Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for triporteur frigorifique
In today’s competitive global marketplace, sourcing an efficient and reliable triporteur frigorifique presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in the fast-evolving sectors of food and pharmaceuticals. With urban logistics becoming increasingly complex, businesses require innovative solutions that not only ensure the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods but also align with sustainability goals. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of triporteur frigorifique, exploring various models, their operational efficiencies, and how they can effectively address the last-mile delivery challenges faced in bustling urban environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will cover essential aspects such as the types of triporteurs available, their specific applications, and the vital considerations for vetting suppliers. Additionally, insights into cost structures and operational efficiencies will empower international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their logistical capabilities while reducing their carbon footprint. By leveraging the information in this guide, businesses can confidently navigate the global market for triporteur frigorifique, ensuring that they choose solutions that meet their unique needs and drive sustainable growth.
Understanding triporteur frigorifique Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Cold Triporteur | Continuous refrigeration using electric compressors | Food delivery, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Precise temperature control, versatile. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires charging. |
| Passive Cold Triporteur | Utilizes pre-chilled elements like eutectic plates | Short-distance deliveries, catering | Pros: Lower cost, no energy consumption. Cons: Limited temperature control, shorter delivery range. |
| Isothermal Triporteur | Maintains temperature without active cooling, insulated design | Transport of temperature-sensitive goods | Pros: Effective for non-perishable items, cost-efficient. Cons: Not suitable for all temperature-sensitive products. |
| Customizable Triporteur | Tailored designs for specific industry needs | Niche markets (e.g., floral, bakery) | Pros: Meets unique requirements, enhances brand identity. Cons: Potentially longer lead times, higher costs. |
| Multi-Temperature Triporteur | Equipped with multiple compartments for varying temperature zones | Diverse product deliveries | Pros: Versatile for different goods, efficient. Cons: More complex design, higher maintenance needs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Active Cold Triporteurs?
Active cold triporteurs utilize electric compressors to provide continuous refrigeration, making them ideal for transporting temperature-sensitive goods like food and pharmaceuticals. They offer precise temperature control, ensuring compliance with health regulations. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the need for regular charging, as these factors can impact operational costs. Ideal for businesses focused on quality and reliability in delivery.
How Do Passive Cold Triporteurs Operate?
Passive cold triporteurs rely on pre-chilled elements, such as eutectic plates, to maintain low temperatures during transport. They are particularly suitable for short-distance deliveries where energy consumption is a concern. While they are cost-effective and simpler to operate, buyers should be aware of their limitations regarding temperature control and the duration of effectiveness. This option is ideal for catering businesses or markets with less stringent temperature requirements.
What Makes Isothermal Triporteurs a Smart Choice?
Isothermal triporteurs are designed to keep items at a stable temperature without active cooling. Their insulated compartments are perfect for transporting non-perishable items or those that can tolerate slight temperature variations. Buyers benefit from lower operational costs, but they should consider that these triporteurs may not be suitable for all temperature-sensitive goods, particularly those requiring strict temperature management.
Why Consider Customizable Triporteurs?
Customizable triporteurs offer tailored solutions for specific industry needs, allowing businesses to enhance their brand identity through unique designs. They are particularly beneficial in niche markets such as floral arrangements or artisanal baked goods. However, potential buyers should note that customization can lead to longer lead times and increased costs, making it essential to evaluate the return on investment.
What Are the Advantages of Multi-Temperature Triporteurs?
Multi-temperature triporteurs feature multiple compartments, enabling the transport of different products requiring various temperature settings. This versatility is advantageous for businesses that deliver a range of goods, maximizing operational efficiency. However, the complexity of design may lead to higher maintenance needs and costs, making it crucial for buyers to assess their specific logistical requirements before investing.
Key Industrial Applications of triporteur frigorifique
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of triporteur frigorifique | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Urban delivery of fresh produce and perishable goods | Ensures product freshness, reduces spoilage, and improves delivery efficiency | Temperature control capabilities, load capacity, and battery life |
| Pharmaceuticals | Distribution of temperature-sensitive medications | Maintains critical temperature ranges, ensuring product efficacy | Compliance with health regulations, insulation quality, and monitoring systems |
| Catering & Events | On-site delivery of chilled meals and beverages | Enhances service quality and customer satisfaction | Size and maneuverability in urban settings, cooling duration, and payload capacity |
| E-commerce | Last-mile delivery of frozen or chilled products | Reduces delivery times and expands delivery capabilities | Compatibility with urban regulations, energy efficiency, and ease of use |
| Agriculture | Transport of dairy and meat products from farms to markets | Minimizes waste and ensures compliance with food safety standards | Robust construction, refrigeration technology, and operational costs |
How Is the triporteur frigorifique Used in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, triporteur frigorifique is utilized for the urban delivery of fresh produce and perishable goods. These vehicles maintain optimal temperature control, ensuring that products like fruits, vegetables, and dairy arrive fresh and safe. This application is crucial for businesses looking to minimize spoilage and enhance delivery efficiency. International buyers should prioritize sourcing triporteurs with reliable refrigeration systems and adequate load capacities to meet their delivery demands.
