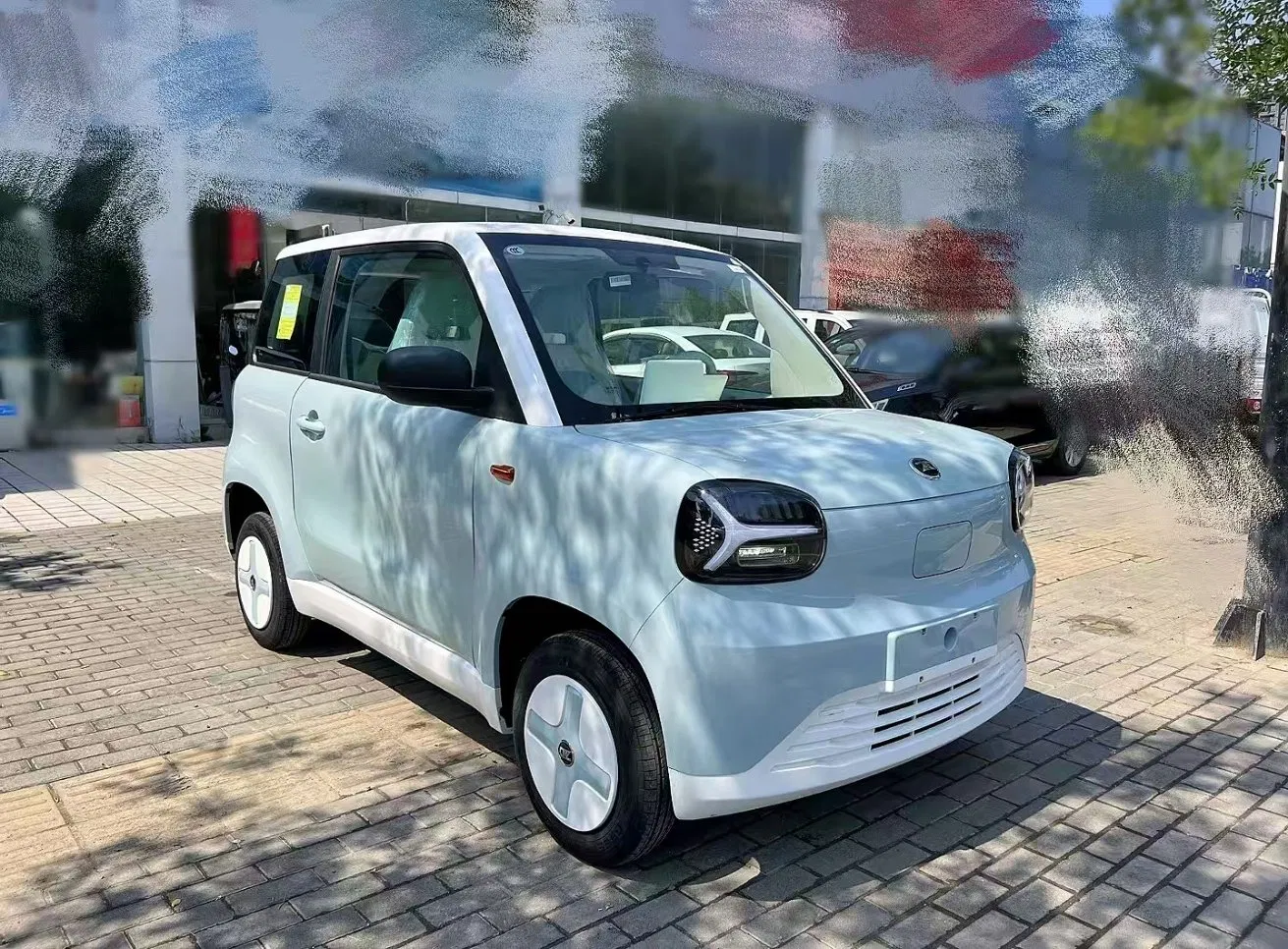
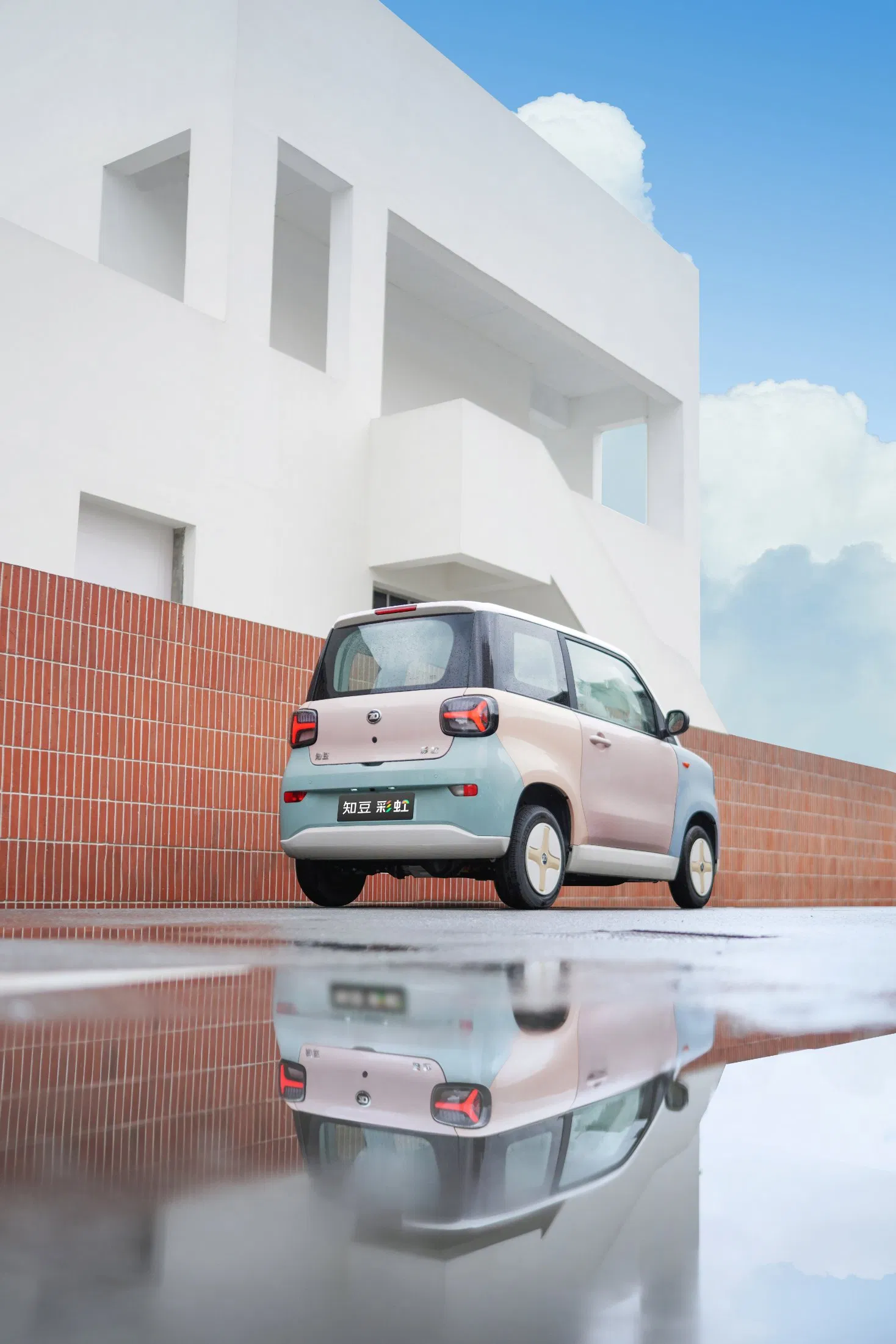
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car eec m1
In an era where sustainable transportation is at the forefront of global discussions, sourcing electric cars that meet EEC M1 standards presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers. The increasing demand for eco-friendly vehicles, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the electric vehicle landscape. This guide is designed to equip international buyers with essential insights into the diverse types of EEC M1 electric cars, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
By exploring various models, specifications, and compliance standards, this guide enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals. Key considerations such as cost analysis, payment terms, and logistical aspects of importing electric vehicles will be thoroughly addressed. Furthermore, we will delve into the importance of selecting reputable suppliers who prioritize quality and customer support, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
With this resource, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing EEC M1 electric cars, empowering them to invest wisely in transportation solutions that enhance mobility while minimizing environmental impact. Whether you are in Germany, Brazil, or any other region looking to adopt electric vehicles, this guide serves as a pivotal tool in your purchasing strategy.
Understanding electric car eec m1 Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEC L6e Electric Cabin Car | Compact design, 2-seat capacity, 72V LiFePo4 battery, max speed 45 km/h | Urban mobility solutions, delivery services | Pros: Eco-friendly, cost-effective, easy maneuverability. Cons: Limited speed and range for long distances. |
