Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for voiture solaire 120 kmh
In the rapidly evolving landscape of sustainable transportation, sourcing a voiture solaire capable of reaching 120 km/h presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. With an increasing global emphasis on eco-friendly solutions, businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are exploring solar-powered vehicles not just as a futuristic concept, but as a viable alternative to traditional combustion engines. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of solar cars, their applications, and the latest technological advancements that make them a promising investment.
As we navigate through the complexities of the solar vehicle market, this guide will equip you with essential insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and operational efficiency. Understanding the nuances of solar vehicle technology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions, especially in regions with diverse regulatory landscapes and market dynamics, such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By analyzing case studies and expert opinions, we aim to empower B2B buyers to confidently engage in sourcing and implementing solar vehicles in their fleets, ensuring both sustainability and profitability. The journey towards a cleaner, greener future starts with informed choices—let this guide be your roadmap.
Understanding voiture solaire 120 kmh Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Hybrid Vehicles | Combines solar panels with traditional fuel sources; enhanced range and efficiency. | Fleet management, logistics, public transport | Pros: Extended range, lower fuel costs. Cons: Higher initial investment, complexity in maintenance. |
| Fully Solar-Powered Cars | Operates solely on solar energy; requires optimal sunlight. | Eco-friendly transport, research, education | Pros: Zero emissions, low operating costs. Cons: Limited range in low-light conditions, requires significant infrastructure. |
| Solar-Assisted EVs | Integrates solar charging with electric vehicle technology; efficient energy management. | Corporate fleets, car-sharing services | Pros: Reduced electricity costs, environmentally friendly. Cons: Dependency on charging infrastructure, potential range anxiety. |
| Solar Racing Vehicles | High-performance, lightweight designs for competitive environments; optimized aerodynamics. | R&D, engineering education, promotional events | Pros: Cutting-edge technology, brand visibility. Cons: Not suitable for everyday use, high development costs. |
| Modular Solar Vehicles | Customizable designs for specific needs; modular components for easy upgrades. | Urban mobility, specialized applications | Pros: Flexibility in design, scalable solutions. Cons: Potentially higher costs, longer lead times for customization. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Solar Hybrid Vehicles?
Solar hybrid vehicles combine solar panels with traditional fuel sources, allowing them to operate efficiently over longer distances. These vehicles are particularly suitable for fleet management and logistics, where extended range and reduced fuel costs are critical. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and maintenance complexity, but the long-term savings on fuel can be substantial.
How Do Fully Solar-Powered Cars Function in Business Applications?
Fully solar-powered cars operate solely on solar energy, making them an excellent choice for eco-friendly transportation solutions in research and educational settings. They are ideal for organizations focused on sustainability, but buyers must be aware of their dependence on sunlight, which can limit range during cloudy conditions. The lack of emissions and low operating costs are significant advantages for businesses aiming to enhance their environmental credentials.
What Are the Benefits of Solar-Assisted EVs for Corporate Fleets?
Solar-assisted electric vehicles (EVs) utilize solar charging to supplement their electric power, making them attractive for corporate fleets and car-sharing services. These vehicles can significantly reduce electricity costs while promoting a greener image. However, businesses should consider the reliance on existing charging infrastructure and the potential for range anxiety among users.
Why Are Solar Racing Vehicles Valuable for R&D and Branding?
Solar racing vehicles are designed for high performance, with a focus on lightweight construction and optimized aerodynamics. They serve as a testing ground for innovative technologies and can enhance brand visibility during promotional events. While they are not practical for everyday use and come with high development costs, their cutting-edge features can attract attention and drive interest in a company’s commitment to sustainability.
How Do Modular Solar Vehicles Address Diverse Business Needs?
Modular solar vehicles offer customizable designs that can be tailored to specific business needs, making them ideal for urban mobility solutions and specialized applications. Their flexibility allows companies to scale and adapt their vehicles as requirements change. However, potential buyers should consider the higher costs associated with customization and the longer lead times for production.
Key Industrial Applications of voiture solaire 120 kmh
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of voiture solaire 120 kmh | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management for solar-powered delivery vehicles | Reduced fuel costs and carbon emissions | Availability of solar charging infrastructure, vehicle durability, and maintenance support |
| Tourism & Hospitality | Solar-powered shuttle services for resorts | Enhanced guest experience and sustainable branding | Compliance with local regulations, operational efficiency, and vehicle comfort and safety features |
| Agriculture | Solar vehicles for farm transport and logistics | Lower operating costs and increased sustainability | Terrain adaptability, load capacity, and energy efficiency under varying weather conditions |
| Urban Mobility | Public transport solutions in urban areas | Improved air quality and reduced traffic congestion | Integration with existing transport systems, passenger capacity, and operational costs |
| Emergency Services | Rapid response vehicles for disaster relief | Quick deployment and reduced reliance on fossil fuels | Reliability in extreme conditions, maintenance accessibility, and energy storage capabilities |
How Can the Transportation and Logistics Industry Benefit from Voiture Solaire 120 kmh?
