Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car coc
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles, sourcing the right Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for electric cars presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This essential document not only verifies that a vehicle meets regulatory safety and environmental standards but also facilitates seamless transactions across borders. Navigating the complexities of different markets, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, demands a comprehensive understanding of the CoC’s implications.
This guide serves as an invaluable resource for B2B buyers, covering various aspects of the electric car CoC, including its types, applications, and the crucial role it plays in supplier vetting. We delve into cost considerations, documentation requirements, and best practices for ensuring compliance with local regulations. By equipping businesses with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide empowers them to mitigate risks associated with vehicle imports and registrations.
Understanding the intricacies of the CoC not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters confidence in the vehicles being procured. As we explore the nuances of the global market for electric car CoCs, buyers will gain insights that are vital for maintaining compliance and ensuring successful market entry. This knowledge is essential for establishing trustworthy relationships with suppliers and navigating the regulatory landscape effectively, ultimately leading to successful business outcomes.
Understanding electric car coc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEC COC (European Economic Community) | Certifies compliance with EU standards, includes detailed specifications. | Import/export of electric vehicles within EU countries. | Pros: Facilitates registration in EU, enhances resale value. Cons: May require additional documentation for non-EU markets. |
| COC for Low-Speed Vehicles | Tailored for vehicles with limited speed capabilities; includes safety features like seat belts and lights. | Sales of electric golf carts, utility vehicles, and urban transport. | Pros: Cost-effective for urban applications. Cons: Limited speed may restrict use in some regions. |
| COC for Commercial Vehicles | Focuses on electric vans and trucks, emphasizing load capacity and operational efficiency. | Logistics, delivery services, and fleet operations. | Pros: Supports sustainable business practices. Cons: Higher initial investment compared to traditional vehicles. |
| Manufacturer’s COC | Issued by the vehicle manufacturer, confirming compliance with local regulations. | Vehicle sales, leasing, and fleet management. | Pros: Simplifies the import process, builds trust. Cons: Variability in quality across manufacturers. |
| COC for Modified Vehicles | Certifies vehicles that have undergone modifications to meet specific market needs. | Custom vehicle sales, specialized transport solutions. | Pros: Allows for unique configurations. Cons: Compliance with regulations can be complex and time-consuming. |
What are the key characteristics of EEC COC vehicles for B2B buyers?
The EEC COC is essential for businesses looking to operate within the European market. It ensures that electric vehicles meet stringent EU safety and environmental standards, facilitating smoother import and registration processes. B2B buyers should prioritize this certification when sourcing vehicles for compliance and resale, as it enhances vehicle credibility and marketability.
How do low-speed vehicle COCs cater to specific business needs?
Low-speed vehicle COCs are specifically designed for vehicles that operate under certain speed limits, such as electric golf carts and utility vehicles. These vehicles often come equipped with safety features mandated by regulations, making them ideal for urban environments and recreational areas. Businesses in tourism, urban transport, or facility management should consider these vehicles for their cost-effectiveness and compliance with local laws.
What advantages do commercial vehicle COCs offer to logistics companies?
Commercial vehicle COCs focus on electric vans and trucks, offering certifications that highlight load capacity and operational efficiency. For logistics and delivery services, these vehicles support sustainable practices while meeting urban transport regulations. B2B buyers in this sector should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including potential savings on fuel and maintenance, against the higher initial purchase price.
Why is a manufacturer’s COC crucial for fleet management?
A manufacturer’s COC provides assurance that a vehicle complies with local regulations, which is vital for fleet management operations. This certification can simplify the import process and foster trust between buyers and manufacturers. B2B buyers should consider the manufacturer’s reputation and the COC’s authenticity when purchasing vehicles to ensure long-term operational success.
What should buyers consider when dealing with COCs for modified vehicles?
COCs for modified vehicles are important for businesses that require specialized configurations, such as unique transport solutions. These vehicles can cater to niche markets but come with the complexity of ensuring compliance with local regulations. B2B buyers should assess the modification’s impact on vehicle performance and compliance requirements, as well as the potential for increased operational flexibility.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car coc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Car COC | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Compliance verification for electric vehicle production | Ensures vehicles meet safety and environmental standards | Understanding local regulations and COC requirements |
| Fleet Management | Registration of electric vehicle fleets | Streamlines fleet operations and legal compliance | Volume purchasing agreements and warranty considerations |
| Public Transportation | Integration of electric vehicles in public transit systems | Reduces carbon footprint and enhances public service | Local government collaboration and compliance with COC |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Use of electric vehicles for eco-friendly transport services | Attracts environmentally-conscious customers | Customization options and local market adaptability |
| Export and Import | Facilitating international trade of electric vehicles | Simplifies cross-border transactions and compliance | Knowledge of international COC standards and logistics |
How is Electric Car COC Applied in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the Certificate of Conformity (COC) is crucial for verifying that electric vehicles meet specific safety and environmental standards before they reach the market. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local compliance requirements is essential. The COC document assures manufacturers and regulators that vehicles are built to the necessary specifications, reducing the risk of costly recalls or legal issues. Buyers must ensure that the COC aligns with both local regulations and international standards.