| EEC L7e Mini Electric Car | Larger interior, 4-seat capacity, 1500W motor, max speed 90 km/h | Family transport, ride-sharing services | Pros: Versatile, good speed, suitable for families. Cons: Higher initial investment compared to L6e. |
| EEC L6e Cargo Electric Car | Designed for cargo, spacious storage, robust build | Logistics, last-mile delivery services | Pros: High loading capacity, efficient for urban deliveries. Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
| EEC L7e Electric Shuttle Bus | Multiple seating options, enhanced safety features | Shuttle services, public transport | Pros: High capacity, suitable for group transport. Cons: Requires more substantial investment and maintenance. |
| EEC L6e Electric Utility Vehicle | Off-road capabilities, rugged design, larger battery for extended range | Construction, utility services | Pros: Durable, versatile for various terrains. Cons: Heavier and less fuel-efficient compared to smaller models. |
What are the Characteristics of EEC L6e Electric Cabin Cars?
The EEC L6e Electric Cabin Car is designed primarily for urban commuting, featuring a compact 2-seat layout and a powerful 72V LiFePo4 battery. With a maximum speed of 45 km/h and a range of 60-70 km, it is ideal for short-distance travel. B2B buyers in the urban mobility sector will find this model particularly appealing due to its eco-friendly attributes and cost-effective operation. Key considerations include its maneuverability in congested city environments and lower maintenance costs.
