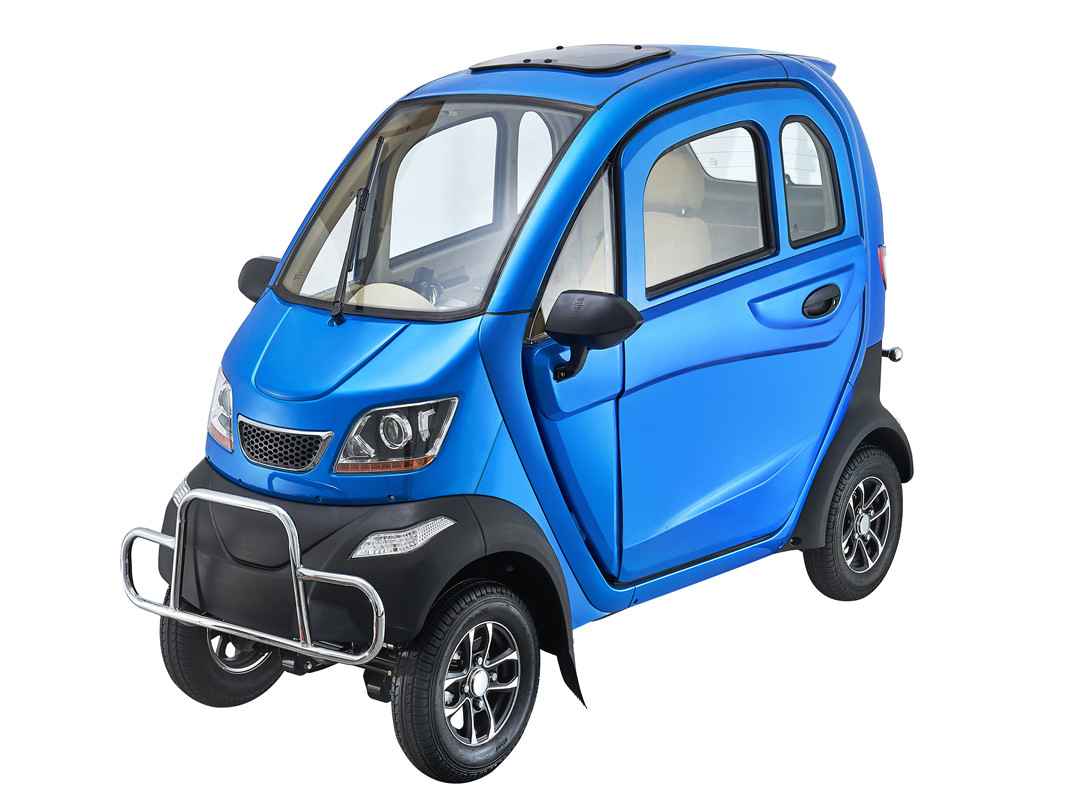
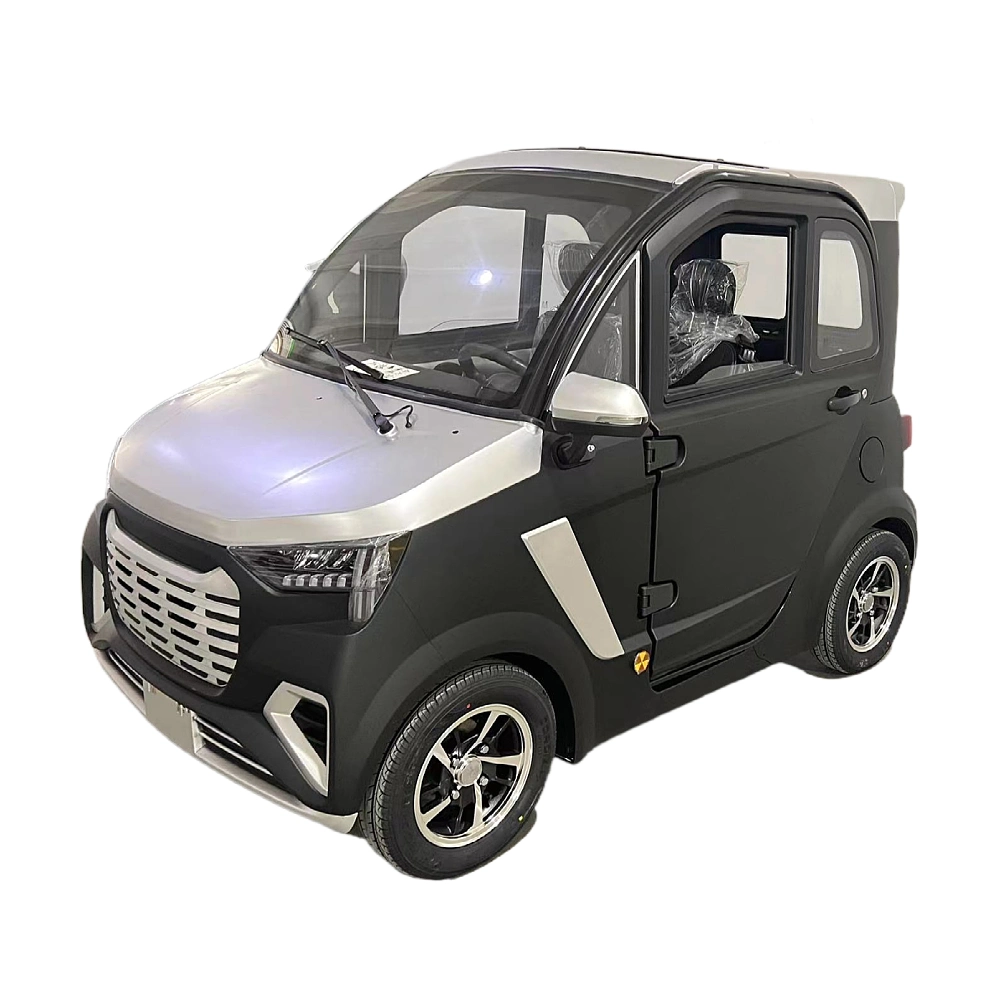
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for approved electric car for disabled
Navigating the global market for approved electric cars for disabled individuals presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers. As demand for eco-friendly, accessible transportation grows, sourcing electric vehicles that meet the diverse needs of disabled drivers can be daunting. Key obstacles include limited design adaptations, insufficient charging infrastructure, and high initial costs. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of selecting approved electric cars for disabled users, providing valuable insights into vehicle types, applications, and essential supplier vetting processes.