What Role Does Electric Car COC Play in Fleet Management?
For companies managing fleets of electric vehicles, the COC simplifies the registration process, ensuring that all vehicles are compliant with local laws. This is particularly beneficial for businesses operating in multiple countries, such as those in Europe or the Middle East, where regulations can vary significantly. The COC facilitates smoother operations by providing proof of compliance, allowing fleet managers to focus on optimizing their logistics rather than navigating bureaucratic hurdles. Key considerations include establishing volume purchasing agreements to leverage cost efficiencies.
How is Electric Car COC Integrated into Public Transportation Systems?
Electric vehicles are increasingly being integrated into public transportation systems to promote sustainability. The COC is essential in this context, as it ensures that the vehicles used comply with local safety regulations and environmental standards. For B2B buyers in public sector roles, the COC can enhance the credibility of electric vehicle bids and proposals. Collaboration with local governments is crucial to ensure that the specifications outlined in the COC meet community needs while adhering to regulatory requirements.
Why is Electric Car COC Important for Tourism and Hospitality?
In the tourism and hospitality sector, electric vehicles are becoming popular for providing eco-friendly transport services. The COC plays a vital role in assuring customers that the vehicles they use are compliant with safety and environmental standards. This can be a significant selling point for businesses looking to attract environmentally-conscious travelers. B2B buyers must consider customization options to meet specific market demands while ensuring compliance with local regulations through the COC.
How Does Electric Car COC Facilitate Export and Import?
When it comes to the export and import of electric vehicles, the COC is a key document that simplifies cross-border transactions. It provides proof of compliance with both the exporting and importing countries’ regulations, thus mitigating risks associated with customs and legal challenges. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, understanding the nuances of international COC standards is critical. This knowledge not only aids in smooth transactions but also enhances the overall efficiency of supply chain operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car coc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The Problem: As international B2B buyers of electric vehicles, navigating regulatory compliance can be a daunting task. Each country has its own set of regulations regarding vehicle safety and environmental standards, and failing to meet these can lead to significant delays or financial penalties. For instance, buyers in the Middle East may find that the specific certifications required differ from those in Europe, leading to confusion and frustration when trying to register vehicles.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to establish a thorough understanding of the regulatory landscape in each target market. Begin by researching the specific requirements for the Certificate of Conformity (CoC) in each country where you plan to sell or register electric vehicles. Collaborate with local regulatory bodies or hire compliance consultants who specialize in automotive regulations to ensure you have up-to-date information. Additionally, consider forming partnerships with local manufacturers who are familiar with the certification processes. This will not only simplify the compliance journey but also enhance your credibility in the market.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Document Authenticity and Integrity
The Problem: The authenticity of the Certificate of Conformity is paramount, especially for buyers involved in cross-border transactions. Counterfeit documents can easily undermine trust and lead to legal disputes, lost investments, and damaged reputations. For example, a buyer in South America purchasing vehicles from Europe may encounter fake CoCs, complicating the registration process and jeopardizing their business operations.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of counterfeit documents, implement a robust verification process. Work directly with manufacturers to obtain the CoC and ensure it is issued in accordance with the proper regulatory standards. Utilize digital tools that provide traceability and verification of the CoC, such as blockchain technology, which can securely store and verify document authenticity. Additionally, educate your procurement team on recognizing legitimate CoCs and encourage them to always request documentation directly from trusted sources. This proactive approach will safeguard your investments and uphold your company’s integrity.
Scenario 3: Handling Variability in Vehicle Specifications
The Problem: Variability in vehicle specifications can lead to complications in sourcing electric vehicles that meet specific market demands. For instance, a buyer in Africa may require electric cars that adhere to local climate conditions and driving habits, while also needing compliance with European standards for resale. This mismatch can result in costly modifications or unsellable inventory.
The Solution: To address this issue, conduct comprehensive market research to understand the specific needs and preferences of your target markets. Develop a checklist of essential specifications that align with both local requirements and international standards. When sourcing vehicles, communicate these specifications clearly with manufacturers and suppliers to ensure that the vehicles are built to meet the necessary criteria. Moreover, consider adopting a flexible sourcing strategy that allows for customization of vehicle features based on local demand. This way, you can ensure that your offerings are not only compliant but also appealing to your target audience, ultimately enhancing your market position.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car coc
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Car COC?
When selecting materials for electric car Certificates of Conformity (COC), understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, steel, composites, and plastics, each with unique characteristics that influence their suitability for electric vehicle applications.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Electric Car Applications?