What Role Does the triporteur frigorifique Play in Pharmaceuticals?
In the pharmaceutical industry, triporteur frigorifique is essential for the distribution of temperature-sensitive medications. These triporteurs help maintain strict temperature ranges, which is critical for ensuring the efficacy of vaccines and other sensitive drugs. Buyers in this sector must consider compliance with health regulations, insulation quality, and advanced monitoring systems to ensure that products remain within required temperature limits during transit.
How Can Catering and Events Benefit from triporteur frigorifique?
Catering companies and event organizers use triporteur frigorifique for on-site delivery of chilled meals and beverages. This application enhances service quality, allowing caterers to serve fresh food directly to events without compromising quality. Sourcing considerations include the triporteur’s size and maneuverability in urban settings, as well as its cooling duration to ensure food safety and customer satisfaction.
How Does E-commerce Leverage the triporteur frigorifique for Last-Mile Delivery?
E-commerce businesses leverage triporteur frigorifique for last-mile delivery of frozen or chilled products. This innovative solution allows them to reduce delivery times while expanding their service capabilities in urban areas. When sourcing these vehicles, companies should consider compatibility with local urban regulations, energy efficiency, and user-friendliness to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences.
What Are the Advantages of Using triporteur frigorifique in Agriculture?
In agriculture, triporteur frigorifique is used to transport dairy and meat products from farms to markets. This application minimizes waste and ensures compliance with food safety standards, which is increasingly important in today’s market. Buyers should focus on robust construction, effective refrigeration technology, and operational costs when selecting triporteurs to ensure a reliable and efficient transport solution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘triporteur frigorifique’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Maintaining Optimal Temperature During Delivery
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of maintaining the required temperature for perishable goods during the last-mile delivery. This is especially crucial in urban environments where traffic congestion and varying weather conditions can lead to temperature fluctuations, risking spoilage and loss of product quality. Food distributors and pharmaceutical companies must ensure that products remain at the optimal temperature throughout the delivery process, but they may struggle with inadequate refrigeration systems in traditional vehicles or ineffective insulation in triporteurs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider investing in triporteurs frigorifiques equipped with advanced active cooling systems. These systems utilize electric compressors and refrigerants to maintain consistent temperatures, allowing precise control from pick-up to delivery. When sourcing a triporteur, look for models that are certified for temperature-sensitive transport, such as those meeting ATP (Agreement on the International Carriage of Perishable Foodstuffs) standards. Implementing a regular maintenance schedule for the refrigeration unit can also help ensure reliability. Additionally, integrating temperature monitoring technology that provides real-time data can help in maintaining optimal conditions and quickly addressing any deviations during transit.
Scenario 2: Navigating Urban Delivery Challenges
The Problem: Urban logistics pose significant challenges for businesses delivering temperature-sensitive goods. Limited access to certain areas, heavy traffic, and strict regulations regarding vehicle emissions can hinder timely deliveries. B2B buyers may find that traditional delivery vehicles are not suitable for the narrow streets and congestion often found in city centers, leading to delays and increased operational costs.
The Solution: Triporteurs frigorifiques offer a solution tailored for urban environments. Their compact size and electric propulsion allow for easy navigation through congested streets and access to areas where larger vehicles cannot go. When selecting a triporteur, buyers should prioritize models that are designed for urban delivery, such as those with a low noise level (certified PIEK) to comply with nighttime delivery regulations. Collaborating with local authorities can provide insights on permissible delivery times and areas, ensuring compliance with urban logistics regulations. Additionally, employing route optimization software can help streamline delivery paths, reducing both time and fuel costs, ultimately improving overall efficiency.
Scenario 3: Understanding Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
The Problem: Businesses involved in the transportation of food and pharmaceuticals must navigate a complex landscape of regulations regarding temperature control, hygiene, and environmental impact. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, product recalls, and damage to reputation. B2B buyers may be overwhelmed by the myriad of certifications and standards their triporteurs must meet to ensure they are legally compliant and safe for use.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance risks, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research into local and international regulations that pertain to the transportation of their specific goods. When sourcing triporteurs frigorifiques, look for models that come with relevant certifications, such as ATP for food transport and CE marking for safety. Vendors should provide documentation of these certifications along with details on the materials and construction of the triporteur to ensure they meet hygiene standards. Additionally, establishing a routine for staff training on compliance and safety protocols can reinforce best practices in handling and transporting sensitive goods. Regular audits of the vehicles and processes can also help identify potential compliance issues before they become problematic.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for triporteur frigorifique
What Are the Key Materials Used in Triporteur Frigorifique Construction?
When selecting materials for triporteurs frigorifiques, several factors must be considered, including thermal insulation, structural integrity, and environmental impact. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these refrigerated cargo bikes: aluminum, polypropylene, polyurethane foam, and stainless steel.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Triporteur Frigorifique Design?
Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant metal, making it an ideal choice for the frame and components of triporteurs frigorifiques. Its key properties include a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal conductivity, which is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures within the refrigerated compartment.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, resistant to rust, and relatively easy to fabricate, which simplifies manufacturing processes. Additionally, its lightweight nature enhances the overall efficiency of the triporteur, especially in urban environments where maneuverability is crucial.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than other materials like steel or plastic. Moreover, while aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can be prone to dents and scratches, potentially affecting its aesthetic appeal over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s thermal properties allow for efficient heat exchange, making it suitable for both active and passive cooling systems. However, buyers should consider local climatic conditions that may affect the longevity of aluminum components.
Why Choose Polypropylene for Triporteur Frigorifique?
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight characteristics. It is commonly used for the construction of insulated boxes and storage compartments in triporteurs frigorifiques.
Pros: Polypropylene is cost-effective and offers good insulation properties, helping to maintain the required temperature for sensitive goods. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals makes it suitable for transporting food and pharmaceuticals.
Cons: While it is durable, polypropylene can become brittle at low temperatures, which may limit its effectiveness in extremely cold environments. Additionally, it may not have the same structural integrity as metals, potentially affecting the overall strength of the triporteur.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is compatible with various media, making it a versatile choice for different types of cargo. International buyers should ensure that the material meets local food safety regulations.
How Does Polyurethane Foam Enhance Insulation in Triporteurs?
Polyurethane foam is widely recognized for its excellent thermal insulation properties, making it a critical material for the insulation of refrigerated compartments in triporteurs frigorifiques.
Pros: This material provides superior insulation, significantly reducing thermal transfer and energy consumption. It is also lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for a custom fit within the triporteur’s design.
Cons: The primary limitation of polyurethane foam is its vulnerability to UV radiation, which can degrade its performance over time if not properly coated. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other insulation materials.
Impact on Application: The effectiveness of polyurethane foam in maintaining temperature makes it ideal for transporting perishable goods. Buyers should verify that the foam complies with international standards for insulation materials.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Triporteur Frigorifique?
Stainless steel is often used for the structural components and exterior finishes of triporteurs frigorifiques due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
Pros: Stainless steel is extremely durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, ensuring a long lifespan even in harsh conditions. Its aesthetic appeal can also enhance the product’s marketability.
Cons: The main downside is its weight, which can affect the overall efficiency and maneuverability of the triporteur. Additionally, stainless steel can be more expensive than other materials, impacting overall production costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, making it suitable for transporting a wide range of products. Buyers should consider the weight implications when selecting materials for their specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Triporteur Frigorifique
| Material | Typical Use Case for triporteur frigorifique | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frame and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, prone to dents | Medium |
| Polypropylene | Insulated boxes and storage compartments | Cost-effective and moisture-resistant | Brittle at low temperatures | Low |
| Polyurethane Foam | Insulation for refrigerated compartments | Superior thermal insulation | Vulnerable to UV degradation | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Structural components and exterior finishes | Extremely durable and rust-resistant | Heavy and higher cost | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials commonly used in triporteurs frigorifiques, offering B2B buyers valuable insights for making informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can significantly impact the performance and suitability of triporteurs for various applications across different international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for triporteur frigorifique
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Triporteur Frigorifique?
The manufacturing of triporteurs frigorifiques involves several critical stages that ensure the product meets both functionality and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about their suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing a triporteur frigorifique is the preparation of materials. Common materials include lightweight metals such as aluminum for the frame, which offers durability without adding excessive weight. Additionally, high-quality insulation materials, such as polyurethane foam, are used to maintain temperature integrity within the refrigerated compartment. The components for the refrigeration system, including compressors and refrigerants, must also be selected based on efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations.
2. Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Molded?
In the forming stage, materials are shaped into the required components using various techniques such as welding, bending, and molding. For example, the aluminum frame is often extruded and then welded to create a sturdy yet lightweight structure. The insulated panels for the refrigeration unit are typically molded to fit precisely within the frame, ensuring minimal thermal loss. This stage is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and thermal efficiency of the triporteur.
3. Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
The assembly process involves combining all manufactured components into a complete unit. This typically occurs on an assembly line where workers or automated systems fit the frame, attach the refrigeration system, and install the cargo compartment. Quality checks are integrated at this stage to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. This often includes checking electrical connections and ensuring that the refrigeration unit operates effectively.
4. Finishing: What Are the Final Touches Applied to the Product?
Finishing touches are essential for both aesthetic appeal and functionality. This may include powder coating the frame to prevent corrosion and enhance visual appeal. The installation of branding elements, safety features, and user interface components, such as temperature control displays, also occurs during this stage. After finishing, the triporteur undergoes final inspections to ensure that it meets the required specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Manufacturing Triporteurs Frigorifiques?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process of triporteurs frigorifiques, ensuring that each unit meets international standards and customer expectations.
1. What International Standards Govern Quality Control?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on maintaining consistent quality across processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like the CE mark in Europe and ATP certification for temperature-controlled transport are critical. These certifications ensure that the products meet safety and environmental regulations, which is particularly important for food and pharmaceutical transport.