With a comprehensive scope, we will explore innovative adaptations such as hand controls and powered tailgates, as well as the importance of accessible charging solutions. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations, including financing options and incentives available in various regions. This guide empowers international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—to make informed purchasing decisions that cater to the needs of disabled individuals.
By leveraging this resource, businesses can enhance their offerings and tap into an underrepresented market, driving inclusivity while capitalizing on the growing demand for electric vehicles. Embrace the opportunity to lead in this vital sector, ensuring that mobility solutions are accessible to all.
Understanding approved electric car for disabled Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle (WAV) | Typically designed with a lowered floor and ramp for easy wheelchair access. | Transport services, healthcare, and mobility rental companies. | Pros: Direct access for wheelchair users. Cons: Limited availability of electric models. |
| Electric Vehicle with Adaptations | Standard electric vehicles modified with assistive technology (e.g., hand controls, swivel seats). | Fleet services, personal mobility solutions. | Pros: Customizable to individual needs. Cons: Potentially higher upfront costs for adaptations. |
| Eco-Friendly Compact EVs | Small, lightweight electric vehicles designed for urban mobility, often with ramps. | Personal use, small business transportation. | Pros: Lower operational costs, compact design. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to larger vehicles. |
| Hybrid Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle | Combines electric and gasoline power, offering flexibility and extended range. | Long-distance transport services, emergency response. | Pros: Versatile power options. Cons: Complexity in maintenance and higher emissions than pure EVs. |
| Luxury Accessible Electric Vehicles | High-end electric vehicles with premium features and advanced accessibility options. | Executive transport, high-end mobility services. | Pros: Enhanced comfort and technology. Cons: High initial investment and ongoing costs. |
What Are Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs) and Their B2B Benefits?
Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs) are specifically designed to accommodate wheelchair users, featuring a lowered floor and a ramp or lift for seamless entry. These vehicles are crucial for transport services, healthcare providers, and mobility rental companies, allowing them to offer inclusive transportation solutions. B2B buyers should consider the limited availability of electric WAVs, as the design of many electric vehicles complicates the necessary modifications. Nonetheless, WAVs provide direct access, significantly enhancing mobility for disabled individuals.
How Do Electric Vehicles with Adaptations Cater to Diverse Needs?
Electric vehicles with adaptations are standard EVs modified to include assistive technologies such as hand controls and swivel seats. These vehicles are ideal for fleet services and personal mobility solutions, enabling organizations to cater to a diverse range of user needs. B2B buyers should evaluate the customization options available and the associated costs, as adaptations can lead to higher upfront expenses. However, the flexibility to tailor vehicles to specific requirements can greatly enhance user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
What Are the Advantages of Eco-Friendly Compact EVs for Businesses?
Eco-friendly compact electric vehicles are designed for urban environments, offering a small footprint and easy maneuverability. These vehicles are suitable for personal use and small business transportation, providing a cost-effective solution with lower operational expenses. B2B buyers should assess the trade-offs, as while these vehicles are economical, they may have limitations in speed and range compared to larger models. Their compact nature makes them ideal for navigating congested city streets, appealing to businesses focused on sustainability.
Why Consider Hybrid Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles for Versatile Applications?
Hybrid wheelchair accessible vehicles combine electric and gasoline power, providing versatility and extended range for long-distance transport services and emergency response. This dual-fuel capability is particularly beneficial for organizations that require flexibility in their operations. B2B buyers should weigh the complexity of maintenance and potential emissions against the advantages of having a vehicle that can operate in various conditions. The ability to switch between power sources can enhance service reliability, making these vehicles a solid investment for diverse applications.
What Makes Luxury Accessible Electric Vehicles a Premium Choice?