In the transportation and logistics sector, the voiture solaire 120 kmh can be utilized as part of a fleet management system for solar-powered delivery vehicles. This application addresses rising fuel costs and regulatory pressures to reduce carbon emissions. Businesses can benefit from significant savings on fuel, while also enhancing their corporate sustainability profile. International buyers should consider the availability of solar charging infrastructure and the vehicle’s durability to ensure operational efficiency.
What Advantages Does the Tourism and Hospitality Sector Gain from Solar-Powered Shuttles?
In the tourism and hospitality industry, solar-powered shuttles can provide transportation services to guests at resorts and attractions. This application not only enhances the guest experience but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable travel options. By using a voiture solaire 120 kmh, resorts can market themselves as eco-friendly destinations, thus attracting environmentally conscious travelers. Buyers need to ensure compliance with local regulations and focus on operational efficiency to maximize this benefit.
How Is the Agriculture Sector Leveraging Voiture Solaire 120 kmh for Transport?
The agriculture sector can implement solar vehicles for farm transport and logistics, significantly reducing operating costs associated with fuel. This application promotes sustainability by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon footprints. Buyers in this sector should focus on the vehicle’s adaptability to various terrains, load capacity for transporting goods, and overall energy efficiency, especially in regions with variable weather conditions.
What Role Can Voiture Solaire 120 kmh Play in Urban Mobility Solutions?
In urban mobility, the voiture solaire 120 kmh can serve as an innovative public transport solution, contributing to improved air quality and reduced traffic congestion. By integrating solar vehicles into existing public transport systems, cities can enhance their sustainability efforts while providing efficient transit options. Key considerations for international buyers include the vehicle’s passenger capacity, compatibility with current transport frameworks, and overall operational costs.
How Can Emergency Services Utilize Solar-Powered Vehicles for Rapid Response?
Emergency services can leverage the capabilities of voiture solaire 120 kmh as rapid response vehicles in disaster relief efforts. These vehicles can be deployed quickly without the need for traditional fuel sources, which is crucial in remote areas. The benefits include reduced operational costs and a lower environmental impact. Buyers must prioritize reliability in extreme conditions, the accessibility of maintenance support, and the vehicle’s energy storage capabilities to ensure effectiveness in critical situations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘voiture solaire 120 kmh’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Uncertain Regulatory Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East face significant challenges due to varying regulations surrounding solar vehicles. With some countries having established frameworks for electric vehicles, others may lack clarity or have restrictive policies. This uncertainty can deter potential investments in solar vehicles, as buyers fear non-compliance with local laws or unexpected changes that could impact their operations.
The Solution: To mitigate regulatory risks, B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research and engage with local automotive associations or legal advisors specializing in transportation regulations. Establishing a compliance checklist tailored to the specific country can ensure that all necessary standards are met. Furthermore, buyers can advocate for the establishment of clearer policies by collaborating with industry groups, thus influencing future regulations that support solar vehicle adoption. Continuous engagement with policymakers can also provide insights into upcoming changes, allowing businesses to adapt proactively.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Technological Limitations in Performance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the performance capabilities of solar vehicles, particularly those that need to operate at high speeds of 120 km/h. Common issues include limitations in energy storage, efficiency under varying weather conditions, and the vehicle’s ability to maintain optimal performance over long distances. These factors can lead to hesitation in adopting solar vehicles, especially for businesses reliant on reliable transportation.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing vehicles equipped with advanced energy management systems and efficient battery technologies. Partnering with manufacturers who specialize in high-performance solar vehicles can provide access to cutting-edge innovations such as adaptive solar panel technologies that adjust to sunlight conditions. Additionally, investing in training for drivers on energy-efficient driving practices can enhance performance and extend the vehicle’s range. Establishing a maintenance protocol that includes regular assessments of the solar panels and battery systems can further ensure sustained operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Addressing High Initial Investment Costs
The Problem: The initial investment required for solar vehicles can be a significant barrier for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets where budgets are tight. The perception of high upfront costs, combined with uncertainty about long-term savings, can lead to reluctance in transitioning to solar vehicles. Buyers may struggle to justify these costs to stakeholders or secure financing.
The Solution: To alleviate concerns about high initial costs, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis that factors in potential savings on fuel, maintenance, and tax incentives associated with solar vehicles. Seeking partnerships with financial institutions that offer green financing options can help spread the upfront costs over time. Additionally, demonstrating the environmental benefits and aligning them with corporate sustainability goals can strengthen the business case for investment. Engaging in pilot programs or trials with manufacturers can also provide valuable data to support larger-scale investments in solar vehicles, showcasing their economic viability and performance in real-world applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for voiture solaire 120 kmh
What Are the Key Materials for Building a Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
In the development of a solar vehicle capable of reaching speeds of 120 km/h, the selection of materials is critical to ensure performance, safety, and sustainability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of solar vehicles, considering their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Performance in Solar Vehicles?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are widely used in the automotive industry for their high strength-to-weight ratio. These materials can withstand significant stress while being lightweight, which is crucial for energy efficiency in solar vehicles. They typically have excellent corrosion resistance and can endure varying temperatures, making them suitable for diverse climates.