2. What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checkpoints assess the quality of components and assemblies. This may include testing the insulation effectiveness and verifying the operation of the refrigeration system.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, finished triporteurs undergo a comprehensive inspection to ensure they meet all specifications, including functionality tests of the refrigeration system and structural integrity assessments.
3. What Common Testing Methods Are Used?
Testing methods for triporteurs frigorifiques may include:
-
Thermal Testing: To ensure that the refrigeration system maintains the required temperature range under various conditions.
-
Load Testing: Assessing the structural integrity and weight capacity of the triporteur.
-
Noise Level Testing: Particularly important for models designed for urban deliveries during nighttime, ensuring compliance with noise regulations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial to ensure product reliability and compliance with local regulations.
1. What Auditing Practices Should Be Considered?
Buyers should consider conducting supplier audits, which can be either announced or unannounced. These audits provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. It is advisable to engage third-party auditors who can provide an unbiased assessment.
2. What Documentation Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request detailed documentation of the manufacturing process, including quality assurance reports, testing certifications, and compliance with international standards. This documentation can provide assurance that the supplier adheres to the necessary quality control measures.
3. How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality control processes of suppliers. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, providing additional assurance that the triporteurs frigorifiques meet the required specifications before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital for successful transactions.
1. How Do Regional Regulations Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific regulations regarding the transport of temperature-sensitive goods. For example, the European Union has stringent regulations for food safety that require compliance with ATP standards. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with these regulations and can provide the necessary certifications.
2. What Should Buyers Know About Compliance Costs?
Buyers must also consider the costs associated with compliance and certification. While some suppliers may offer competitive pricing, the long-term costs of non-compliance can be significant. It is crucial to evaluate suppliers not just on price but on their ability to meet quality and regulatory standards.
3. How Can Buyers Build Long-term Relationships with Suppliers?
Building strong relationships with suppliers based on trust and transparency can lead to better quality assurance and service. Regular communication about quality expectations and performance can help both parties align on goals and ensure mutual satisfaction.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for triporteurs frigorifiques, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their supply chain efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘triporteur frigorifique’
To aid B2B buyers in the procurement of triporteur frigorifique, this guide offers a clear, step-by-step checklist. This resource is designed to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers are well-informed and equipped to make strategic decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning your search, establish the specific technical requirements for your triporteur frigorifique. Consider factors such as load capacity, refrigeration method (active or passive), and the dimensions of the unit. Clearly defining these specifications will help you narrow down options and ensure that the selected model meets your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Investigate the relevant local and international regulations that govern the transportation of temperature-sensitive goods in your target markets. Ensure that any triporteur you consider complies with certifications such as ATP (for food transport) and PIEK (for noise regulations). Compliance not only ensures legal operation but also enhances the credibility of your logistics operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Request company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in the industry. Investigate their production capabilities and after-sales support, as these factors are crucial for long-term partnerships.
Step 4: Assess Product Features and Technology
Examine the specific features of the triporteurs you are considering. Key aspects include:
– Refrigeration Technology: Look for details on the cooling systems used (e.g., active cooling with electric compressors vs. passive cooling with eutectic plates).
– Construction Materials: Ensure the materials are durable and suitable for your operational environment.
– Usability Features: Consider ergonomic designs for ease of loading and unloading, as well as maintenance requirements.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline all costs involved. Look for transparency in pricing, including initial purchase costs, maintenance fees, and potential energy consumption. This comparison will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and financial strategy.
Step 6: Test the Product Before Purchase
If possible, arrange for a demonstration or trial period with the triporteurs you are considering. This will allow you to evaluate the unit’s performance in real operational conditions. Pay attention to the efficiency of the refrigeration system, ease of maneuverability, and overall build quality during the test.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once you have selected a supplier, enter negotiations to finalize the terms of the purchase. Discuss warranty options, service agreements, and delivery timelines. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings and set the foundation for a successful partnership.
This checklist equips B2B buyers with essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process for triporteur frigorifique, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and compliance in the transportation of sensitive goods.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for triporteur frigorifique Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Triporteur Frigorifique?
Understanding the cost structure of triporteurs frigorifiques is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of high-quality materials such as aluminum for the frame, insulated panels, and refrigeration components significantly impacts the overall price. Advanced materials like recyclable plastics and special coatings for durability may incur additional costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and can influence the final pricing. Skilled labor is essential for assembling the refrigeration units and ensuring quality standards are met.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, which can be a negotiating point.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom designs can be substantial. Buyers should consider whether the investment in custom tooling will yield long-term savings through reduced per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each unit meets specific performance and safety standards can add to the manufacturing costs. Certifications such as ATP and PIEK may require additional testing and documentation, impacting the overall price.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary based on the shipping method, distance, and Incoterms. Buyers should factor in potential tariffs or duties when sourcing internationally.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the final price. This varies based on market conditions and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Triporteur Frigorifique Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of triporteurs frigorifiques:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate better terms based on volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as enhanced refrigeration technology or specific design elements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet higher quality standards or specific certifications typically come at a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better after-sales support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Choosing the right Incoterms can minimize logistics costs and risks associated with international shipping.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Triporteurs Frigorifiques?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing triporteurs frigorifiques, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially if you are placing a large order. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential savings from energy-efficient models. This holistic view can justify a higher upfront cost.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Different regions may have varying market conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic factors that can influence pricing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct market research to anticipate these changes.