Luxury accessible electric vehicles offer high-end features and advanced accessibility options, catering to executive transport and high-end mobility services. These vehicles provide enhanced comfort and technology, making them suitable for businesses aiming to deliver a premium experience. However, B2B buyers should be prepared for the high initial investment and ongoing costs associated with luxury models. The appeal of luxury accessible EVs lies in their ability to combine elegance with functionality, making them an attractive option for organizations focused on superior customer service.
Key Industrial Applications of approved electric car for disabled
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of approved electric car for disabled | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient transportation services for individuals with disabilities | Enhanced mobility solutions that improve patient satisfaction and reduce wait times for transport. | Compliance with accessibility regulations and availability of charging infrastructure. |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Accessible rental vehicles for tourists with disabilities | Attracts a wider range of customers, enhancing the overall travel experience and increasing revenue. | Partnerships with local charging stations and maintenance services for EVs. |
| Public Transportation | Integration into municipal transport systems for disabled individuals | Provides an inclusive transport option, enhancing community mobility and compliance with social responsibility standards. | Coordination with local government regulations and accessible charging point locations. |
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery services for disabled clients | Expands service offerings and demonstrates corporate social responsibility, appealing to a broader customer base. | Adaptations for loading and unloading mobility devices and ensuring vehicle accessibility. |
| Nonprofit Organizations | Transportation for disabled individuals to events and services | Facilitates access to essential services, improving community engagement and support. | Affordability and availability of vehicles that meet specific mobility needs. |
How Are Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Utilized in Healthcare?
In the healthcare sector, approved electric cars for disabled individuals are increasingly used for patient transportation services. These vehicles allow healthcare providers to transport patients with mobility challenges to and from appointments efficiently. By offering specialized adaptations such as ramp access and secure wheelchair spaces, these electric vehicles enhance patient satisfaction and reduce wait times for transport. Buyers in this sector should prioritize compliance with accessibility regulations and ensure the availability of charging infrastructure to support operational efficiency.
What Role Do Approved Electric Cars Play in Tourism and Hospitality?
Tourism and hospitality industries can leverage approved electric cars for disabled individuals by offering accessible rental vehicles. This approach attracts a broader customer base, allowing tourists with disabilities to explore destinations independently. The inclusion of features like adjustable seating and easy access ramps ensures a seamless experience. For international B2B buyers, forming partnerships with local charging stations and maintenance services is essential to guarantee the reliability and accessibility of these vehicles.
How Can Public Transportation Systems Integrate Approved Electric Cars?
Municipal public transportation systems can integrate approved electric cars for disabled individuals to enhance community mobility. By providing accessible transport options, cities can comply with social responsibility standards and improve the quality of life for residents with disabilities. These vehicles can be adapted to meet specific community needs, but it is critical for buyers to coordinate with local government regulations and identify suitable locations for accessible charging points to ensure operational success.
In What Ways Do Logistics and Delivery Services Benefit from Approved Electric Cars?
Logistics and delivery services can incorporate approved electric cars to cater to disabled clients, expanding their service offerings. By providing accessible delivery options, businesses can demonstrate corporate social responsibility while appealing to a broader customer base. Buyers in this sector should consider adaptations for loading and unloading mobility devices, ensuring that vehicles are equipped to handle specific accessibility needs while maintaining efficiency in delivery operations.
How Do Nonprofit Organizations Use Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Individuals?
Nonprofit organizations often utilize approved electric cars to facilitate transportation for disabled individuals to events and essential services. These vehicles enable greater community engagement and support for individuals facing mobility challenges. When sourcing vehicles, nonprofits should focus on affordability and the availability of models that meet specific mobility needs, ensuring they can effectively serve their target populations while maximizing the impact of their services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘approved electric car for disabled’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Insufficient Accessible Charging Infrastructure
The Problem: B2B buyers in the automotive sector are often confronted with the inadequate charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) designed for disabled drivers. This lack of accessible charging stations presents a significant barrier, particularly in regions where the infrastructure is still developing. Buyers are concerned about the usability of charging points, such as the weight of charging cables and the need for dropped kerbs, which are often overlooked in the design phase. This can lead to frustrations for disabled drivers who rely on public charging, particularly in urban areas where home charging is not an option.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should advocate for and invest in partnerships with local governments and infrastructure developers to ensure compliance with the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899). This can include engaging in community initiatives to promote the installation of accessible charging stations. B2B buyers can also evaluate the potential of investing in mobile charging solutions or portable charging units that can be deployed in public areas. By collaborating with technology providers who specialize in accessible EV charging, buyers can help ensure that all EVs, including those designed for disabled drivers, have reliable access to charging facilities. Additionally, offering training and resources to local councils on the importance of accessible charging can foster a more inclusive environment for disabled drivers.
Scenario 2: Limited Options for Wheelchair Accessible Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers face a significant challenge when attempting to source wheelchair accessible electric vehicles (eWAVs). The current market offers limited options, primarily due to the design constraints of electric vehicles, where battery placement can obstruct the necessary modifications for accessibility. This situation is particularly frustrating for organizations looking to provide inclusive transportation solutions for their clients or employees who use wheelchairs.