Pros: Composites are durable and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for aerodynamic designs. They also reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, enhancing energy efficiency and performance.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, which may deter some manufacturers. Additionally, composites may have lower impact resistance compared to metals, necessitating careful design considerations.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for the chassis and body panels of solar vehicles, where weight reduction is essential for maximizing solar energy efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider the availability of composite materials and local manufacturing capabilities. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties is crucial.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solar Vehicle Construction?
Aluminum is another popular choice for solar vehicle construction due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It is often used in structural components, including the frame and suspension systems.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive compared to other lightweight metals, and its recyclability aligns with sustainability goals. It also offers good thermal conductivity, which can be beneficial for battery management systems.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it may not provide the same level of strength as steel in certain applications. Additionally, welding aluminum can be more challenging, requiring specialized skills and equipment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for both structural and non-structural components, contributing to the overall weight reduction and energy efficiency of the vehicle.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to relevant standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Understanding local market prices and availability is also important, especially in regions with developing infrastructure.
How Does Polycarbonate Improve Solar Vehicle Design?
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic material known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It is often used for windows and protective covers in solar vehicles.
Pros: Polycarbonate is lightweight and can be molded into various shapes, making it versatile for design applications. Its high impact resistance ensures safety in case of accidents.
Cons: Polycarbonate can be prone to scratching and may require coatings for UV protection, which can increase costs. It also has a lower thermal resistance compared to glass.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is ideal for transparent components, allowing sunlight to reach solar panels while providing protection from the elements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for polycarbonate materials that meet international standards such as ASTM D635 for flammability. Understanding local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact is also essential.
Why Is Steel Still Relevant in Solar Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel, particularly high-strength steel, remains a viable option in solar vehicle manufacturing, especially for safety-critical components like the chassis and crash structures.
Pros: Steel is strong, cost-effective, and widely available. It provides excellent durability and can withstand significant loads, making it suitable for safety applications.
Cons: The weight of steel can be a disadvantage in energy-efficient vehicle design, potentially reducing overall performance. Additionally, steel is more prone to corrosion unless treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in areas requiring high strength and safety, such as the vehicle’s frame and support structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that steel products meet relevant standards, such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. Understanding local sourcing options and pricing will also be beneficial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Voiture Solaire 120 km/h
| Material | Typical Use Case for voiture solaire 120 km/h | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite Materials | Body panels, chassis | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex and costly manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Frame, suspension systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Challenging welding | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Windows, protective covers | High impact resistance | Prone to scratching | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis, crash structures | Strong and cost-effective | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials best suited for solar vehicles, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for voiture solaire 120 kmh
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Producing a Voiture Solaire Capable of 120 km/h?
The manufacturing of a voiture solaire (solar car) capable of reaching speeds of 120 km/h involves several critical stages. These stages are designed to ensure that the vehicle is not only efficient in energy consumption but also meets the stringent safety and performance standards expected in the automotive industry.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Voiture Solaire?
-
Material Preparation:
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting appropriate materials that balance weight, strength, and cost. Common materials include lightweight composites, aluminum alloys, and high-strength plastics. These materials are prepared through cutting, shaping, and treating processes to enhance their properties and ensure they meet the specifications for durability and aerodynamics. -
Forming:
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the components of the vehicle. Techniques such as stamping, molding, and extrusion are commonly used. For instance, the body panels may be created using advanced molding techniques to achieve optimal aerodynamic shapes, which are critical for energy efficiency. -
Assembly:
In the assembly stage, the various components are brought together to form the complete vehicle. This includes integrating the solar panels, battery systems, and electric drive components. Precision in this stage is crucial; any misalignment can affect performance and safety. Advanced robotics and automated systems are often employed to enhance accuracy and efficiency. -
Finishing:
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes such as painting, coating, and surface treatment. These processes not only improve the aesthetic appeal of the vehicle but also provide protection against environmental factors. The finishing stage is where quality assurance checks are essential to ensure that the vehicle meets all regulatory standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Voiture Solaire?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of solar cars, ensuring that every aspect of the vehicle meets international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers must be aware of various international standards that govern the automotive manufacturing industry, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Applicable to components and systems used in the vehicle that may involve hydraulic or pneumatic systems.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are essential at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that defects are identified and rectified early. The typical checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first line of defense, where raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps in identifying any deviations from the standards in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the vehicle is shipped, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure that all components function correctly and that the vehicle meets all safety and performance criteria.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance for Voiture Solaire?
To ensure the vehicle’s performance and safety, several testing methods are commonly employed:
- Durability Testing: This involves subjecting the vehicle to various stress conditions to assess its resilience and longevity.