Aluminum is renowned for its lightweight properties and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in electric vehicle manufacturing. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F (315°C), which is suitable for various automotive applications.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances vehicle efficiency and performance. However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including battery components, is beneficial for electric vehicles. Its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, particularly in humid or coastal environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider local availability and cost implications, as aluminum may be sourced from different suppliers. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, is essential for ensuring quality.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel remains a staple in automotive manufacturing due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. With a temperature rating generally around 1,500°F (815°C), it can withstand extreme conditions.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of steel is its strength, which provides structural integrity to electric vehicles. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which may negatively impact energy efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless treated, which can lead to increased maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for components that require high strength, such as the chassis and frame. Its compatibility with welding processes makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should be aware of the varying steel grades and their respective standards. Compliance with local regulations is crucial for ensuring that steel components meet safety and environmental requirements.
How Do Composites Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Composites, often made from a combination of materials like carbon fiber and resin, are increasingly used in electric vehicles due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) depending on the resin used.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their ability to reduce vehicle weight significantly, enhancing efficiency. However, they can be costly and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful for body panels and interior components, where weight reduction is critical. Their resistance to corrosion and fatigue makes them suitable for various environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers should consider the availability of composite materials and the expertise required for their manufacturing. Compliance with international standards such as JIS is crucial for ensuring product quality.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastics in Electric Vehicles?
Plastics are widely used in electric vehicles for various applications, including interior components and battery casings. They typically have a temperature rating of around 200°F (93°C), making them suitable for many automotive environments.
Pros and Cons: The lightweight nature of plastics contributes to overall vehicle efficiency, and they are often less expensive than metals. However, plastics may not provide the same structural integrity as metals and can be less resistant to high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with a range of media and can be molded into complex shapes, making them ideal for intricate designs. Their resistance to corrosion is also a significant advantage in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider the availability of high-quality plastics that meet international standards. Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations is essential for market acceptance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Car COC
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Car COC | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, battery casings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis, structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composites | Body panels, interior components | Significant weight reduction | High cost, specialized processes | High |
| Plastics | Interior components, battery casings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower structural integrity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car coc
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Cars with a Certificate of Conformity (COC)?
The manufacturing of electric cars that require a Certificate of Conformity (COC) involves several critical stages that ensure compliance with international safety and environmental standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is sourcing high-quality materials. This includes metals, plastics, and composites that meet regulatory standards. Suppliers must provide documentation proving that their materials comply with international standards, such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). B2B buyers should ensure that materials are traceable and certified to minimize risks associated with non-compliance. -
Forming
This stage involves shaping raw materials into components. Techniques like stamping, extrusion, and injection molding are commonly employed. Precision in this phase is crucial, as it impacts the vehicle’s overall performance and safety. Manufacturers often use Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines for enhanced accuracy. Buyers should inquire about the technology used and the precision levels achieved during this process. -
Assembly
During the assembly phase, various components are integrated to form the complete vehicle. This includes the installation of the electric powertrain, battery systems, and electronic controls. Automated assembly lines equipped with robotics are increasingly utilized to improve efficiency and reduce human error. B2B buyers should verify whether the manufacturer employs lean manufacturing techniques, which can significantly reduce waste and enhance quality. -
Finishing
The final stage involves surface treatment, painting, and final inspections. This not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also protects components from corrosion and wear. Manufacturers often utilize eco-friendly paints and coatings to comply with environmental regulations. Buyers should look for certifications indicating that manufacturers are following best practices in finishing processes.
How Does Quality Control (QC) Ensure Compliance in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality Control (QC) is vital in ensuring that electric cars meet both international and industry-specific standards. The QC process typically includes several checkpoints and testing methods.
-
International and Industry-Specific Standards
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) is essential. Additionally, electric vehicles must adhere to specific regulations like CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers have the necessary certifications to validate their quality assurance processes. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the manufacturing process. It ensures that only materials that meet specified standards are used.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC checks are performed at various stages to catch defects early. This includes visual inspections and functional tests of components as they are assembled.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the vehicle is fully assembled, FQC involves comprehensive tests, including performance evaluations, safety checks, and emissions testing to ensure compliance with the COC. -
Common Testing Methods
Electric vehicles undergo various tests, including:
– Durability Testing: Simulates extended use to ensure components can withstand wear and tear.
– Crash Testing: Validates the vehicle’s safety features and compliance with safety regulations.
– Environmental Testing: Assesses the vehicle’s performance under different environmental conditions, ensuring reliability in various climates.