How Does the EEC L7e Mini Electric Car Stand Out?
The EEC L7e Mini Electric Car offers a larger interior space and a 4-seat configuration, making it suitable for family transport and ride-sharing applications. With a maximum speed of 90 km/h and a 1500W motor, it provides a balance of performance and comfort. B2B buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s capacity to accommodate more passengers and its versatility for various urban applications. While it may come with a higher upfront cost, its reliability and safety features make it a worthwhile investment.
What Makes EEC L6e Cargo Electric Cars Ideal for Logistics?
The EEC L6e Cargo Electric Car is specifically designed for transporting goods, boasting a spacious storage area and robust construction. This vehicle is particularly suited for logistics and last-mile delivery services, where efficiency and load capacity are crucial. Buyers should focus on its high loading capabilities and the potential for reducing operational costs through electric power. However, its limited passenger capacity may restrict its use in mixed transport scenarios.
Why Choose EEC L7e Electric Shuttle Buses for Public Transport?
EEC L7e Electric Shuttle Buses provide an excellent solution for public transport and shuttle services, featuring multiple seating options and enhanced safety features. This type of electric vehicle caters to group transport needs, making it ideal for businesses looking to offer shuttle services. B2B buyers must consider the higher investment and maintenance costs associated with larger vehicles, but the potential for high passenger capacity and reliability in transportation makes it a strong contender.
How Do EEC L6e Electric Utility Vehicles Perform in Various Terrains?
EEC L6e Electric Utility Vehicles are built for durability and off-road capabilities, making them suitable for construction and utility services. With a larger battery for extended range and rugged design, these vehicles can handle various terrains effectively. B2B buyers should assess their operational needs against the vehicle’s performance in demanding environments. While they may not be as fuel-efficient as smaller models, their versatility and strength in tough conditions justify the investment.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car eec m1
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car eec m1 | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transportation | Short-distance commuter vehicles in cities | Reduces urban congestion and pollution, enhancing mobility | EEC homologation compliance, battery capacity, and charging infrastructure availability |
| Hospitality and Tourism | Shuttle services for hotels and resorts | Eco-friendly transportation option improves guest experience | Vehicle aesthetics, maintenance services, and operational costs |
| Delivery and Logistics | Last-mile delivery vehicles in urban areas | Efficient, zero-emission transport lowers operational costs | Payload capacity, range per charge, and loading/unloading ease |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee commuting solutions | Cost-effective and sustainable transport for staff | Fleet management capabilities, warranty terms, and charging solutions |
| Educational Institutions | Campus transportation for students and staff | Safe, reliable, and environmentally friendly travel option | Safety features, seating capacity, and service agreements |
How is the electric car eec m1 utilized in urban transportation?
In urban transportation, the electric car eec m1 serves as an ideal solution for short-distance commuter vehicles. With its compact design and zero-emission capabilities, it effectively reduces congestion in busy city centers while promoting eco-friendly commuting. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions like Europe and South America, where there is a strong push towards sustainable urban mobility. Buyers should consider the vehicle’s EEC homologation compliance and charging infrastructure availability to ensure seamless integration into existing transport networks.
What role does the electric car eec m1 play in hospitality and tourism?
The electric car eec m1 can be effectively deployed as shuttle services for hotels and resorts, providing guests with a sustainable and comfortable travel option. This enhances the overall guest experience while aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly practices in the hospitality industry. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on vehicle aesthetics, maintenance services, and operational costs to ensure the fleet meets the brand’s standards and guest expectations.
How can the electric car eec m1 optimize delivery and logistics?
In the delivery and logistics sector, the electric car eec m1 addresses the challenge of last-mile delivery in urban settings. Its compact size and efficient energy consumption allow businesses to navigate through congested streets, lowering operational costs while maintaining a zero-emission profile. For international B2B buyers, key considerations should include the vehicle’s payload capacity, range per charge, and ease of loading and unloading to maximize efficiency.
Why is the electric car eec m1 a viable choice for corporate fleets?
For corporate fleets, the electric car eec m1 offers a cost-effective and sustainable transport option for employee commuting. This not only reduces transportation costs but also enhances the company’s image as a socially responsible organization. Buyers should evaluate fleet management capabilities, warranty terms, and available charging solutions to ensure a smooth operation and long-term viability.
How does the electric car eec m1 enhance transportation at educational institutions?
Educational institutions can utilize the electric car eec m1 for campus transportation, ensuring safe and reliable travel for students and staff. Its eco-friendly nature aligns with educational values promoting sustainability. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on safety features, seating capacity, and service agreements to provide a reliable transport solution that meets the needs of their community.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car eec m1’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges in Electric Vehicle Purchases
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and South America, often face complex regulatory landscapes when sourcing electric vehicles like the EEC M1. The EEC homologation standard varies significantly between countries, which can lead to confusion over compliance requirements. Buyers may struggle to determine which models meet local regulations, risking potential fines or operational delays if they inadvertently import non-compliant vehicles.