- Performance Testing: The vehicle is tested under different driving conditions to evaluate its speed, acceleration, and energy efficiency.
- Safety Testing: Ensures that the vehicle meets all safety regulations, including crash testing and emergency response evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is paramount. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help verify that the supplier adheres to the necessary quality standards and practices. This includes reviewing their quality management systems and manufacturing processes.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QA processes, results of inspections, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When engaging with international suppliers, particularly from diverse regions, buyers must consider the following nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural approaches to quality and business practices can aid in establishing effective communication and expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding vehicle manufacturing. Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international standards.
- Logistical Considerations: The transportation of solar vehicles and components may be subject to specific regulations that could impact delivery timelines and costs.
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for a voiture solaire capable of 120 km/h involve meticulous planning and execution. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is crucial in making informed decisions when sourcing solar vehicles, ensuring they meet both performance and safety standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘voiture solaire 120 kmh’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring solar vehicles capable of reaching speeds of 120 km/h. With sustainability and innovation at the forefront of the automotive industry, understanding the essential steps in sourcing these vehicles is crucial for making informed decisions. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right solar vehicle for your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s vital to establish your technical requirements. This includes defining performance metrics such as speed, range, and energy efficiency. Knowing your specifications will help in identifying vehicles that meet your operational needs.
– Consider factors like battery capacity and solar panel efficiency.
– Assess the vehicle’s suitability for your intended use, whether for urban commuting or long-distance travel.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest advancements in solar vehicle technology. Understanding current trends can provide insights into what features are becoming standard and what innovations may soon be available.
– Look for vehicles that incorporate cutting-edge technologies, such as improved aerodynamics or advanced battery management systems.
– Pay attention to market reports and industry publications that highlight emerging players and successful case studies.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
A thorough evaluation of potential suppliers is essential to ensure quality and reliability. Assess their track record in producing solar vehicles that meet your specifications.
– Request detailed company profiles, including their experience in solar technology and past projects.
– Seek references from other businesses in your region or industry to gauge customer satisfaction and performance.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the solar vehicle complies with local regulations and safety standards. Different countries and regions may have varying requirements for vehicle safety, emissions, and solar technology.
– Check for certifications that demonstrate adherence to safety standards.
– Understand the import/export regulations that may affect your procurement process.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
After-sales support is a critical aspect of your procurement decision. Evaluate the warranty terms offered by suppliers and the availability of maintenance services.
– Inquire about the supplier’s customer support services and response times for repairs or issues.
– Ensure that the warranty covers essential components like batteries and solar panels for a reasonable duration.
Step 6: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond the initial purchase price, analyze the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with the vehicle. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential savings from fuel alternatives.
– Calculate expected savings from reduced fuel consumption and tax incentives for using solar vehicles.
– Factor in potential resale value and any additional costs related to infrastructure, such as solar charging stations.
Step 7: Pilot Testing Before Full-Scale Purchase
Before committing to a large order, consider conducting a pilot test with a small number of vehicles. This step allows you to evaluate performance in real-world conditions and gather feedback from users.
– Monitor vehicle performance, energy efficiency, and user satisfaction during the pilot phase.
– Use insights gained from the pilot to refine your final procurement decision and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solar vehicles capable of 120 km/h, ensuring a successful integration of sustainable transport solutions into their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for voiture solaire 120 kmh Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
When sourcing a solar vehicle capable of reaching 120 km/h, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The core materials for a solar vehicle consist of lightweight composites for the body, solar panels, batteries, and electrical components. High-quality photovoltaic cells are crucial for efficiency and significantly impact the overall cost. The choice between domestic and imported materials can also affect pricing, especially due to varying tariffs and transportation costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for the design, assembly, and testing of solar vehicles. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the country of origin. For instance, countries with lower labor costs may provide a more economical option but could compromise on quality if not managed properly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, allowing for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for specialized equipment can be substantial. Investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better production efficiency and lower costs in the long term.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards. This is particularly important for solar vehicles, where safety and performance are paramount.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can greatly influence the final price, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties need to be considered.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
Several factors can influence the pricing of solar vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to lower per-unit costs. Manufacturers are generally more willing to negotiate prices with larger orders, making this an attractive option for B2B buyers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customizing vehicles to meet specific requirements can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of tailored features against their budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly affects durability and performance. Additionally, vehicles that meet higher quality and safety certifications may command a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capacity, and reliability can influence pricing. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service agreements.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) used in transactions is critical. They dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs in Sourcing Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms, especially for bulk purchases. Suppliers may offer discounts or favorable payment terms based on order size or commitment to future purchases.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance, fuel savings from solar energy, and the vehicle’s lifespan.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of market trends and pricing fluctuations in the solar vehicle sector. Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best deals.