-
Be Cautious with Indicative Prices: Always ask for detailed quotes and avoid relying solely on indicative prices, which can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above.
By understanding these components, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints while ensuring they meet their operational needs effectively.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing triporteur frigorifique With Other Solutions
In today’s competitive market, businesses are increasingly seeking efficient and sustainable solutions for transporting temperature-sensitive goods. The triporteur frigorifique, or refrigerated tricycle, stands out as a versatile option for urban deliveries. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate other alternatives available in the market to make an informed decision. This analysis compares the triporteur frigorifique with two alternative solutions: refrigerated vans and traditional bicycles equipped with thermal boxes.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Triporteur Frigorifique | Refrigerated Vans | Traditional Bicycles with Thermal Boxes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for last-mile delivery; maintains optimal temperatures through active/passive refrigeration. | High capacity and range; suitable for larger deliveries but may struggle in congested areas. | Limited capacity; best for small deliveries but may not maintain temperature effectively. |
| Cost | Lower upfront and operational costs compared to vans; minimal maintenance. | Higher initial purchase and operational costs; requires fuel or electricity. | Low initial investment; however, may incur additional costs for thermal insulation and ice packs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick to deploy in urban settings; requires minimal infrastructure. | Requires designated parking and may face regulatory challenges in urban areas. | Very easy to implement; no special licenses needed, but limited by load capacity. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to fewer mechanical parts; electric systems are generally reliable. | Higher maintenance costs due to engine and complex systems. | Minimal maintenance; mainly requires care for the bicycle and thermal box. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for food delivery, pharmaceuticals, and small businesses in urban environments. | Best for larger deliveries and longer distances; suitable for supermarkets and large restaurants. | Suitable for small local deliveries; great for niche markets or low-volume businesses. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Refrigerated Vans
Refrigerated vans offer a robust solution for transporting large quantities of temperature-sensitive goods over longer distances. They have the capacity to maintain controlled temperatures effectively, making them suitable for restaurants, supermarkets, and distribution centers. However, they come with higher operational costs, including fuel, maintenance, and insurance. Additionally, they may struggle in congested urban environments where parking is limited and traffic congestion can delay deliveries.
Traditional Bicycles with Thermal Boxes
Traditional bicycles equipped with thermal boxes provide a cost-effective solution for small-scale deliveries. They are easy to implement, require minimal regulatory compliance, and incur lower operational costs. However, their effectiveness in maintaining temperature may be limited compared to triporteurs and refrigerated vans, as they rely heavily on ice packs or gel packs, which can be less reliable. They are best suited for local businesses or niche markets that require small deliveries.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate delivery solution for temperature-sensitive goods, B2B buyers should consider factors such as the volume of goods transported, delivery distance, and operational costs. The triporteur frigorifique excels in urban settings for businesses needing efficient last-mile delivery without the high costs associated with refrigerated vans. Conversely, businesses requiring large-scale transport might find refrigerated vans more suitable, while those focused on local deliveries could benefit from traditional bicycles with thermal boxes. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific logistical needs and operational constraints of each business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for triporteur frigorifique
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Triporteur Frigorifique?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a triporteur frigorifique is crucial for B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact operational efficiency, compliance, and overall performance in urban logistics. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Refrigeration System Type
– Active Cold vs. Passive Cold: Active cold systems utilize electrical components to generate continuous refrigeration, making them ideal for products requiring strict temperature control. Passive cold systems rely on pre-chilled elements, like eutectic plates, to maintain temperature without active energy consumption. B2B buyers should consider the nature of the goods being transported when selecting between these systems, as this impacts reliability and energy costs. -
Payload Capacity
– This specification refers to the maximum weight that the triporteur can carry, typically divided into front and rear load capacities (e.g., 60 kg rear and 25 kg front). Understanding payload capacity is vital for businesses to ensure compliance with local regulations and to optimize delivery routes without exceeding weight limits, which can lead to fines or vehicle damage. -
Insulation Material
– High-performance insulation materials, such as polyurethane or advanced composite panels, are crucial for minimizing thermal loss. Effective insulation maintains the desired temperature longer, reducing the energy needed for active refrigeration systems. For B2B buyers, the choice of insulation can influence operational costs and product integrity during transit. -
Autonomy and Temperature Range
– Autonomy refers to how long the refrigeration system can maintain the required temperature without external power, often specified in hours (e.g., 8 hours). The temperature range (e.g., 0°C to 10°C) indicates the specific thermal conditions maintained during transport. These factors are essential for businesses transporting perishable goods, as they determine the feasibility of longer delivery routes and the types of products that can be handled. -
Compliance Certifications
– Certifications like ATP (Agreement on the International Carriage of Perishable Foodstuffs) and PIEK (for noise regulations) are vital for ensuring that the triporteur meets industry standards. These certifications not only enhance marketability but also ensure legal compliance, making them essential considerations for international buyers.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Triporteur Frigorifique Market?