What Steps Can B2B Buyers Take to Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying the QC processes of suppliers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing and QC processes. Buyers can request to see the documentation of internal audits and corrective actions taken for any non-conformities. -
Review QC Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that outline their testing methodologies, results, and compliance with relevant standards. These reports should be transparent and available for review at any time. -
Engage Third-Party Inspections
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing and QC processes. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and the authenticity of certifications. -
Assess Supplier Certifications
B2B buyers should scrutinize the certifications held by their suppliers. Certifications should be current and from recognized bodies. This ensures that the supplier adheres to industry standards and practices.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality assurance. Here are some considerations:
-
Understanding Local Regulations
Different countries have varying regulations regarding vehicle compliance. Buyers must be aware of the specific requirements in their target markets, including emissions standards and safety regulations. -
Logistics and Supply Chain Factors
The complexity of international logistics can impact the quality of components. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that materials are sourced and shipped under conditions that maintain quality. -
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards
Cultural perceptions of quality can vary significantly between regions. B2B buyers should establish clear communication channels to ensure that all parties understand the expected quality levels and compliance requirements. -
Long-Term Partnerships
Building long-term relationships with suppliers can enhance quality assurance. Consistent communication and collaboration can lead to improvements in manufacturing processes and QC measures over time.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electric cars requiring a Certificate of Conformity are intricate and multi-faceted. B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure compliance and quality, leveraging audits, certifications, and third-party inspections to mitigate risks and enhance their supply chain’s reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car coc’
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle market, securing a Certificate of Conformity (COC) is crucial for international B2B buyers. This document not only ensures compliance with safety and environmental regulations but also facilitates seamless vehicle registration across different markets. This practical sourcing guide outlines key steps to effectively procure electric car COCs, ensuring your transactions are compliant and efficient.
Step 1: Understand Local Regulations
Before initiating the sourcing process, familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your target market. Each region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may have distinct requirements regarding vehicle safety and emissions standards. Understanding these regulations will help you identify the necessary compliance documentation needed for the COC.
Step 2: Identify Reputable Manufacturers
Select manufacturers with a proven track record in producing electric vehicles that meet international standards. Research their reputation within the industry and check for certifications that affirm their compliance with safety and environmental regulations. Key considerations include:
– ISO Certifications: Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications that indicate adherence to quality management standards.
– Industry Affiliations: Membership in relevant automotive or electric vehicle associations can also signal credibility.
Step 3: Request COC Documentation
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, request a copy of their COC documentation. This document should detail compliance with the relevant safety and environmental standards, including specifications such as the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and model information. Ensure that:
– The COC is issued directly by the manufacturer.
– It covers all necessary technical data required by your local regulatory body.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, verify that the supplier holds valid certifications for the vehicles they produce. This step is critical to ensure that the vehicles will be compliant once imported. Look for:
– EEC or equivalent certifications: These demonstrate compliance with European standards, which are often accepted in various international markets.
– Third-party audit reports: These can provide additional assurance regarding the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards.
Step 5: Cross-check Compliance with Local Authorities
Engage with local regulatory authorities to confirm that the COC provided by the supplier meets all local compliance requirements. This proactive approach can prevent potential legal issues and registration delays. Important actions include:
– Consulting with local vehicle registration agencies: They can provide insights into the specific documentation needed for successful registration.
– Verifying the authenticity of COCs: Local authorities may have methods to validate the COC directly with the manufacturer.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you are satisfied with the supplier’s credentials and documentation, negotiate terms that protect your interests. This includes:
– Delivery timelines: Ensure that the supplier can provide timely delivery of the vehicles along with the necessary COCs.
– After-sales support: Discuss the support available for any compliance issues that may arise post-purchase.
Step 7: Maintain Records and Documentation
After procurement, keep organized records of all COC documents, supplier communications, and compliance confirmations. This documentation will be invaluable for future transactions and regulatory checks. Ensure that:
– All documents are easily accessible for audits or inspections.
– You have a clear log of any correspondence with suppliers regarding compliance.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric car COCs, ensuring compliance and facilitating smooth transactions in the international market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car coc Sourcing
When sourcing electric cars and their corresponding Certificate of Conformity (CoC), understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The following analysis breaks down the key components of cost, price influencers, and actionable tips for effective negotiation and procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Car CoCs?
-
Materials: The costs associated with the materials used in the vehicle production directly impact the overall price of the CoC. This includes components like batteries, electric motors, and body materials. Higher-quality materials often lead to a more expensive CoC, reflecting the vehicle’s compliance with stringent safety and environmental standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality assurance. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, the overall expense may be elevated compared to manufacturers in lower-cost countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these overheads, leading to better pricing for CoCs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for electric vehicle production can be capital-intensive. This cost is often amortized over the production run, impacting pricing for smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure vehicles meet regulatory standards, which adds to the cost. However, investing in quality can reduce long-term risks associated with non-compliance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and transportation logistics are significant, especially for international buyers. These can vary widely based on the Incoterms agreed upon during the purchase.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin within their pricing structure. Understanding the competitive landscape can assist buyers in negotiating favorable terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Car CoCs?