-
Regional Considerations: Understanding regional market dynamics, such as local incentives for solar energy adoption or government regulations, can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and geographic factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for precise quotations tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing voiture solaire 120 kmh With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Voiture Solaire 120 km/h
As the automotive industry pivots towards sustainable solutions, the voiture solaire (solar car) capable of reaching 120 km/h presents a compelling option. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives that can also meet transportation needs while addressing sustainability, efficiency, and operational costs. Below, we compare the voiture solaire with two viable alternatives: electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs).
| Comparison Aspect | Voiture Solaire 120 km/h | Electric Vehicle (EV) | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 120 km/h | Max speed: 200 km/h | Max speed: 180 km/h |
| Cost | High initial investment | Moderate to high | High initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires solar infrastructure | Relatively easy; requires charging stations | Complex; requires hydrogen infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low (fewer moving parts) | Moderate (battery care) | Moderate to high (fuel cell maintenance) |
| Best Use Case | Long-distance travel in sunny regions | Urban commuting and long trips | Fleet applications and long-distance travel |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Electric Vehicles (EVs)?
Electric vehicles have gained significant traction due to their versatility and growing charging infrastructure. They can typically reach speeds exceeding 200 km/h, making them suitable for both urban commuting and longer distances. However, the initial costs can be high, and the need for regular battery maintenance can add to the operational complexity. EVs are ideal for businesses focused on urban environments where charging stations are abundant, but their reliance on grid electricity raises concerns in regions with unstable power supply.
How Do Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs) Compare?
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer a sustainable alternative by emitting only water vapor. They provide a driving range similar to gasoline vehicles and can be refueled in a matter of minutes. However, like solar cars, FCVs require significant investment in infrastructure, as hydrogen refueling stations are still limited. They are particularly well-suited for fleet applications or long-distance travel where quick refueling is essential. While they offer impressive performance, the complexity and cost of hydrogen production and distribution remain significant barriers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs?
When selecting between a voiture solaire, electric vehicles, or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including operational costs, infrastructure availability, and specific use cases. For businesses operating in sunny regions with the capacity to invest in solar technology, the voiture solaire could be a game-changer. Conversely, if rapid refueling and higher speeds are priorities, electric vehicles or hydrogen fuel cells might be more suitable. Analyzing these aspects will help businesses align their transportation solutions with their sustainability goals and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for voiture solaire 120 kmh
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of a solar vehicle that can reach speeds of 120 km/h is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive and renewable energy sectors. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Solar Panel Efficiency
– Definition: This refers to the percentage of sunlight that can be converted into usable electrical energy by the solar panels installed on the vehicle.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency means more energy generation per square meter, which is vital for maximizing range and performance. Buyers should prioritize vehicles with panels that achieve at least 20% efficiency to ensure optimal functionality. -
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– Definition: The total amount of energy that a vehicle’s battery can store, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
– B2B Importance: A larger battery capacity allows for extended driving ranges and less frequent charging. Buyers need to assess how battery capacity aligns with operational requirements, especially in regions with limited charging infrastructure. -
Weight-to-Power Ratio
– Definition: The ratio of the vehicle’s weight (in kilograms) to its power output (in kilowatts).
– B2B Importance: A lower weight-to-power ratio enhances acceleration and overall performance. This is particularly significant in competitive markets where speed and efficiency are critical for consumer satisfaction. -
Aerodynamic Drag Coefficient (Cd)
– Definition: A dimensionless number that quantifies the drag or resistance of an object in a fluid environment, in this case, air.
– B2B Importance: A lower drag coefficient leads to improved energy efficiency and speed. For solar vehicles, a Cd value below 0.2 is optimal, making it essential for buyers to consider this metric when evaluating performance. -
Charging Time (Fast Charging Capabilities)
– Definition: The duration required to recharge the vehicle’s battery from a depleted state to a full charge using high-voltage charging stations.
– B2B Importance: Shorter charging times enhance the vehicle’s usability and appeal, particularly in commercial applications. Buyers should seek vehicles that can achieve an 80% charge in under 30 minutes.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Related to Voiture Solaire 120 km/h?
Familiarity with industry jargon can help B2B buyers navigate procurement processes more effectively. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers looking to source parts or collaborate on vehicle development, ensuring that they are working with reliable suppliers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Buyers need to be aware of MOQ requirements to plan inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or understocking issues, especially when introducing solar vehicles to new markets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A business process in which a company solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs helps buyers compare prices and terms from various suppliers, enabling informed decision-making in the procurement of solar vehicle components. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers involved in international trade, ensuring clarity on shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities when acquiring solar vehicles or components. -
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
– Definition: A technique to assess environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s life, from cradle to grave.
– Importance: Buyers focusing on sustainability should consider the LCA of solar vehicles to ensure that their procurement aligns with environmental goals and market demands for green technology. -
Smart Grid Integration
– Definition: The incorporation of digital technology into the electricity supply network to optimize the production and distribution of electricity.
