: “11,000 lbs.”, “range”: “125 miles”…
5. Ford – e-Transit & Volkswagen – ID. Buzz Cargo
Domain: topgear.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: 1. Ford e-Transit: Available in medium and high heights, three lengths (medium, long, extended), cargo space: 9.5 to 15.1 cubic metres, electric motor: 180 or 265bhp, battery options: 68kWh or 89kWh, range: up to 249 miles.
2. Volkswagen ID. Buzz Cargo: Cargo space: 3.9 cubic metres, electric motor: up to 282bhp, battery: 79kWh, range: 276 miles.
3. Canoo LDV: Two versions – LDV 130 (payload: 13…
6. Chevrolet – BrightDrop 400 & 600
Domain: chevrolet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 400 starting at $46,425 after cash offers; 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 600 starting at $47,925 after cash offers. BrightDrop 400 max cargo volume: 412.1 cu. ft., max payload: 3,710 lbs., max GVWR: 11,000 lbs. BrightDrop 600 max cargo volume: 614.7 cu. ft., max payload: 3,350 lbs., max GVWR: 11,000 lbs. Up to 272 mi. estimated combined city/hwy range for BrightDrop 400; up t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric vans and trucks
In conclusion, the shift towards electric vans and trucks presents a transformative opportunity for businesses worldwide. The variety of models available, from the versatile Volkswagen ID.Buzz to the robust Ram ProMaster EV, showcases the expanding landscape of electric commercial vehicles tailored to diverse operational needs. Strategic sourcing of these vehicles not only enhances sustainability efforts but also drives down operational costs, contributing to long-term profitability.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the implications of transitioning to electric fleets. By investing in electric vans and trucks, companies can significantly reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and improve their brand image, aligning with global sustainability goals. Moreover, the availability of government incentives for electric vehicle purchases can further enhance financial feasibility.
As you explore your options, prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer comprehensive support, including financing, maintenance, and charging solutions. Embrace this pivotal moment to electrify your fleet and position your business for a sustainable and economically viable future. The time to act is now—let your journey towards electrification begin today.