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly influence pricing. Higher volumes usually result in lower per-unit costs, making bulk purchases more economical for B2B buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Vehicles with specific features or customizations may incur additional costs. Buyers should assess whether these features are necessary or if standard options will suffice to optimize spending.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications such as EEC for European markets ensure compliance with local regulations. Vehicles with more certifications may carry higher prices but offer better assurance of quality and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and geographical location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their perceived quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can impact the total cost of ownership. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB, CIF, and DDP to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Negotiation Strategies for International Buyers?
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand standard pricing and available options. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations and helps identify reasonable price ranges.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs that yield better pricing. Suppliers are often more flexible with pricing for larger orders.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying the supplier base can create competition and provide leverage in negotiations, potentially leading to better pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the vehicle, including maintenance, fuel savings, and resale value. A higher upfront cost may be justified if it leads to lower TCO.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Favorable payment terms can enhance cash flow. Consider negotiating for extended payment terms or discounts for early payments.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of cost and pricing for electric car CoCs is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. It is essential to note that prices can vary widely based on market conditions and individual supplier circumstances, so ongoing due diligence is recommended.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car coc With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in the Electric Vehicle Market
As the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) continues to rise globally, understanding the various solutions available for compliance and market entry is crucial for international B2B buyers. The Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for electric cars serves as an essential document that verifies compliance with safety and environmental standards. However, other alternatives exist that can also facilitate the importation and registration of electric vehicles. This section explores these alternatives to help buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison of Electric Car CoC with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car CoC | Importing Vehicles Without CoC | Local Compliance Certificates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Ensures compliance with EU standards, enhancing marketability | May face registration issues in certain countries | Varies by country, may not meet all international standards |
| Cost | Generally low cost for compliance | Potentially high costs due to fines or rework | Costs vary widely based on local regulations |
| Ease of Implementation | Streamlined process for registration in EU markets | Complicated and time-consuming | Can be straightforward but varies greatly by jurisdiction |
| Maintenance | Minimal, mostly documentation management | High, if vehicles need modifications | Varies; some may require regular inspections |
| Best Use Case | Best for exporting/importing to EU countries | Suitable for markets with lax regulations | Ideal for local markets with specific compliance needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Importing Vehicles Without CoC
Importing vehicles without a CoC can be a tempting option for buyers looking to minimize upfront costs. However, this approach carries significant risks. While it may seem straightforward in regions with less stringent regulations, it often leads to complex registration hurdles and potential fines. Additionally, vehicles may require costly modifications to meet local standards, which can negate any initial savings. This method is best suited for markets where compliance is less rigorously enforced, but it is fraught with uncertainty.
2. Local Compliance Certificates
Local compliance certificates serve as an alternative to the electric car CoC by ensuring that vehicles meet specific regional standards. This can be a viable option for businesses focused on local markets. The process of obtaining these certificates can be straightforward, depending on the local regulations. However, the variability in standards across different countries can lead to complications, especially for companies looking to operate in multiple jurisdictions. While this option allows for flexibility in local markets, it may not provide the same level of assurance as a CoC in terms of international compliance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your B2B Needs
For international B2B buyers, the decision on whether to use an electric car CoC or an alternative solution should be based on several factors, including the target market, regulatory environment, and long-term business strategy. The CoC offers a robust and recognized method for ensuring compliance, particularly within the EU. In contrast, alternatives like importing without a CoC or relying on local compliance certificates might provide short-term flexibility but come with increased risks and potential costs. Assessing the specific needs of your business and understanding the regulatory landscape will guide you to the most effective solution for your electric vehicle transactions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car coc
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Electric Car COCs?
In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs), the Certificate of Conformity (CoC) plays a pivotal role in facilitating international trade and ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards. Understanding the technical specifications outlined in a CoC is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Specifications to Consider in Electric Car COCs
-
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
The VIN is a unique code assigned to each vehicle, serving as its fingerprint. It encapsulates information about the car’s manufacturer, model, and year of production. For B2B transactions, a valid VIN is vital for confirming the vehicle’s identity, ensuring accurate record-keeping, and preventing fraud. -
Motor Power Rating (kW)
This specification indicates the power output of the electric motor, usually measured in kilowatts (kW). Higher power ratings generally translate to better performance and acceleration. For businesses, understanding motor power is essential for aligning vehicle capabilities with customer expectations and regulatory requirements in different markets. -
Maximum Speed
The maximum speed rating indicates how fast the electric vehicle can travel. This figure is crucial for compliance with local traffic regulations, especially in urban environments where low-speed vehicles are common. B2B buyers must consider this aspect to ensure that the vehicles meet local laws and customer preferences. -
Battery Capacity (Ah)
Measured in ampere-hours (Ah), battery capacity defines how much energy the battery can store and directly impacts the vehicle’s range. A higher capacity allows for longer distances between charges, making it essential for fleet operators and rental services. Buyers should assess battery capacity to optimize their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. -
Charging Time
The time required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery is a critical factor for fleet management. Shorter charging times can enhance productivity, particularly in commercial applications. Understanding this metric allows B2B buyers to evaluate the feasibility of integrating electric vehicles into their operations. -
Curb Weight
Curb weight refers to the total weight of the vehicle when it is ready for operation, including all fluids and a full tank of fuel (or fully charged battery). It impacts performance, energy consumption, and regulatory classifications. Buyers should evaluate curb weight to ensure compliance with local transportation regulations and to optimize vehicle performance.
What Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know About Electric Car COCs?
Navigating the electric vehicle market involves understanding specific trade terminology that affects purchasing decisions and compliance processes.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that are then marketed by another company under its own brand. In the electric vehicle industry, OEMs are responsible for producing vehicles that meet specific standards. For B2B buyers, partnering with reputable OEMs ensures product quality and compliance with local regulations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it directly impacts inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategy and budget accordingly. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For electric vehicles, issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms, ensuring they secure the best deal. -
Incoterms
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. They clarify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. B2B buyers must understand Incoterms to mitigate risks associated with international shipping and customs compliance. -
EEC (European Economic Community) Certification
This certification indicates that a vehicle complies with European safety and environmental standards. For international buyers, particularly in Europe, ensuring that vehicles have EEC certification is essential for legal compliance and market acceptance. -
Type Approval
Type approval is the process of certifying that a vehicle meets specific regulatory standards before it can be sold in a particular market. This certification is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that the vehicles they purchase are legally compliant and safe for operation.
By understanding these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing electric vehicles and ensure compliance with international standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car coc Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric Car COC Sector?
The electric car market is experiencing transformative growth, driven by a combination of regulatory pressure, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing compliance and safety standards, making the Certificate of Conformity (COC) a critical document. This certification ensures that electric vehicles (EVs) meet local regulatory requirements, providing assurance to buyers that the vehicles are safe and environmentally friendly.
Emerging trends in the sourcing of electric vehicles include a heightened focus on digital platforms for procurement, facilitating seamless transactions across borders. Buyers are leveraging technology to access real-time data on vehicle specifications, availability, and compliance status, enhancing decision-making processes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in sourcing from manufacturers that prioritize innovation, such as those incorporating advanced battery technologies and smart vehicle systems. As countries in Africa and South America ramp up their EV adoption, the demand for compliant and certified vehicles will only intensify, creating opportunities for suppliers who can navigate these complex dynamics effectively.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Electric Car COC Sector?
Sustainability is not just a buzzword; it is becoming a core principle guiding the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the electric car sector. The environmental impact of sourcing practices is under scrutiny, with stakeholders demanding transparency in supply chains. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can demonstrate adherence to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and processes. Certifications like ISO 14001 and various ‘green’ labels are becoming essential for manufacturers seeking to attract international buyers.
Ethical sourcing is also crucial, particularly for buyers in regions sensitive to labor practices and environmental degradation. Suppliers who can provide documentation and certifications regarding their sourcing methods stand to gain a competitive edge. This focus not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also resonates with consumers who are increasingly making purchase decisions based on a company’s commitment to ethical practices. In this context, the COC becomes more than just a regulatory requirement; it reflects a company’s dedication to sustainability and ethical sourcing, enhancing its brand value and marketability.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Electric Car COC Sector?
The evolution of the electric car COC sector can be traced back to the early 2000s when regulatory frameworks began to emerge in response to growing environmental concerns and the need for standardized vehicle safety. Initially, COCs were predominantly a European requirement, facilitating the movement of vehicles across member states. However, as electric vehicles gained popularity globally, the significance of the COC expanded, influencing markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Today, the COC not only serves as a compliance document but also acts as a trust-building tool in international trade. It assures buyers that vehicles conform to the necessary safety and environmental standards, paving the way for smoother transactions. As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, the COC will play an increasingly critical role in shaping the dynamics of sourcing and compliance, making it an indispensable element for B2B buyers in the electric car sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car coc
-
How do I obtain a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for electric vehicles?
To obtain a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for electric vehicles, you must contact the manufacturer or authorized dealer. The CoC is issued by the vehicle manufacturer and confirms that the vehicle complies with local safety and environmental regulations. Ensure you provide all necessary vehicle details, including the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and model specifications. Keep in mind that different regions may have specific requirements, so familiarize yourself with local regulations to streamline the process. -
What are the key benefits of having a CoC for electric vehicles in international trade?