The Solution: To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers with a proven track record of meeting EEC homologation standards. Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, ensuring they provide documentation demonstrating compliance with local laws. It’s beneficial to establish a relationship with a local compliance expert or legal advisor who understands the nuances of vehicle regulations in your target market. Additionally, consider requesting vehicles that come with comprehensive warranty and support services to ensure that any compliance issues can be swiftly addressed post-purchase.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Range Anxiety in Urban Applications
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers is range anxiety associated with electric vehicles, particularly in urban environments where the EEC M1 is expected to operate. Buyers may worry that the vehicle’s maximum range of 60-70 km will be insufficient for daily operations, especially for businesses relying on frequent short-distance trips. This can deter companies from transitioning to electric models, fearing operational disruptions or increased logistical costs.
The Solution: To alleviate range anxiety, buyers should evaluate the specific operational needs of their fleet and assess routes to optimize vehicle usage. Consider investing in a fleet management software solution that provides real-time data on vehicle performance and energy consumption. This data can help identify patterns and maximize efficiency. Additionally, explore options for implementing charging infrastructure at strategic locations, such as warehouses or client sites, to ensure vehicles can be charged during downtime. It’s also advisable to consider purchasing models with larger battery capacities or supplementary battery packs to extend operational range without substantial additional investment.
Scenario 3: Addressing Maintenance and Service Concerns
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently worry about the maintenance and service support for electric vehicles like the EEC M1. This concern is heightened in regions where electric vehicle service infrastructure is still developing. Buyers may fear high downtime due to the unavailability of skilled technicians or spare parts, which can lead to significant disruptions in business operations.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing electric vehicles from manufacturers that offer robust after-sales support, including access to a network of certified service centers. It’s crucial to inquire about warranty terms and the availability of replacement parts to ensure minimal downtime. Additionally, consider training programs for in-house maintenance staff offered by the manufacturer. This can empower your team to perform basic maintenance and troubleshooting, reducing reliance on external service providers. Building a strategic partnership with your supplier for ongoing support and maintenance can also enhance reliability and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car eec m1
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Car EEC M1 Manufacturing?
In the production of electric cars, particularly the EEC M1 models, material selection plays a crucial role in determining performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Car EEC M1 Design?
Aluminum is widely used in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°C and can withstand significant pressure, making it suitable for structural components.
Pros: Aluminum’s low density contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, enhancing energy efficiency and range. Its natural resistance to corrosion reduces maintenance costs over time.
Cons: The primary downside is its higher cost compared to steel. Additionally, aluminum requires specialized welding techniques, which can complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for frames and body panels, where weight savings are critical for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheets. Understanding local recycling regulations is also essential, as aluminum is highly recyclable.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Car EEC M1 Manufacturing?
Steel is another common material, known for its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various components, including the chassis and safety structures.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers. Its high tensile strength provides excellent crash protection.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. It is also more prone to corrosion unless treated, which can increase long-term maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is primarily used in structural components where strength is paramount, such as the chassis and safety cages.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like DIN EN 10025 is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers should also consider local supply chains for sourcing high-quality steel.
How Does Plastic Contribute to Electric Car EEC M1 Functionality?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like ABS and polypropylene, are increasingly used in electric vehicles for interior components and body panels. These materials are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: Plastics offer excellent resistance to corrosion and can be produced at a lower cost than metals. They also allow for greater design flexibility.
Cons: While plastics are durable, they may not provide the same level of structural integrity as metals. They can also be susceptible to UV degradation over time.
Impact on Application: Used for interior panels, dashboards, and exterior body parts, plastics enhance aesthetic appeal and reduce weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 11469 for plastic materials. Understanding local recycling capabilities is vital, as plastics can have varied disposal regulations.
What Advantages Does Lithium-Ion Battery Technology Offer for Electric Car EEC M1?
Lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of electric vehicle power systems, providing high energy density and efficiency. These batteries can operate effectively in a wide temperature range and offer good cycle life.
Pros: Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy-to-weight ratio, which is essential for maximizing range. They also charge quickly and have a long lifespan compared to other battery technologies.
Cons: The initial cost of lithium-ion batteries is relatively high, and they require careful thermal management to avoid overheating. Additionally, sourcing raw materials can raise ethical concerns.
Impact on Application: These batteries are critical for powering the electric motor, directly affecting vehicle performance and range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like IEC 62133 for battery safety is essential. Buyers should also be aware of local regulations regarding battery disposal and recycling.
Summary of Material Selection for Electric Car EEC M1
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car eec m1 | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels and frames | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis and safety structures | Strong, cost-effective | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Interior components and body panels | Lightweight, design flexibility | Less structural integrity, UV degradation | Low |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Power system | High energy density, quick charging | High initial cost, thermal management | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials crucial for the production of electric car EEC M1 models. Understanding these materials and their implications will aid international B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car eec m1
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Cars Like the EEC M1?
The manufacturing process of electric cars, specifically the EEC M1 model, comprises several critical stages that ensure the vehicle meets both performance and safety standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. High-quality materials are vital for the structural integrity and performance of the vehicle. Key components include:
- Chassis Materials: Typically, high-strength steel or aluminum is used for the chassis to ensure durability and safety.