– Importance: Understanding this concept is vital for buyers interested in how solar vehicles can interact with energy systems, potentially enhancing energy efficiency and cost savings.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market needs in the rapidly evolving solar vehicle sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the voiture solaire 120 kmh Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the Voiture Solaire 120 km/h Sector?
The voiture solaire 120 km/h sector is witnessing a transformative shift driven by global environmental concerns, advancements in technology, and changing consumer preferences. The push for sustainable transportation solutions has accelerated the development of solar-powered vehicles, with many manufacturers exploring innovative designs and materials. The increasing demand for energy-efficient vehicles is particularly pronounced in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where rising fuel costs and regulatory pressures on emissions are compelling businesses to consider alternative energy sources.
Emerging technologies, such as high-efficiency solar panels and lightweight materials, are enhancing the viability of solar vehicles. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize research and development in these areas. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT for energy management and predictive maintenance, is becoming a key focus for manufacturers. This trend is especially relevant for international buyers who require robust supply chains that can adapt to rapid technological advancements.
Another significant market dynamic is the rise of public-private partnerships and government incentives aimed at promoting solar mobility. Countries in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia are investing in infrastructure to support the adoption of solar vehicles, creating opportunities for B2B collaborations that can leverage local knowledge and resources. As a result, understanding these dynamics is critical for international buyers looking to navigate the evolving landscape of the voiture solaire sector.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Voiture Solaire 120 km/h Sector?
Sustainability is at the core of the voiture solaire 120 km/h sector, influencing both sourcing strategies and product development. As businesses increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their operations, ethical sourcing has become a priority. For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
The importance of ethical supply chains extends to the materials used in manufacturing solar vehicles. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer ‘green’ certifications for their materials, ensuring that they meet environmental standards. This includes sourcing materials like recycled aluminum for vehicle frames or using biodegradable composites in interior designs. Moreover, engaging with suppliers that invest in renewable energy sources for their production processes can further reduce the carbon footprint of solar vehicles.
Investing in sustainable sourcing not only mitigates environmental risks but can also yield long-term cost savings. As regulations around emissions tighten globally, businesses that proactively adopt sustainable practices are likely to benefit from reduced compliance costs and enhanced market competitiveness. Thus, for international B2B buyers, integrating sustainability into sourcing decisions is not merely a trend but a strategic imperative.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of the Voiture Solaire Sector?
The concept of solar-powered vehicles dates back to the 19th century, but it wasn’t until the late 20th century that significant technological advancements made them a feasible option for mainstream use. Early prototypes were primarily experimental, often used in educational settings to demonstrate the potential of solar energy. However, as concerns over fossil fuel reliance and greenhouse gas emissions intensified, the focus shifted towards developing commercially viable solar vehicles.
In the early 2000s, various automotive manufacturers began investing in solar technology, leading to the creation of prototypes capable of achieving speeds of 120 km/h. This period marked a turning point as public interest grew, driven by a combination of environmental awareness and technological innovation. Fast forward to today, the voiture solaire sector is on the cusp of broader adoption, with advancements in battery technology and solar efficiency paving the way for practical applications in everyday transportation.
The evolution of this sector is not just a testament to technological progress but also reflects changing societal values towards sustainability. For B2B buyers, understanding this history provides valuable insights into market maturity and the potential for future innovations within the solar vehicle landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of voiture solaire 120 kmh
-
How can I evaluate the reliability of suppliers for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
To assess supplier reliability, start by researching their market reputation and history. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients, and verify their certifications related to solar technology and automotive standards. Engage in direct communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to share detailed product information. Consider visiting their facilities if possible, or conducting virtual audits to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Establishing a good rapport can also provide insights into their reliability and commitment to customer service. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among manufacturers, often depending on the scale of production and customization requirements. Generally, for niche products like solar cars, MOQs can range from 5 to 50 units. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility on MOQs for initial orders or long-term partnerships. Understanding their production capabilities will help you gauge what quantities they can accommodate and under what terms. -
What customization options are available for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
Customization options for solar vehicles typically include modifications in design, color, interior features, and technological enhancements such as battery capacity or solar panel configurations. Suppliers may also offer bespoke solutions tailored to specific business needs, such as fleet branding or integration of telematics systems. When discussing customization, ensure you communicate your requirements clearly and inquire about the implications on lead times and costs, as bespoke designs may extend production timelines. -
What payment terms are generally offered for international purchases of voiture solaire 120 km/h?