Familiarity with trade terminology is critical for effective negotiation and procurement in the B2B market. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of triporteurs, OEMs may provide specialized refrigeration units or components essential for maintaining compliance and performance standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term specifies the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory effectively and negotiate better terms, especially when entering new markets or scaling operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. For triporteur frigorifique procurement, issuing an RFQ allows businesses to compare options and negotiate favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to manage logistics costs, risk, and responsibilities during transport. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the context of triporteurs, shorter lead times can be crucial for businesses needing quick turnaround for perishable goods, making this a significant factor in supplier selection. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– TCO encompasses the total cost of acquiring, operating, and maintaining equipment over its lifetime. For triporteurs, understanding TCO helps businesses make informed decisions that consider not just the purchase price but also operational efficiencies, maintenance, and potential resale value.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right triporteur frigorifique that meets their logistical and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the triporteur frigorifique Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends for Triporteur Frigorifique?
The triporteur frigorifique sector is experiencing significant growth driven by urbanization, the demand for sustainable logistics solutions, and the increasing need for efficient last-mile delivery systems. As cities expand and traffic congestion worsens, traditional delivery vehicles struggle to navigate urban environments. Triporteurs offer an agile and environmentally friendly alternative, allowing for efficient transport of temperature-sensitive goods, such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the landscape, with advancements in electric propulsion and innovative refrigeration systems enhancing performance and energy efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus is shifting towards sourcing triporteurs that not only meet regulatory standards but also provide flexible solutions for diverse logistical challenges. The integration of smart technologies, such as temperature monitoring via mobile applications, is becoming a critical factor in procurement decisions, ensuring compliance and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Additionally, the market is witnessing a rise in demand for models that comply with stringent environmental regulations, such as those that limit greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, suppliers who prioritize sustainability and technological innovation in their offerings will likely capture a more significant share of the market.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Triporteur Frigorifique Sector?
Sustainability is a cornerstone of modern B2B sourcing strategies, particularly in the triporteur frigorifique sector. The environmental impact of logistics operations is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to seek solutions that minimize their carbon footprint. Triporteurs, especially electric models, present a compelling case for reducing emissions compared to traditional vehicles.
Ethical sourcing practices are increasingly important as businesses aim to align with global sustainability goals. Buyers are now considering suppliers that adhere to eco-friendly manufacturing processes and use recyclable materials in their triporteur designs. Certifications such as CE and ATP not only assure compliance with safety standards but also enhance the credibility of suppliers committed to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of green certifications and materials is becoming a pivotal factor for buyers. Suppliers that leverage innovative technologies, such as those using ammonia-based refrigeration systems or passive cold solutions, can appeal to eco-conscious buyers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical supply chains, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the expectations of increasingly environmentally aware consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Triporteur Frigorifique in B2B Logistics?
The triporteur frigorifique has evolved significantly since its inception, originating from traditional cargo tricycles used for local deliveries. Initially popularized in urban centers, these vehicles have adapted to meet the growing demands of modern logistics, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. The introduction of electric propulsion and advanced refrigeration technologies has transformed the triporteur into a versatile tool for last-mile delivery, capable of efficiently transporting temperature-sensitive products while adhering to stringent health and safety regulations.
As urbanization continues to rise, the triporteur frigorifique is positioned to play an increasingly vital role in sustainable logistics, offering a solution that balances efficiency with environmental responsibility. This historical context underscores the importance of innovation in meeting the evolving needs of B2B buyers across diverse markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of triporteur frigorifique
-
1. What are the key benefits of using a triporteur frigorifique for urban deliveries?
Triporteurs frigorifiques offer significant advantages for urban logistics, particularly in crowded areas. They are environmentally friendly, reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional delivery vehicles. Their electric propulsion allows for quieter operations, making them ideal for nighttime deliveries. Additionally, they maintain strict temperature control for sensitive goods, ensuring product quality and compliance with health regulations. Cost savings on fuel and parking further enhance their attractiveness for businesses looking to streamline their delivery processes. -
2. How do I choose the right triporteur frigorifique model for my business needs?
Selecting the right triporteur frigorifique hinges on your specific delivery requirements. Consider factors such as load capacity, refrigeration type (active or passive), and the type of goods you’ll transport (e.g., food or pharmaceuticals). Evaluate the model’s size and maneuverability for urban environments. Look for certifications like ATP and PIEK, which ensure compliance with safety and noise regulations. It’s also wise to consult with suppliers about customization options to tailor the triporteur to your unique operational needs. -
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for triporteur frigorifique?
Minimum order quantities for triporteur frigorifique can vary significantly by supplier and model. Generally, manufacturers may have an MOQ ranging from 1 to 10 units for standard models, while custom designs may require larger orders. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and see if they can accommodate smaller orders, especially if you’re a new business testing the market. -
4. How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing triporteur frigorifique?
To ensure quality assurance, start by vetting potential suppliers thoroughly. Check for relevant certifications like ISO or CE that indicate compliance with international quality standards. Request samples or conduct factory visits to assess manufacturing processes and materials used. Additionally, inquire about warranty and after-sales support, as these factors are critical in maintaining the operational efficiency of your triporteur. Establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier will also help address any quality concerns proactively. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing triporteur frigorifique?