The Solution: To overcome this limitation, buyers should proactively engage with manufacturers specializing in eWAVs and encourage innovation through collaboration. By forming strategic alliances with conversion companies, buyers can push for the development of new models that prioritize accessibility from the outset. Furthermore, conducting market research to identify consumer demand for eWAVs can provide manufacturers with the business case needed to expand their offerings. Buyers can also explore funding options or incentives available through government grants aimed at promoting accessible transportation solutions, thereby reducing the financial burden associated with acquiring these specialized vehicles.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers is the high initial cost associated with purchasing electric vehicles, especially those adapted for disabled drivers. This is particularly pronounced in regions where economic conditions may limit access to financing options. Many organizations may struggle to justify the higher upfront investment despite the lower long-term running costs, making it challenging to transition their fleets to more sustainable options.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should explore various financing models that can alleviate the initial cost burden. For example, leasing options or financial assistance programs like the Motability Scheme can provide a pathway for organizations to afford eWAVs without the heavy upfront costs. Additionally, buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including savings on fuel, maintenance, and potential tax incentives for electric vehicles, which can make a compelling case for the investment. Partnering with financial institutions to create tailored financing solutions for electric vehicles can also open up more accessible pathways for organizations to adopt these vehicles. By promoting awareness of these financial options, buyers can facilitate a smoother transition to electric vehicles for disabled drivers.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for approved electric car for disabled
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
When considering the development and manufacturing of electric cars designed for disabled drivers, selecting the right materials is crucial. The materials chosen must not only meet performance and safety standards but also cater to the specific accessibility needs of users. Below are analyses of four common materials used in this sector, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various automotive applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved vehicle efficiency and range, which is particularly beneficial for electric vehicles (EVs). However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as battery enclosures and body panels. This is especially relevant in regions with high humidity or saline conditions, common in parts of Africa and the Middle East.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers should also consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs and ensure availability.
Steel: Strength and Versatility
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability. It can be treated to enhance corrosion resistance and is available in various grades, each suitable for different applications.
Pros & Cons: Steel is generally more affordable than aluminum and offers excellent crash safety performance, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its heavier weight can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the chassis and structural framework of vehicles, providing the necessary strength to support additional adaptations for disabled drivers, such as ramps and lifts.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected steel grades comply with local regulations and standards, particularly in regions like South America, where materials may be subject to varying quality controls.
Composite Materials: Lightweight and Customizable
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, offer high strength while being significantly lighter than metals. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their weight reduction, which can enhance EV efficiency. However, they are often more expensive and require specialized manufacturing processes, which may not be readily available in all regions.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components, allowing for innovative designs that improve accessibility. Their customization potential can lead to tailored solutions for specific user needs.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the availability of composite manufacturing capabilities in their region. Additionally, understanding the lifecycle and recyclability of these materials is increasingly important in markets focused on sustainability.
Thermoplastics: Flexible and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Thermoplastics are versatile materials that can be molded into various shapes and are resistant to impact and chemicals. They can also be produced in a range of colors and finishes.
Pros & Cons: Thermoplastics are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for mass production. However, they may not offer the same level of structural integrity as metals, which could be a concern for safety-critical components.
Impact on Application: These materials are often used for interior components, such as dashboard elements and seating, where flexibility and comfort are paramount for disabled drivers.
Specific Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards is crucial, especially in regions with stringent automotive regulations. Buyers should also assess local manufacturing capabilities to ensure quality control.
Summary Table of Materials for Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers
| Material | Typical Use Case for approved electric car for disabled | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, battery enclosures | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Steel | Chassis, structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier, impacting range | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interior components | Lightweight and customizable | Expensive and requires specialized manufacturing | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, seating | Cost-effective and flexible | Lower structural integrity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide highlights the importance of choosing the right materials for approved electric cars designed for disabled drivers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can significantly impact product performance and user satisfaction in diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for approved electric car for disabled
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
The manufacturing of electric cars designed specifically for disabled drivers involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets both functional and regulatory requirements. Here, we break down the main stages of manufacturing and the techniques employed at each stage.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
-
Material Preparation:
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing materials that are lightweight yet durable. Common materials include high-strength steel for the chassis, aluminum for body panels, and composite materials for interior components. It is crucial to select materials that not only meet safety standards but also contribute to the overall accessibility features of the vehicle. -
Forming:
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into components through processes such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. For electric cars aimed at disabled drivers, particular attention is paid to the design of the floor plan, door mechanisms, and space allocation for mobility aids. Advanced techniques like 3D printing are increasingly used to create complex shapes that enhance accessibility features, such as low entry points for wheelchair users. -
Assembly:
The assembly phase integrates all the formed components into a complete vehicle. For electric cars, this includes the installation of the battery pack, electric motors, and any assistive technologies that facilitate ease of use for disabled drivers. During assembly, adaptability features such as swivel seats and powered ramps are integrated. Skilled labor and robotic automation often work in tandem to ensure precision and efficiency. -
Finishing:
The final stage involves painting and detailing the vehicle. For electric cars for disabled drivers, finishing touches may also include the installation of safety features such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that help prevent accidents. Quality assurance practices are embedded in this stage to ensure that the vehicle is aesthetically pleasing and meets all safety regulations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing, especially for vehicles that cater to a vulnerable segment of the population. Here’s an overview of the QA processes and standards applicable to electric cars for disabled drivers.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance for Electric Cars?