A CoC is crucial for ensuring that electric vehicles meet the required safety and environmental standards in the importing country. It facilitates smoother customs clearance and registration, reduces the risk of compliance issues, and enhances buyer confidence. For B2B transactions, having a CoC can significantly ease the resale process, as it serves as proof of compliance, making vehicles more attractive to potential buyers in various markets. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of electric vehicles with CoC?
When vetting suppliers, verify their reputation and experience in the industry. Check for proper certifications, including the CoC for the vehicles they offer. Request references or case studies from previous B2B clients. Evaluate their production capacity, quality assurance processes, and responsiveness to inquiries. It’s also wise to assess their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery and support, especially if you are importing from regions with varying regulations. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric vehicles with CoC?
The MOQ for electric vehicles with a Certificate of Conformity can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific vehicle models. Generally, it ranges from 1 to 10 units for smaller manufacturers, while larger manufacturers may require higher MOQs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Additionally, consider how the MOQ aligns with your market demand to avoid overstocking. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric vehicles with CoC?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation and the balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms, such as net 30 or net 60 days after delivery, depending on the business relationship. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., T/T, L/C) and ensure that the terms are documented in a formal agreement to protect both parties. -
How can I customize electric vehicles according to my business needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for electric vehicles, including color, features, and technical specifications. To customize, communicate your requirements clearly during the initial discussions with the supplier. Request information on their customization capabilities and any associated costs or lead times. Customization can enhance the appeal of the vehicles to your target market, so ensure that the modifications align with local regulations and consumer preferences. -
What quality assurance processes should I look for in electric vehicle suppliers?
Quality assurance is vital in ensuring that electric vehicles meet the required standards. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous testing protocols throughout the manufacturing process, including safety, performance, and environmental compliance tests. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies and after-sales support to ensure you have recourse in case of defects or issues. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric vehicles?
When importing electric vehicles, consider shipping methods, transit times, and costs. Ensure that the supplier can handle logistics, including customs clearance and delivery to your location. Familiarize yourself with import regulations, including tariffs and taxes that may apply. It’s also beneficial to work with logistics partners experienced in handling vehicle imports to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with local regulations, particularly in diverse markets like Africa and South America.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Car Coc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EV Remarketing – Certificate of Conformity
Domain: ev-remarketing.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: COC document (Certificate of Conformity) is an official certification issued by vehicle manufacturers, ensuring compliance with European safety and environmental standards. It includes comprehensive technical data about the vehicle such as brand, model, year of manufacture, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The COC document is crucial for vehicle registration, especially for imported vehicl…