- Battery Components: Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePo4) batteries are common due to their stability and performance characteristics.
- Interior and Exterior Materials: Non-toxic, high-strength plastics and leather for interiors are preferred to enhance comfort and safety.
Suppliers should provide documentation that details their sourcing practices and material certifications, ensuring compliance with international standards.
How Is the Forming Process Implemented in Electric Car Manufacturing?
After materials are prepared, the next step is the forming process, where raw materials are shaped into usable components. This phase utilizes various techniques:
- Stamping: Metal sheets are stamped to create the body panels. Advanced stamping technologies enhance precision and minimize waste.
- Molding: Plastics used for dashboards and interior components are molded, allowing for intricate designs and improved aesthetics.
- Welding and Joining: Automated robotic welding systems are employed to join chassis components, ensuring structural integrity and consistency.
The forming process is critical for achieving the desired specifications and can be optimized through the use of advanced manufacturing technologies.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like for Electric Vehicles?
Assembly is where all the components come together to form the complete vehicle. This stage involves:
- Sub-Assembly Lines: Components such as the battery pack, motor, and electronic systems are assembled separately before being integrated into the vehicle.
- Main Assembly Line: The vehicle body is combined with the chassis, followed by the installation of the drivetrain, electrical systems, and interior fittings. This is often performed using a modular assembly approach, which allows for flexibility and efficiency.
Efficient assembly lines can significantly reduce production time while ensuring that each vehicle meets quality standards.
How Is Finishing Handled in the Manufacturing of Electric Cars?
The finishing stage includes painting and quality checks before the vehicle is delivered. Key aspects include:
- Surface Treatment: The vehicle undergoes various treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. This may include anti-corrosion baths and powder coating.
- Final Inspection: Each vehicle is subjected to a thorough inspection process to verify that it meets all specifications. This may include checking for paint quality, fit and finish, and overall appearance.
A robust finishing process ensures that the vehicle not only performs well but also meets the aesthetic expectations of consumers.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is crucial in the manufacturing process of electric vehicles. For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant standards can aid in supplier selection.
Which International Standards Should Electric Car Manufacturers Comply With?
Many international standards apply to the manufacturing of electric vehicles, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in production processes.
- ISO 26262: This standard pertains to functional safety in automotive systems, ensuring that electrical and electronic systems perform reliably.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Suppliers should provide documentation proving compliance with these standards, offering assurance of their quality management practices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Important QC stages include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks are performed during the manufacturing stages to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before delivery, a comprehensive inspection of the completed vehicle is conducted to verify compliance with quality standards.
These checkpoints are essential for maintaining high standards and can help mitigate risks associated with product defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is vital. Here are some effective strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits allows buyers to assess the quality management systems in place. This can include reviewing processes, documentation, and compliance with standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance metrics and historical quality data.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
These measures can help establish a reliable partnership and ensure that the products meet the necessary standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Quality control and certification can vary significantly between regions, which is crucial for B2B buyers to understand.
- Regional Regulations: Different countries may have specific regulations that impact the manufacturing and certification of electric vehicles. For instance, buyers in Europe must be aware of EU regulations, while those in Africa or South America may face different compliance requirements.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in communication and business practices is vital. Suppliers may not always proactively share information; thus, establishing a clear communication channel is essential for effective collaboration.
B2B buyers should be prepared to navigate these nuances to ensure a successful procurement process.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Electric Car Manufacturing
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric cars like the EEC M1 are intricate and multi-faceted. B2B buyers must assess suppliers on various criteria, including compliance with international standards, robust quality control checkpoints, and thorough verification processes. By understanding these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain reliability and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car eec m1’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure the EEC M1 electric car. The electric vehicle market is expanding, and understanding the nuances of sourcing can significantly impact your purchasing decision. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of specifications, supplier evaluation, and logistical considerations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, outline the specific technical requirements for the electric car. Consider factors such as battery capacity, motor power, and safety features, which are essential for meeting your operational needs. Ensure that your specifications align with local regulations and standards for electric vehicles in your region.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Demand
Understanding current market trends is vital for making informed decisions. Investigate the demand for electric vehicles in your target markets, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This insight will help you determine the right model and features that appeal to local consumers, enhancing your competitive edge.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from other clients, particularly those in similar markets. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in electric vehicle manufacturing and a strong commitment to quality and customer service.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with EEC Standards
Ensure that the electric car complies with EEC homologation standards. This is crucial for legality and safety in the markets you intend to operate. Request documentation that demonstrates compliance, including test reports and certifications, to avoid any legal or operational setbacks.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Examine the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your order volume and delivery timelines. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and capacity for customization. A reliable supplier should demonstrate flexibility and scalability in their production operations.