Payment terms for international purchases often depend on the relationship with the supplier and the size of the order. Common arrangements include upfront deposits ranging from 30% to 50% with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect your investment while also accommodating the supplier’s cash flow needs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO standards or other relevant automotive certifications. Consider establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor quality during production. Regular communication and updates throughout the manufacturing process can also help catch potential issues early. Additionally, arranging for third-party inspections before shipment can provide an unbiased assessment of quality. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing voiture solaire 120 km/h?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Determine the most efficient shipping method based on cost and urgency—ocean freight is typically more economical for large orders, while air freight is faster but more expensive. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country, and ensure all necessary documentation is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international trade can streamline this process. -
What are the key market trends influencing the demand for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
The demand for solar vehicles is being driven by increasing environmental awareness and government incentives for sustainable transportation. Innovations in solar technology, such as more efficient photovoltaic panels and lightweight materials, are also enhancing vehicle performance and appeal. Additionally, as urbanization rises, there’s a growing need for eco-friendly transport solutions in densely populated regions. Monitoring these trends can help buyers anticipate market shifts and align their purchasing strategies accordingly. -
How can I assess the total cost of ownership for voiture solaire 120 km/h?
To evaluate the total cost of ownership, consider not only the initial purchase price but also factors such as maintenance costs, energy savings from solar charging, insurance, and potential government incentives. Calculate the expected lifespan of the vehicle and project its resale value. Additionally, factor in operational costs, such as charging infrastructure and any training required for staff to manage solar technology. This comprehensive assessment will provide a clearer picture of the long-term financial implications of your investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Voiture Solaire 120 Kmh Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Éclipse ÉTS – Véhicules Solaires Innovants
Domain: etsmtl.ca
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Éclipse ÉTS, fondé en 1992, conçoit des véhicules solaires capables de parcourir des milliers de kilomètres sur des routes publiques lors de compétitions internationales, avec des parcours allant jusqu’à 3000 KM. L’objectif est de développer des solutions adaptables aux entreprises de demain, en mettant l’accent sur l’efficacité énergétique et la conception durable. L’équipe mécanique se concentre…
2. Solar Team – La Punch Two
Domain: solarteam.be
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
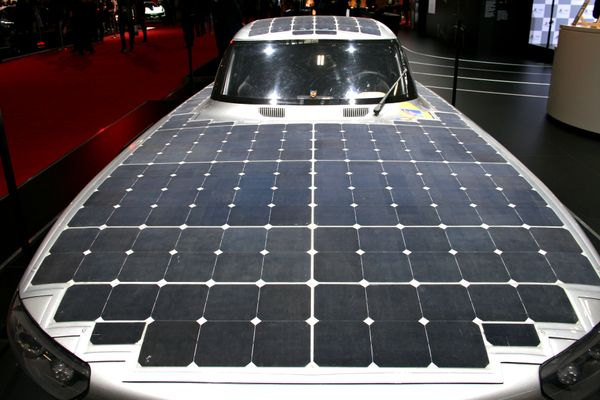
Introduction: La Punch Two est la septième voiture solaire belge, conçue et construite par 21 étudiants ingénieurs de la KU Leuven. Elle est plus légère (130 kilos, soit 30 kilos de moins que son prédécesseur) et plus petite, avec seulement quatre mètres carrés de panneaux solaires, ce qui est moins que la version précédente. Malgré cette réduction, la Punch Two atteint une vitesse de pointe de 120 km/h et roul…
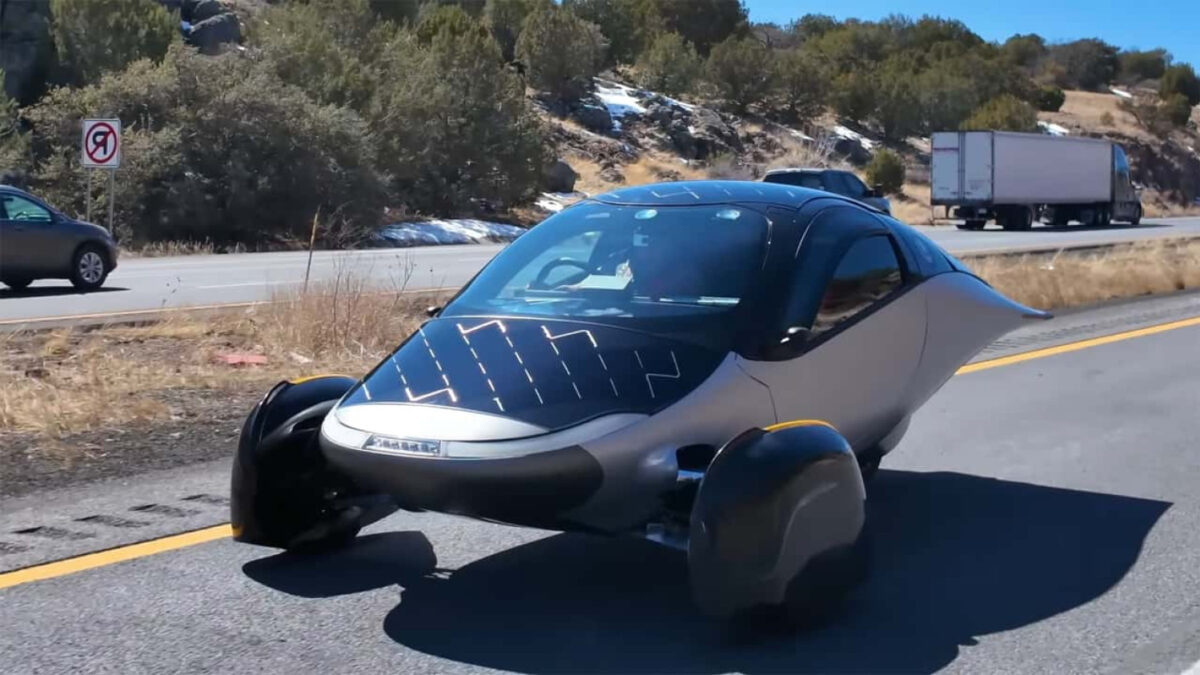
3. Aptera – 100% Electric Solar Vehicle
Domain: futura-sciences.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: – Vehicle Name: Aptera
– Type: 100% electric solar vehicle
– Road Trip: Completed a journey of 480 kilometers on Route 66 using only solar energy
– Design: Unique aerodynamic design with two front wheels and a single rear wheel, featuring a photovoltaic roof