Payment terms for triporteur frigorifique can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payments, deposits (often 30-50%), and the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for bulk orders. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring that you receive a secure and reliable transaction process. -
6. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing triporteur frigorifique?
When importing triporteur frigorifique, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Engage a freight forwarder experienced in handling specialized cargo to navigate customs regulations effectively. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including import permits and health certifications, is in order. Additionally, factor in local transportation arrangements upon arrival, as well as any potential tariffs or taxes that may apply to your order. -
7. How can I customize my triporteur frigorifique for specific market needs?
Customization options for triporteur frigorifique can include modifications to size, insulation materials, and refrigeration systems to meet local market requirements. Some suppliers offer bespoke designs tailored to your branding and operational needs, such as color schemes, logos, and compartment configurations. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to determine feasibility and costs associated with customization. -
8. What are the maintenance requirements for triporteur frigorifique?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of triporteur frigorifique. This includes routine checks on the refrigeration system, battery health, and electrical components to ensure optimal performance. Inspect tires, brakes, and structural integrity frequently, especially if used in demanding urban environments. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and scheduling periodic professional servicing will help prevent breakdowns and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Triporteur Frigorifique Manufacturers & Suppliers List
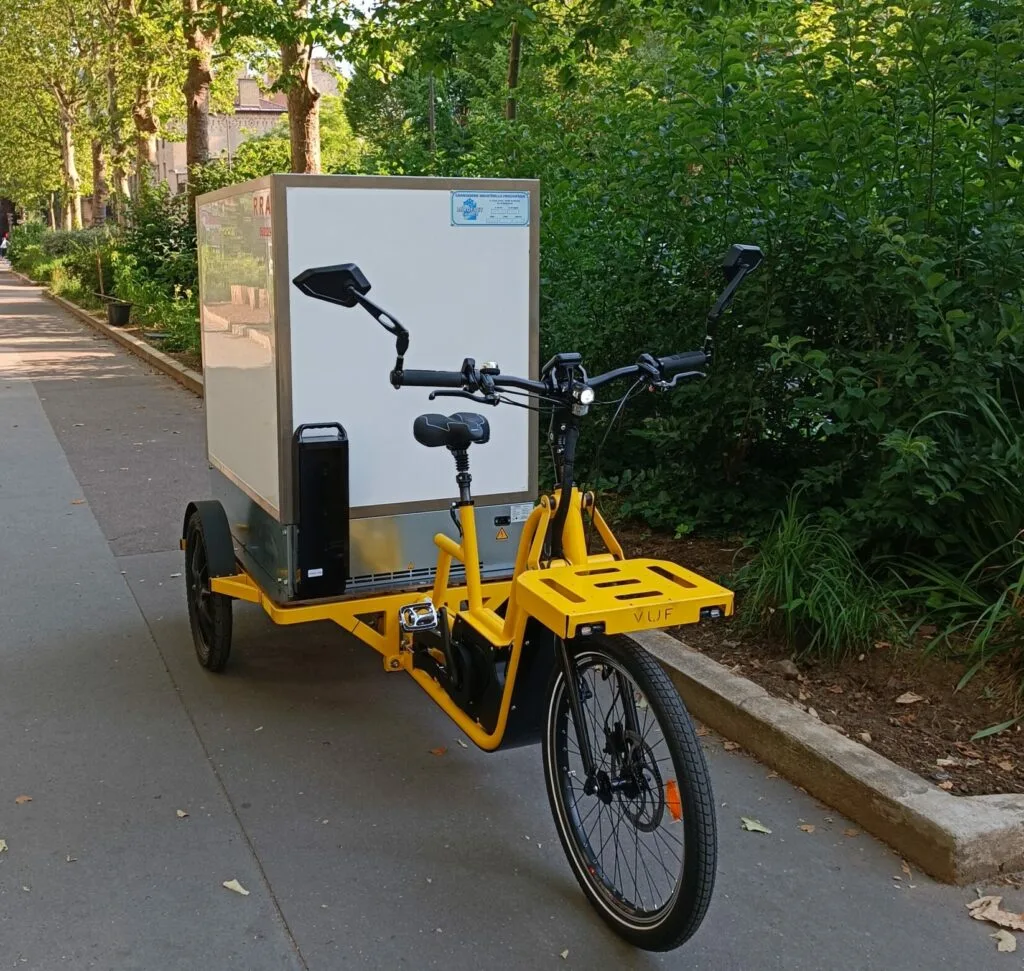
1. Vufbikes – Triporteur Isotherme Keep Cold
Domain: vufbikes.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Triporteurs frigorifiques et isothermes certifiés PIEK et ATP pour le transport de denrées alimentaires et produits pharmaceutiques. Modèles : 1. Triporteur isotherme Keep Cold : – Charge utile : 150 kg arrière, 25 kg avant – Poids du caisson : 44 kg – Matériaux : aluminium et polypropylène alvéolaire – Ouverture : latérale et arrière – Serrures : mécanique ou RFID – 100% compatible centres-villes…
2. Yokler – Triporteur Frigorifique U Cool
Domain: yokler.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Triporteur frigorifique Yokler U Cool, électrique, isotherme, conçu pour la livraison de produits frais. Contenance de 400L grâce à 4 boxs isothermes de 95L, permettant de conserver les produits au frais pendant plus de 4 heures. Destiné aux professionnels de la livraison et restaurateurs. Modèles disponibles : Yokler XXL (2m3), Yokler XL (1,5m3), Yokler U (1m3), Yokler J (pick-up), Yokler T (vélo…
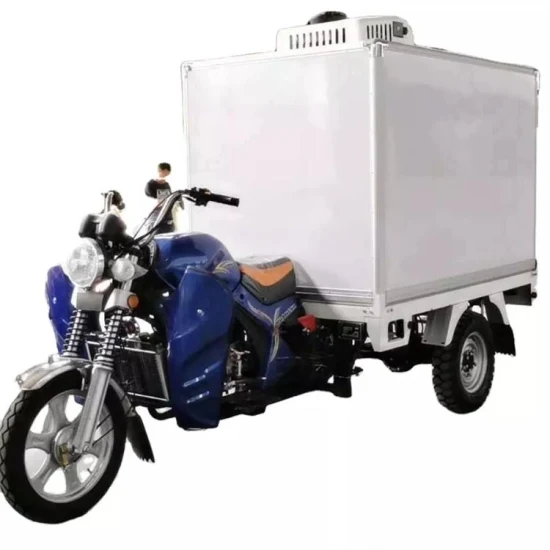
3. FALCON – Triporteur Frigorifique 2020
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Triporteur frigorifique FALCON STRONG, modèle 2020, garantie 1 an.
4. Quai des Glaces – Triporteur Réfrigéré Autonome
Domain: quaidesglaces69.fr