Step 6: Negotiate Payment Terms and Conditions
Discuss payment terms that align with your financial strategy. Common options include T/T (telegraphic transfer) or L/C (letter of credit). Ensure that the payment structure offers protection against potential risks, such as delays or non-compliance with specifications.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and After-Sales Support
Develop a logistics plan for transporting the vehicles to your market. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and warehousing. Additionally, assess the supplier’s after-sales support, including warranty services and parts availability, which are critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and vehicle performance.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing EEC M1 electric cars effectively, ensuring a successful procurement process that meets both regulatory requirements and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car eec m1 Sourcing
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis for electric car EEC M1 sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The cost components involved in the manufacturing and procurement of these vehicles encompass several key areas.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Car EEC M1?
-
Materials: The cost of materials forms a significant part of the overall budget. This includes lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, electric motors, chassis components, and interior fittings. The selection of materials can impact both performance and durability, thus affecting pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. Countries with lower wage rates may offer more competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the skill level and training of the workforce. Highly skilled labor can improve product quality, which in turn can justify higher prices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these overhead costs, which is beneficial for overall pricing strategies.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and molds can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. These costs are typically amortized over the production run, so higher volume orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards is critical. QC processes add to the cost but are essential for maintaining brand reputation and compliance with regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the distance to the buyer’s location, shipping methods, and any tariffs or duties applicable to international trade. Efficient logistics management is vital for minimizing these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin on top of the costs incurred. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Electric Car EEC M1?
- Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary or if standard models meet their needs.
- Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (e.g., EEC homologation) can influence both costs and pricing. Higher-quality materials may command a premium but can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) through enhanced durability and performance.
- Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge higher prices, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
- Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms chosen for the transaction is crucial. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the total landed cost of the vehicles.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Electric Car EEC M1?
To maximize cost-efficiency, buyers should engage in thorough market research to understand typical pricing structures and negotiate effectively. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Additionally, considering the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just upfront costs can provide a clearer picture of the vehicle’s value over time.
Buyers from diverse regions must also be aware of local regulations and incentives for electric vehicles, which can influence pricing strategies and sourcing decisions.
What Are the Pricing Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of pricing in different markets is essential. Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxation can all affect the final price. It is advisable to request indicative prices and comprehensive quotes to avoid unexpected costs.
In summary, navigating the comprehensive cost and pricing analysis for electric car EEC M1 sourcing requires an understanding of multiple components and influencers. Buyers should leverage this knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and financial goals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car eec m1 With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Electric Vehicle Solutions
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, businesses must evaluate various options to meet their transportation needs effectively. The EEC M1 electric car stands as a compelling solution for urban commuting, but it’s essential to explore alternative technologies that can fulfill similar requirements. This analysis compares the EEC M1 against two viable alternatives: the traditional gasoline vehicle and the electric scooter. This comparison will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car EEC M1 | Traditional Gasoline Vehicle | Electric Scooter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max Speed: 45 km/h, Range: 60-70 km | Max Speed: 120 km/h, Range: 500 km | Max Speed: 25-30 km/h, Range: 30-50 km |
| Cost | Moderate upfront cost, low operating cost | High fuel costs, moderate maintenance | Low upfront cost, minimal operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Widely available fuel stations | Simple charging, minimal space required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to engine complexity | Very low maintenance, few mechanical parts |
| Best Use Case | Short urban commutes, eco-friendly transport | Long-distance travel, versatile usage | Short trips, delivery services in urban settings |
Analyzing Alternatives: Pros and Cons
Traditional Gasoline Vehicle
Traditional gasoline vehicles offer robust performance, including higher speeds and longer ranges, making them suitable for long-distance travel. They are widely available, with an extensive network of fueling stations. However, they incur higher fuel costs and require regular maintenance due to their complex engines. For businesses needing reliable transportation over longer distances, gasoline vehicles might be the best choice, but the environmental impact and rising fuel prices may discourage eco-conscious buyers.
Electric Scooter
Electric scooters are an increasingly popular alternative for short-distance travel, especially in urban environments. They are cost-effective, both in terms of initial investment and operating costs, and offer minimal maintenance requirements. Scooters are perfect for quick trips and can navigate congested traffic easily. However, their limited speed and range make them less suitable for longer journeys or transporting multiple passengers. For businesses focusing on last-mile delivery or short commutes, electric scooters can be an ideal solution.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
When selecting the right transportation solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental goals. The EEC M1 electric car excels in urban commuting with its eco-friendly design and low maintenance requirements, making it a solid choice for businesses prioritizing sustainability. Traditional gasoline vehicles may serve well for long-distance travel, while electric scooters offer a practical solution for short trips. By analyzing these alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational strategies and sustainability objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car eec m1
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars Under EEC M1 Standards?
Understanding the essential technical properties of electric cars, particularly those classified under EEC M1 standards, is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications not only define the vehicle’s performance but also ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and market expectations.