-
ISO 9001:
This international standard for quality management systems emphasizes a process approach to ensure customer satisfaction. Manufacturers of electric cars must comply with ISO 9001 to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. -
CE Marking:
In Europe, CE marking signifies that a product conforms to health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For electric cars aimed at disabled drivers, this is crucial to ensure compliance with EU regulations. -
API Standards:
The American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may also apply to electric vehicles, particularly in the context of battery manufacturing and performance. Compliance with these standards ensures that the vehicles are equipped with reliable and safe energy sources.
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that all components meet predefined standards. Here are the key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This phase occurs at the beginning of the manufacturing process, where raw materials and components are inspected for quality before they are used in production. This helps to eliminate defects early on. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that processes adhere to set standards. This includes testing components for durability, safety, and functionality as they are assembled. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
After assembly, the finished vehicles undergo comprehensive testing to verify their performance, safety features, and accessibility adaptations. This stage often includes real-world testing scenarios to assess usability for disabled drivers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring the quality of electric cars for disabled drivers involves several verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This helps to establish trust and reliability in the supply chain. -
Quality Reports:
Requesting detailed quality reports that outline compliance with international standards and internal QA protocols can help buyers gauge the effectiveness of a supplier’s quality management system. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and quality control practices of potential suppliers. This is particularly important for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct in-house evaluations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges when sourcing electric cars for disabled drivers. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Regulatory Compliance:
Different countries have varying regulations regarding vehicle safety and accessibility. Buyers must ensure that the vehicles comply with local laws in their target markets. -
Cultural Considerations:
Accessibility needs can vary widely across different regions. Understanding local demographics and specific requirements for disabled drivers is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. -
Logistical Challenges:
Importing vehicles can involve complex logistics, including customs regulations and transportation. Buyers should factor in these challenges when assessing supplier capabilities.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance for approved electric cars for disabled drivers are vital to ensure that these vehicles meet the diverse needs of their users. By understanding the manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Moreover, awareness of international standards and regulatory nuances can help facilitate successful transactions in a competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘approved electric car for disabled’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure approved electric cars specifically designed for disabled individuals. Given the unique requirements of this demographic, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to ensure that the vehicles meet safety, accessibility, and performance standards. This checklist will help streamline the procurement process and facilitate informed decision-making.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring the electric vehicles meet the unique needs of disabled drivers. Consider factors such as wheelchair accessibility, driving aids, and adaptations that may be required. This step will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the vehicles align with your operational requirements.
- Accessibility Features: Look for features like adjustable ramps, swivel seats, and sufficient cargo space for mobility devices.
- Adaptation Compatibility: Ensure the vehicle can accommodate necessary adaptations such as hand controls or pedal modifications.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Before making any procurement decisions, it’s essential to verify that the electric vehicles comply with local and international regulations. This includes safety standards, emissions guidelines, and accessibility specifications such as the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899).
- Safety Certifications: Check for certifications from recognized authorities that validate the vehicle’s safety and accessibility.
- Local Regulations: Be aware of any specific regulations in your region that might impact vehicle specifications or procurement processes.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conducting a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers is vital to ensure reliability and quality. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers who have procured similar vehicles.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing accessible electric vehicles.
- Service Support: Inquire about after-sales support, warranty terms, and maintenance services to ensure ongoing vehicle performance.
Step 4: Assess Accessibility Infrastructure
Consider the accessibility of the charging infrastructure available in your target market. The success of deploying electric vehicles for disabled drivers relies heavily on the availability of accessible charging stations.
- Charging Point Accessibility: Evaluate the number of accessible charging stations and their locations to ensure easy access for users.
- Future Expansion: Investigate plans for expanding accessible infrastructure to meet growing demand.
Step 5: Conduct Cost-Benefit Analysis
Perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to understand the financial implications of procuring electric vehicles for disabled drivers. This analysis should include initial purchase costs, operational costs, and potential funding options like government grants or financial assistance programs.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in maintenance, charging costs, and potential savings from lower emissions.
- Funding Opportunities: Research available programs that support the procurement of accessible vehicles, such as the Motability Scheme.
Step 6: Pilot Testing and Feedback Collection
Before full-scale procurement, consider conducting pilot testing with a small batch of vehicles. Gather feedback from users to identify any usability issues and assess overall satisfaction.
- User Experience: Collect insights on the vehicle’s accessibility features and any challenges faced by disabled drivers.
- Adaptations Needed: Identify any necessary modifications based on real-world usage to enhance vehicle performance and accessibility.
Step 7: Finalize Procurement and Establish Partnerships
Once all evaluations and assessments are complete, proceed with finalizing the procurement process. Establish partnerships with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and adapt to future needs.
- Contract Negotiation: Ensure that the contracts include provisions for maintenance, support, and any necessary adaptations.