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Quai des Glaces – Triporteur réfrigéré autonome – Lyon. Utilisé pour la vente ambulante, disponible en location ou à l’achat. Design adapté pour circulation en milieu urbain, alternative aux voitures et camions de livraison. Coût inférieur aux food trucks. Gamme de triporteurs professionnels : triporteurs de livraison, triporteurs à glaces, triporteurs à crêpes. Garantie d’un an pièces et main d’œ…
5. Clovis – Vélo Cargo Frigorifique
Domain: clovis.biz
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Vélo cargo avec caisse frigorifique, conçu pour le transport de marchandises périssables, capacité de charge élevée, idéal pour les livraisons en milieu urbain, respectueux de l’environnement, options de personnalisation disponibles.
6. Petit Forestier – K-Ryole Remorque Frigorifique Électrique
Domain: petitforestier.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: K-Ryole: Nouvelle remorque frigorifique électrique. Caractéristiques principales: 1. Efficacité: Évite les embouteillages et les contraintes de stationnement. 2. Écologie: Solution 100% électrique, durable et responsable. 3. Simplicité: S’adapte à tous les vélos. 4. Capacité: Près de 1 m3 de froid positif, volume utile de 900 L, charge utile de 130 kg, PTAC de 425 kg. 5. Autonomie: 6 à 8 heures. 6…
7. Les Triporteurs Français – Livraison Urbaine Écologique
Domain: lestriporteursfrancais.fr
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Les Triporteurs Français est une entreprise spécialisée dans la livraison urbaine depuis 14 ans, utilisant des triporteurs, des véhicules électriques et GNV. Voici les détails des produits et services proposés :
1. **Triporteur** : Encombrement réduit, charge utile de 250 kg, adapté pour tout type de colis.
2. **Triporteur plateau** : Conçu pour le transport de palettes, charge utile jusqu’à 250 …
8. Techni-Contact – Triporteur Réfrigéré
Domain: techni-contact.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Triporteur réfrigéré à température positive
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for triporteur frigorifique
In the rapidly evolving landscape of urban logistics, the triporteur frigorifique stands out as a game-changer for businesses focused on efficient and sustainable delivery solutions. This innovative vehicle not only addresses the challenges of transporting temperature-sensitive goods but also aligns with stringent environmental regulations and urban mobility needs. By leveraging electric propulsion and advanced refrigeration technologies, companies can significantly reduce their operational costs while enhancing service reliability.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of triporteurs frigorifiques offers a dual advantage: meeting the rising demand for fresh and safe products while positioning your business as a leader in sustainability. As cities become increasingly congested and regulations tighten, investing in these eco-friendly delivery solutions will be crucial for maintaining competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the adoption of triporteurs frigorifiques is set to grow, driven by technological advancements and increasing consumer expectations for quality and sustainability. Now is the time for businesses to explore these opportunities, ensuring they are well-equipped to meet future demands in urban logistics. Embrace the future of delivery—invest in triporteurs frigorifiques today.