-
Battery Capacity (Ah and Voltage)
The battery capacity, often expressed in ampere-hours (Ah) and voltage (V), is fundamental in determining the range and performance of the vehicle. For example, a 72V 50Ah lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery provides a balance of capacity and weight, enhancing both the vehicle’s range (typically 60-70 km) and its efficiency. B2B buyers must consider battery specifications to align with local energy regulations and consumer expectations for electric vehicle range. -
Motor Power (kW)
The motor power, usually rated in kilowatts (kW), indicates the vehicle’s performance capabilities. A six-phase 3 kW motor can significantly enhance acceleration and climbing ability, making it suitable for various terrains. Understanding motor specifications helps buyers assess the vehicle’s suitability for specific markets, especially where steep inclines or varied road conditions are common. -
Curb Weight (Kg)
The curb weight refers to the total weight of the vehicle when ready for operation, excluding passengers or cargo. For instance, a curb weight of 450 kg for an electric vehicle is advantageous for energy efficiency and handling. Buyers should evaluate curb weight in relation to local regulations regarding vehicle size and weight, especially in urban environments where space and mobility are critical. -
Charging Time (Hours)
Charging time is a crucial property that impacts user convenience. A vehicle that charges in approximately three hours is more appealing for daily use compared to longer charging periods. This specification is essential for B2B buyers to consider, especially when marketing to consumers who prioritize quick turnaround times for their electric vehicles. -
Safety Features
Safety features, including the brake system and structural integrity, are vital for compliance with international safety standards. Features such as hydraulic disc brakes and reinforced chassis contribute to passenger safety. Buyers need to prioritize these specifications to mitigate liability and enhance consumer trust in the product.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Electric Vehicle Sector?
In addition to technical properties, understanding trade terminology is critical for navigating the B2B landscape of electric vehicles.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the electric vehicle industry, OEMs provide crucial components like batteries and motors. B2B buyers should establish relationships with reliable OEMs to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the electric vehicle market, MOQs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and product type. Understanding MOQs is essential for buyers to manage inventory costs and supply chain efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the electric vehicle sector, issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare different suppliers and negotiate better deals. This process is fundamental for securing competitive pricing in a global marketplace. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping responsibilities and costs, particularly when importing electric vehicles from overseas manufacturers. -
EEC Homologation
EEC homologation is the process of certifying that a vehicle meets European Union standards for safety, emissions, and performance. Understanding this term is essential for B2B buyers targeting the European market, as compliance with EEC regulations is mandatory for market entry.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric vehicles under EEC M1 standards, ensuring they meet market demands and regulatory requirements effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car eec m1 Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Electric Car EEC M1 Market?
The electric car EEC M1 sector is experiencing significant growth driven by global trends towards sustainability, urbanization, and technological advancements. A key driver is the increasing demand for eco-friendly transportation options as cities strive to reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality. This is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where urban centers are expanding rapidly and congestion is a growing concern.
Emerging sourcing trends include the adoption of advanced battery technologies, such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePo4), which provide longer ranges and quicker charging times. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies in vehicles—such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and connected features—offers enhanced safety and user experiences. B2B buyers are also focusing on the total cost of ownership (TCO), driving interest in models that promise lower maintenance costs and higher efficiency.
Market dynamics are shifting towards localized production and sourcing to reduce lead times and shipping costs, especially in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations are pushing for more localized supply chains. For buyers in Africa and South America, partnerships with local manufacturers can facilitate market entry and foster community support, ensuring that products meet regional needs and preferences.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your B2B Strategy?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a core component of business strategy in the electric vehicle sector. For B2B buyers in the electric car EEC M1 market, understanding the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions is crucial. Vehicles that are manufactured using sustainable materials and processes not only reduce the carbon footprint but also resonate with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Ethical sourcing practices, including ensuring fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of materials, are essential for maintaining brand integrity and consumer trust. B2B buyers should look for suppliers that possess green certifications, such as ISO 14001 or those that adhere to the EU’s environmental regulations. Moreover, investing in electric vehicles that utilize recycled materials or sustainable production methods can enhance corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles and align with global sustainability goals.
As the market evolves, companies that prioritize sustainability in their supply chains will likely gain a competitive edge, attracting a growing segment of environmentally-aware customers and investors.
What Is the Historical Context of the Electric Car EEC M1 Sector?
The electric car EEC M1 sector has evolved significantly over the last two decades. Initially, electric vehicles (EVs) were viewed as niche products with limited appeal due to high costs and range anxiety. However, advancements in battery technology, government incentives, and increased awareness of climate change have transformed the landscape.
The introduction of the European Economic Community (EEC) regulations played a pivotal role in standardizing electric vehicles, making them more accessible to a broader market. As manufacturers began to innovate, models like the EEC L6e and EEC L7e emerged, emphasizing compact design and urban utility. This evolution has positioned electric cars as viable alternatives for daily commuting, particularly in urban environments where space and sustainability are paramount.
In summary, the electric car EEC M1 sector is not only growing but also adapting to the dynamic needs of global markets. By understanding these trends and prioritizing sustainability, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with both market demands and ethical practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car eec m1
-
How do I determine the right electric car EEC M1 model for my business needs?