- Long-term Relationships: Consider forming long-term relationships with suppliers to facilitate future purchases and upgrades as technology evolves.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for approved electric car for disabled Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing approved electric cars designed for disabled drivers, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of materials can vary widely based on the specifications of the electric vehicle (EV). High-quality batteries, lightweight materials for body construction, and specialized adaptive equipment for accessibility are significant cost drivers. Sourcing sustainable materials can also impact pricing, as eco-friendly options may come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve skilled workers required for assembly and installation of adaptive technologies. The complexity of modifications for disabled accessibility, such as ramps, swivel seats, and specialized driving aids, necessitates a workforce trained in both automotive engineering and disability support.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs related to production, including utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. For manufacturers focusing on EVs for disabled individuals, investing in specialized machinery for adaptations can further increase overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specialized adaptations can be substantial. This is particularly relevant for manufacturers looking to produce wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAVs) or electric wheelchair accessible vehicles (eWAVs). Custom tooling may be required to cater to specific designs, which can further escalate costs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring compliance with safety and accessibility standards necessitates rigorous quality control processes. This includes testing vehicles for usability by disabled individuals, which can add to the overall cost structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location, which is especially pertinent for international buyers. Factors such as customs duties and tariffs can also significantly impact the final cost.
-
Margin: Profit margins for manufacturers may vary based on market demand and competition. Manufacturers must balance the need for affordable pricing against the costs of specialized adaptations and quality assurance.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
Several factors influence pricing dynamics in the B2B market for electric cars designed for disabled individuals:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk can significantly reduce unit prices. Manufacturers often provide discounts based on minimum order quantities (MOQs), making it advantageous for large-scale buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features tailored to specific needs can increase costs. Buyers should consider their requirements carefully to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both cost and quality. High-performance components may enhance the vehicle’s longevity and efficiency but come at a higher upfront cost.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles that meet international standards and certifications typically command higher prices. Buyers should factor in the long-term benefits of investing in certified vehicles that ensure safety and accessibility.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and service, justifying a higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to shipping and delivery. This is crucial for international transactions, where terms can dictate who bears certain costs and risks.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing electric cars for disabled drivers:
-
Negotiation: Engage in active negotiation with suppliers. Understanding market rates and being clear about your requirements can help secure better deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, insurance, and operational costs, which can significantly impact long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of local regulations and market conditions in your region. Factors such as currency fluctuations and import duties can affect overall costs.
-
Explore Financing Options: Many manufacturers offer financing or leasing options that can make acquiring electric vehicles more manageable for businesses.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost components mentioned are indicative and may vary based on specific models, market conditions, and geographic factors. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing approved electric car for disabled With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers
As the market for electric vehicles (EVs) continues to grow, the need for accessible transportation solutions for disabled drivers remains paramount. While approved electric cars for disabled individuals offer a promising option, various alternative solutions and technologies may provide additional benefits. This analysis compares the approved electric car for disabled drivers with two notable alternatives: hybrid vehicles and dedicated mobility scooters.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Approved Electric Car For Disabled | Hybrid Vehicle | Dedicated Mobility Scooter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, quiet operation | Moderate range, efficient fuel use | Limited speed, designed for short trips |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower running costs | Moderate initial cost, varying fuel efficiency | Lower purchase cost, no fuel expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires adaptations, charging infrastructure needed | Minimal adaptations, fuel stations widely available | Ready to use, minimal setup needed |
| Maintenance | Regular EV maintenance, fewer moving parts | Standard hybrid maintenance, more complex than EVs | Low maintenance, battery replacement needed |
| Best Use Case | Urban and suburban travel, longer distances | Mixed-use, longer trips with fuel backup | Short distances, errands, and community mobility |
Analyzing Hybrid Vehicles as an Alternative
Hybrid vehicles combine traditional fuel engines with electric power, providing a versatile solution for mobility. They typically offer a lower initial cost than fully electric vehicles, making them more accessible for some buyers. However, they may require more complex maintenance due to their dual systems. While hybrids can be adapted for some disabled drivers, they generally do not provide the same level of accessibility as approved electric cars. Their fuel dependency also limits their environmental benefits compared to fully electric options.
Exploring Dedicated Mobility Scooters
Dedicated mobility scooters are designed specifically for individuals with mobility challenges. They are typically less expensive than electric cars and can be used in various settings, including urban areas and shopping centers. Their compact size allows for easy navigation and parking. However, mobility scooters are limited in speed and range, making them unsuitable for long-distance travel. Additionally, they may not be equipped with the same safety features as cars, which could be a consideration for some users.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right transportation solution for disabled individuals, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. Approved electric cars for disabled drivers provide a robust solution for urban mobility and longer trips, particularly when adapted with the necessary modifications. However, hybrid vehicles may appeal to those seeking a balance between cost and fuel efficiency, while dedicated mobility scooters serve as a practical option for short-distance travel. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the specific needs of the end users, their travel requirements, and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for approved electric car for disabled
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
When considering electric vehicles (EVs) designed for disabled drivers, several technical properties are crucial to ensure accessibility and functionality. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
1. Wheelchair Accessibility Design
This specification involves the vehicle’s structural modifications to accommodate wheelchair users. Key features include lowered floors, ramps, and secure locking mechanisms. The importance of this property lies in its ability to provide independence and ease of use for disabled drivers, making it a significant selling point for manufacturers targeting this niche market.