– Daily Range: Approximately 65 kilometers on solar energy
– Solar Power: Capable of generating 520 W in good weather with a maximum of 700 W…
4. Hyundai Kona – E-Auto für Pendler
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: – E-Auto für tägliche Fahrleistung von 120 km
– Geplante Anschaffung eines gebrauchten Fahrzeugs
– Preisklasse: 20.000 – 25.000 €
– Bevorzugte Modelle: Hyundai Kona, ID3, Cupra Born, MG4
– Hyundai Kona hat eine Reichweite von ca. 300 km
– Jährliche Fahrleistung: 30.000 km
– Nutzung als Pendelfahrzeug und für kurze Einkaufstrips
– Familien-/Reiseauto bleibt der Passat Variant
– PV-Anlage mit 9 kWp …
5. Feu Vert – Launch Edition Aptera
Domain: feuvert-entreprises.fr
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Les voitures solaires commencent à être commercialisées, utilisant des cellules photovoltaïques pour recharger leur batterie sans nécessiter de borne de recharge. Les modèles disponibles incluent : 1. Launch Edition Aptera : – Équipée de trois moteurs électriques de 128 kW. – Vitesse maximale de 160 km/h. – Habitacle recouvert de cellules photovoltaïques pour maximiser l’énergie solaire. – Possibi…
6. Enerzine – Voiture Solaire Apollo VI
Domain: enerzine.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: La voiture solaire “Apollo VI” peut atteindre plus de 120 km/h. Elle mesure 4,7 mètres de longueur, 1,8 m de largeur et 1,1 m de hauteur, et pèse environ 130 kilos sans le pilote et la batterie. Le véhicule est recouvert de cellules solaires monocristallines à haut rendement “Back Contact” sur une surface de 6 mètres carrés. Sa consommation d’énergie est de 20 Watts par kilomètre. Les cellules sol…
7. Leman Bleu – Voiture Solaire Aletsch
Domain: lemanbleu.ch
Introduction: La voiture solaire ‘Aletsch’ a été construite par des étudiants de l’EPFZ. C’est un véhicule de 188 kilos, entièrement alimenté par l’énergie solaire, capable d’atteindre des vitesses de pointe de 120 km/h. Les étudiants ont développé cette voiture électrique pendant environ un an et ont dû passer plusieurs tests de sécurité pour participer au World Solar Challenge, une course de 3000 kilomètres à…
8. Yangwang – U9 Supercar Électrique
Domain: techno-science.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Nom du produit: Yangwang U9
Type: Supercar électrique
Capacité de saut: Peut sauter par-dessus des obstacles à plus de 120 km/h
Poids: 2 500 kg
Puissance: 1 287 chevaux
Système de suspension: DiSus-X, suspension hydraulique intelligente
Caractéristiques de la suspension: Ajuste en temps réel la hauteur de chaque roue, capable de sauter, danser sur place, rouler sur trois roues
Accélération: 0 à 10…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for voiture solaire 120 kmh
The emergence of solar-powered vehicles, particularly those capable of reaching speeds of 120 km/h, presents a transformative opportunity for international B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As global demand shifts towards sustainable transportation solutions, strategic sourcing becomes crucial in identifying and partnering with innovative manufacturers dedicated to advancing solar technology.
Key takeaways emphasize the importance of collaboration with suppliers who prioritize not only efficiency and sustainability but also the integration of cutting-edge engineering solutions. Investing in solar vehicles can significantly reduce operational costs and enhance corporate social responsibility, aligning businesses with global sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, the solar vehicle market is poised for significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing regulatory support for eco-friendly transportation. B2B buyers should proactively engage with manufacturers and technology providers to secure their position in this evolving landscape. By embracing solar vehicle solutions now, companies can lead the charge toward a greener future while reaping the economic benefits of sustainable innovation. The time to act is now—position your business at the forefront of this revolution.