To select the appropriate electric car EEC M1 for your business, consider factors such as your target market, intended use (e.g., short-distance commuting or urban logistics), and passenger capacity requirements. Evaluate the vehicle’s specifications, including battery capacity, range, and speed, to ensure they align with your operational needs. Additionally, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and charging infrastructure, to make a well-informed decision that maximizes your investment. -
What is the best way to vet suppliers for electric cars EEC M1?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their market reputation and customer reviews. Request product certifications, such as EEC homologation, to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards. Conduct direct interviews with potential suppliers to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities, if feasible, to assess production capabilities and quality control processes firsthand. -
What customization options are available for electric car EEC M1 models?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options for electric car EEC M1 models, including color choices, interior features, and additional technology integrations (e.g., multimedia systems or enhanced safety features). Discuss specific requirements with your supplier to explore possibilities such as branding, seating configurations, and battery specifications. Customization can help tailor the vehicle to your market’s unique needs, enhancing its appeal and functionality. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cars EEC M1?
Minimum order quantities for electric cars EEC M1 can vary significantly between suppliers. Generally, orders may start as low as 2-4 units for smaller manufacturers, while larger suppliers may have higher MOQs ranging from 10 to 20 units or more. It’s essential to clarify MOQ details during your initial discussions to determine if a supplier aligns with your business scale and financial capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric cars EEC M1?
Payment terms typically include options like T/T (telegraphic transfer) or L/C (letter of credit), depending on your supplier’s policies. T/T usually requires a deposit upfront, with the balance due before shipment. L/C offers more security, particularly for larger orders, as it guarantees payment upon meeting specified conditions. Always negotiate terms that are favorable to your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s credibility and reliability. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for electric cars EEC M1?
Implement a robust QA process by requesting detailed product specifications, testing reports, and compliance certifications from your supplier. Establish clear quality standards and conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify that the vehicles meet your expectations. Building a close relationship with your supplier can facilitate ongoing communication and collaboration to address any quality concerns proactively. -
What logistics considerations should I account for when importing electric cars EEC M1?
When importing electric cars EEC M1, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and local transportation infrastructure. Evaluate the total landed cost, including freight, insurance, and import duties, to avoid unexpected expenses. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the import process, ensuring timely delivery while navigating potential challenges such as customs clearance. -
What are the after-sales support options for electric cars EEC M1?
After-sales support is crucial for maintaining the operational efficiency of electric cars EEC M1. Inquire about warranty terms, spare parts availability, and service agreements when negotiating with suppliers. Many manufacturers provide training for maintenance staff and access to technical support to assist with any issues that arise post-purchase. Ensuring robust after-sales support can significantly enhance your investment’s longevity and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Electric Car Eec M1 Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Universeecar – EEC M1 Electric Car
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Universeecar electric car EEC M1 is a high-quality electric car product featuring luxury equipment and a lithium battery. It is categorized under affordable electric car choices and is designed as an eco-friendly urban vehicle.
2. Bossgoo – D2S Electric Vehicle
Domain: bossgoo.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: {“Model No”: “D2S”, “Body Type”: “Closed”, “Front Tire”: “145/60 R13”, “Rear Tire”: “155/50 R14”, “EPS”: “Escl Standard”, “Range in Nedc (27kwh)”: “≥250km”, “ABS”: “Optional”, “Cooling/Heating”: “Standard”, “Air-Bag for Driver”: “Optional”, “Hill-Start Assist”: “Optional”, “Wheelbase”: “1765mm”, “Max Speed”: “105km/H”, “Range in Nedc (17kwh)”: “≥150km”, “Max Gradability”: “25%”, “Battery Capacity”…
3. LOJO – LOJO-W300+ Macaron
Domain: lojoev.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: LOJO-W300+ Macaron: Passed EEC certificate in July 2024, successfully passed crash test in China. LOJO-E10 and E20 trucks: Passed EEC certificate in July 2024. LOJO-BB: First and only EV in China to pass all EEC M1 Electric passenger Car tests, including crash test, in May 2010.
4. Eec – M1 Electric Smart Roadster
Domain: china.org.ru
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Eec M1 Electric Smart Roadster Electric Car”, “Type”: “Sedan”, “Model Number”: “EV300-M1”, “Seating Capacity”: “2 Seater”, “Drive Type”: “FWD”, “Steering”: “Right Drive”, “Battery Capacity”: “60Ah / 120Ah”, “Max Range (NEDC)”: “101~200 km”, “Battery Type”: “Lithium”, “Battery Warranty”: “120000 – 150000 km”, “Place of Origin”: “China, Zhejiang”, “Certificates”: “EEC/COC”, “Price …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car eec m1
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business in the Electric Vehicle Market?
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) landscape, particularly for the EEC M1 segment, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical tool for B2B buyers. By aligning procurement strategies with the latest technological advancements and market trends, businesses can secure competitive pricing, ensure product quality, and enhance supply chain reliability. The EEC L6e electric cabin car exemplifies a robust investment opportunity, providing a sustainable solution for urban mobility with its zero-emission profile and efficient design.
As you consider sourcing electric vehicles, focus on suppliers that offer comprehensive support, including flexible payment terms and efficient logistics solutions. This not only mitigates risks but also fosters strong partnerships that can lead to long-term growth.
Looking ahead, the demand for electric vehicles is set to rise globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with manufacturers and explore collaborations that can pave the way for innovative mobility solutions. Embrace the future of transportation by making informed sourcing decisions that align with your business objectives.