2. Battery Placement and Capacity
The positioning of batteries in electric vehicles is critical, especially for Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs). Batteries are typically located beneath the vehicle floor, which can limit modifications necessary for wheelchair access. A higher battery capacity (measured in kWh) is essential for longer driving ranges, thus enhancing the practicality of the vehicle for everyday use. For B2B buyers, understanding battery specifications can help assess vehicle performance and suitability for target markets.
3. Adaptive Driving Controls
These include modifications such as hand controls and pedal adaptations that allow individuals with limited mobility to operate the vehicle. The integration of adaptive technologies is vital for compliance with accessibility standards and enhancing user experience. For businesses, offering vehicles with these adaptations can broaden market reach and cater to diverse customer needs.
4. Charging Compatibility
Electric vehicles must be compatible with various charging infrastructures, including public and home charging stations. The ability to connect to multiple charging types (e.g., Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging) is essential for convenience and can significantly influence purchasing decisions. B2B buyers should prioritize vehicles that support a wide range of charging options to enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Safety Features
Safety specifications, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), are critical in electric vehicles. Features like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control not only enhance safety for all drivers but are especially important for those with disabilities. For B2B buyers, emphasizing safety can improve marketability and align with regulatory standards.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Electric Vehicle Market?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for navigating the electric vehicle market effectively. Here are several key terms relevant to approved electric cars for disabled drivers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, OEMs are crucial as they provide the foundational components that ensure compliance with accessibility standards. Understanding OEM partnerships can help buyers evaluate the quality and reliability of the vehicles.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term denotes the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. It also influences pricing strategies and overall procurement planning.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs can facilitate competitive pricing and ensure that they receive the best value for the vehicles they intend to purchase.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers, as they outline shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk transfer, which can significantly affect overall costs and logistics.
5. PAS (Publicly Available Specification)
Specifically, PAS 1899 relates to accessible charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. This standard is crucial for ensuring that charging stations are usable by disabled drivers. B2B buyers should look for compliance with such specifications to ensure their products meet market demands.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions and better serve their customers in the growing market for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the approved electric car for disabled Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Market for Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Individuals?
The market for approved electric cars for disabled individuals is gaining momentum, driven by several global trends. The increasing emphasis on sustainability and the transition to electric vehicles (EVs) are pivotal factors, especially in light of government mandates to phase out fossil fuel vehicles in various regions by 2035. This shift is creating a fertile ground for innovation in vehicle design, particularly in the context of accessibility.
Emerging technologies such as assistive driving aids, automated parking systems, and advanced battery solutions are reshaping the landscape. Companies are increasingly investing in research and development to create vehicles that cater specifically to the needs of disabled drivers, such as adjustable seating and easy access for wheelchair users. The rise of mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms is also noteworthy, as they are promoting shared electric mobility solutions that prioritize inclusivity.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and consumer preferences is crucial. Markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are experiencing rapid urbanization, which heightens the demand for accessible transportation solutions. Buyers must also consider the infrastructure landscape, including the availability of charging stations that accommodate disabled individuals, to ensure a seamless integration of EVs into their operations.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Approved Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of the automotive industry, especially for B2B buyers in the approved electric car sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials for electric vehicles, such as lithium for batteries, raises questions about ethical supply chains. Companies are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure they are not contributing to environmental degradation or human rights violations.
B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that adhere to ‘green’ certifications and sustainable practices. This includes the use of recycled materials, renewable energy in production, and responsible mining practices for battery components. Companies that can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability are likely to gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Additionally, as public awareness of environmental issues grows, consumers are demanding more transparency regarding the sourcing of materials. Buyers who can showcase their commitment to ethical sourcing can enhance their brand reputation and foster customer loyalty, particularly in regions where social responsibility is a significant purchasing factor.
What Is the Evolution of Approved Electric Cars for Disabled Individuals?
The evolution of approved electric cars for disabled individuals reflects a broader shift towards inclusivity in the automotive sector. Initially, the focus was predominantly on internal combustion engine vehicles, with minimal consideration given to the accessibility needs of disabled drivers. However, with the advent of electric vehicles, manufacturers are beginning to recognize the importance of catering to this demographic.
In recent years, we have seen a surge in the development of Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs) and electric models that incorporate adaptive technologies. Innovations such as powered tailgates, adjustable seating, and simplified access for mobility devices are becoming standard features. As regulations tighten around vehicle emissions and accessibility standards, the industry is poised for further transformation, driven by both consumer demand and regulatory requirements.
This evolution not only enhances mobility for disabled individuals but also presents a significant opportunity for B2B buyers to invest in a growing market segment that prioritizes inclusivity and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of approved electric car for disabled
-
How do I ensure the electric cars I purchase are compliant with international accessibility standards?
To ensure compliance with international accessibility standards, research the specific regulations that apply in your target markets, such as the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899) in the UK. Collaborate with manufacturers who have a proven track record of producing vehicles that meet these standards. Additionally, consult local regulatory bodies or organizations focused on disability advocacy to stay updated on best practices and required adaptations for electric vehicles. -
What is the best electric car model for disabled drivers?
The best electric car model for disabled drivers depends on individual needs, such as space for mobility devices and ease of access. Models like the Eco M offer features like adjustable ramps for wheelchair users, while larger options may provide more storage for mobility equipment. It’s essential to assess the specific requirements of your clientele and conduct test drives to ensure the chosen models meet accessibility needs. -
How can I customize electric vehicles for disabled drivers?