2. Fodauto – FWD-QH4 Electric Passenger Vehicle
Domain: fodauto.com
Introduction: {“Model”:”FWD-QH4″,”Driving Type”:”Electric”,”Use For”:”Passenger”,”Body Type”:”Closed”,”Certification”:”EEC”,”Dimension (L*W*H)”:”2605*1295*1610MM”,”Net Weight”:”341kg (Without batteries weight)”,”Maximum Speed”:”25-45km/h”,”Max Load”:”225kg”,”Driving Range”:”60km”,”Motor”:”brushless 60V 2200W”,”Battery”:”60V 58AH”,”Charging Time”:”8-10 hours”,”Tyre”:”125/65-12*4″,”Passenger”:”2-3 (2 doors, 3 sea…
3. Mini Electric Car – FWD-QH4
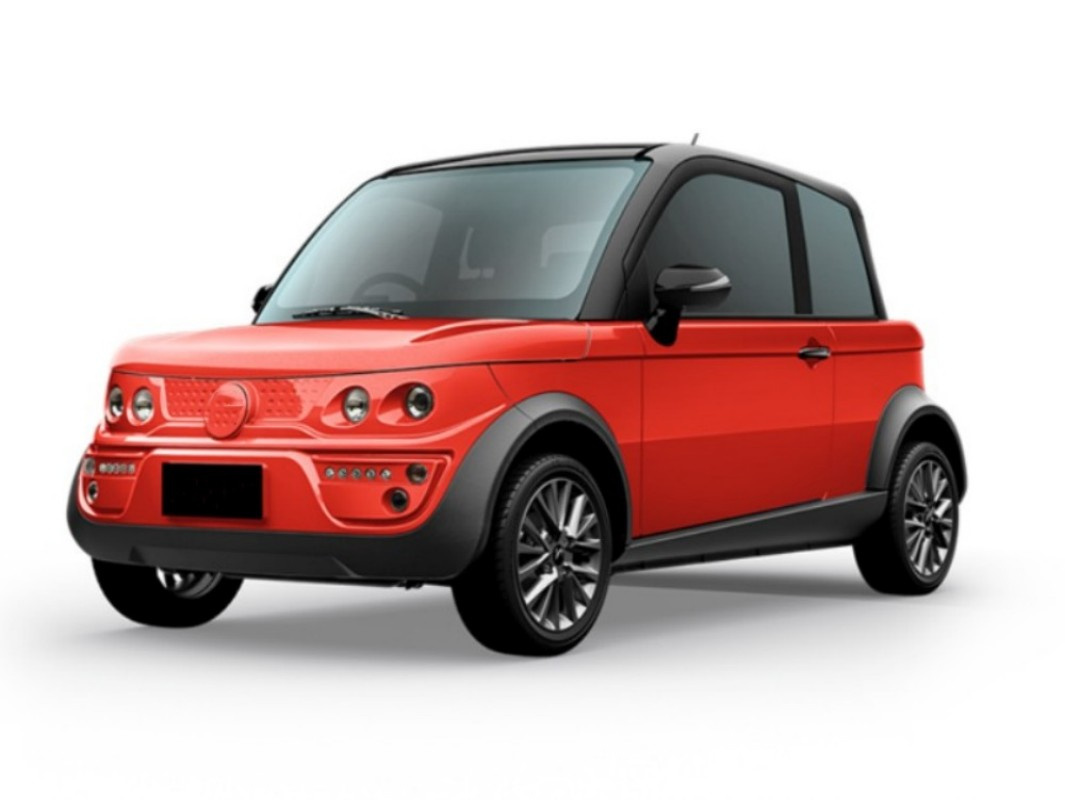
Domain: automaticelectriccar.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
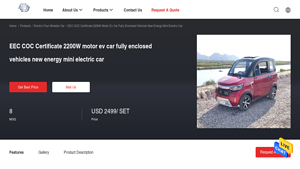
Introduction: {“Product Name”:”Mini Electric Car”,”Model Number”:”FWD-QH4″,”Motor Power”:”2200W brushless motor”,”Certification”:”EEC COC Certificate”,”Place of Origin”:”China”,”Price”:”USD 2499/SET”,”Body Type”:”Fully enclosed”,”Seating Capacity”:”3 seats (1 driver, 2 passengers)”,”Dimensions”:”2605*1295*1610MM”,”Net Weight”:”341kg (without batteries)”,”Maximum Speed”:”25-45 km/h”,”Max Load”:”225kg”,”Driving R…
4. Main New Energy – Electric Vehicles Manufacturer
Domain: main-newenergy.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Electric Car With Coc – Manufacturer from China. Products include a variety of electric vehicles such as electric mini cars, electric trucks (LHD/RHD), high-speed electric trucks, extended-range electric trucks, electric city buses, and electric pickups. The company offers certifications including GB, ISO/TS16949, ISO14001, ISO9001, CE, and more. Main markets include Africa, Americas, Asia, Europe…
5. ITE – CoC in Electric Vehicle Charging System
Domain: ite.edu.sg
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Course Title: CoC in Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging System
Institution: Institute of Technical Education (ITE)
Campus: ITE College East
Industry: Aerospace, Air Transport, Energy & Chemicals, Energy & Power, Engineering Services, Environmental Services
Course Type: Part-time
Certification: SkillsFuture Certificate of Competency (CoC)
Course Duration: 14 hours
Target Audience: Introductory course f…
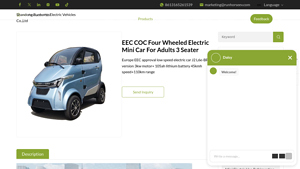
6. Runhorse – EEC COC Four Wheeled Electric Mini Car J2
Domain: runhorseev.com
Introduction: Product Name: EEC COC Four Wheeled Electric Mini Car for Adults 3 Seater
Manufacturer: Runhorse Electric Vehicles
Model: J2
Motor: 3kw
Battery: 105ah lithium battery
Top Speed: 45 km/h
Range: 110 km on a single charge
Seating Capacity: 3 seats
Certification: EEC and COC certified
Design: Mid-steering, compact size for easy maneuverability
Use Case: Ideal for commuting, errands, and urban explorati…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car coc
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, the Certificate of Conformity (COC) has emerged as a pivotal document for international B2B transactions involving electric vehicles. It ensures compliance with stringent safety and environmental standards, facilitating smoother vehicle registration across various jurisdictions. For international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the significance of the COC can streamline the sourcing process, mitigate risks, and enhance market entry strategies.
Strategic sourcing of electric vehicles, coupled with the necessary certifications like the COC, provides a competitive edge in meeting local regulatory requirements while fostering trust with stakeholders. As global demand for electric vehicles continues to surge, the ability to source compliant vehicles efficiently will be crucial for businesses looking to capitalize on this trend.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing partners who not only provide high-quality electric vehicles but also ensure that all necessary certifications are in place. By doing so, companies can position themselves favorably in the marketplace and seize new opportunities as they arise. Embrace the future of mobility by aligning your sourcing strategies with compliance and innovation in the electric vehicle sector.