Customization options for electric vehicles can include adaptations like hand controls, swivel seats, and hoists for easier access. Work closely with specialized vehicle conversion companies that understand the needs of disabled drivers. Ensure that any modifications comply with local safety regulations and that they enhance the overall driving experience without compromising the vehicle’s integrity. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for sourcing approved electric cars for disabled drivers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for sourcing approved electric cars can vary significantly by manufacturer and model. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs, especially for new entrants in the market, while others might require bulk orders to maintain cost-effectiveness. It’s advisable to directly contact suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business’s operational capabilities and market demand. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric cars internationally?
Payment terms when sourcing electric cars can range from upfront payments to 30-90 days after delivery. It’s essential to clarify terms during negotiations and consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your investment. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the contract to prevent any misunderstandings. -
How do I vet suppliers for electric cars for disabled drivers?
Vetting suppliers involves checking their industry reputation, certifications, and compliance with accessibility standards. Request references from previous clients and assess their production capabilities. Conducting factory visits and audits can also provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, ensuring that they meet your expectations and regulatory requirements. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing electric vehicles?
Implementing quality assurance measures includes establishing a robust inspection process at various stages of production. This can involve pre-production samples, in-process inspections, and final quality checks before shipment. Collaborate with third-party quality control firms to ensure that vehicles meet both your specifications and international safety standards, minimizing the risk of defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars for disabled drivers?
When importing electric cars, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and local transportation infrastructure. Ensure that your logistics partner has experience with automotive imports and is familiar with the specific requirements for transporting electric vehicles. Additionally, factor in potential delays in customs clearance and ensure that all necessary documentation is in order to facilitate a smooth import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Approved Electric Car For Disabled Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. BraunAbility – Electric Car Adaptations
Domain: braunability.eu
Introduction: BraunAbility offers adaptations for electric cars, including hybrids and fully electric vehicles. Key considerations include:
1. **Hybrids and Electric Cars Built on Fossil Fuel Platforms**:
– **Examples**: Peugeot e-208, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Ford Kuga.
– **Pros**: Easier adaptations due to shared design elements with standard cars, standardized 12V power for electric functions, and comp…
2. Tesla – Mobility Modifications
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Tesla vehicles can be modified for drivers with limited mobility, including adaptations like a second accelerator pedal and modified steering wheels. Modifications must be performed by certified auto mobility companies, as Tesla does not handle these changes directly. Supercharger locations may have wider spaces for accessibility, but the availability and usability of these spaces can vary. Some s…
3. Allied Mobility – Peugeot eHorizon™
Domain: alliedmobility.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Peugeot eHorizon™
Type: Fully electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle (WAV)
Seating Capacity: 2-5 seats | 1 wheelchair
Engine: Electric 50 KWH 136
Range: 199 miles (WLTP)
Battery: 50 kWh
Dimensions:
– Wheelchair Travelling Position: Width 800 mm, Length 1,120 mm, Seated eyeline 1,275 mm, Height 1,430 mm, Weight 200 kg
Ramp Dimensions:
– Ramp Width: 830 mm
– Ramp Length: 1,248 mm…
4. Swincar – Electric Off-Road Quadricycle for All
Domain: swincar.net
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Electric off-road car designed for people with reduced mobility and disabilities. Key features include: 1. Lightweight all-terrain electric quadricycle suitable for disabled persons. 2. 4-wheel drive and steering capabilities. 3. Silent operation for a peaceful outdoor experience. 4. Adapted for leisure centers, adventure parks, and outdoor activities. 5. Aimed at both B2C and B2B customers. 6. Pr…
5. Dr. Handicap – Top Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers
Domain: drhandicap.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Dr. Handicap – Top Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. GEM – Electric Vehicles
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GEM Electric Vehicles include models e2, e4, e6, eL XD, and a Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle (WAV).
– e2: Small electric car for local trips, light cargo, and tight parking; up to 113 miles of range; seats 1-2.
– e4: Most popular and versatile electric car; up to 106 miles of range; seats 1-4.
– e6: Ultimate electric shuttle; alternative to SUVs or vans; up to 86 miles of range; seats 1-6.
– eL XD…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for approved electric car for disabled
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of approved electric cars for disabled individuals presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers. As the electric vehicle (EV) market expands, there is a growing demand for vehicles that are accessible and cater to the needs of disabled drivers. Key takeaways include the importance of collaboration between manufacturers and vehicle adaptation specialists to overcome design limitations and improve accessibility features. Additionally, investing in charging infrastructure that complies with accessibility standards is crucial for fostering an inclusive EV environment.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus should be on sourcing vehicles that not only meet regulatory standards but also prioritize user experience for disabled drivers. By leveraging the advancements in assistive technology and engaging with manufacturers like EcoCentre, businesses can lead the charge in providing sustainable and accessible mobility solutions.
As we look to the future, it is essential to champion these initiatives, ensuring that every disabled individual has the freedom to travel independently. Now is the time to engage with suppliers and invest in the next generation of electric vehicles that truly serve all members of society.