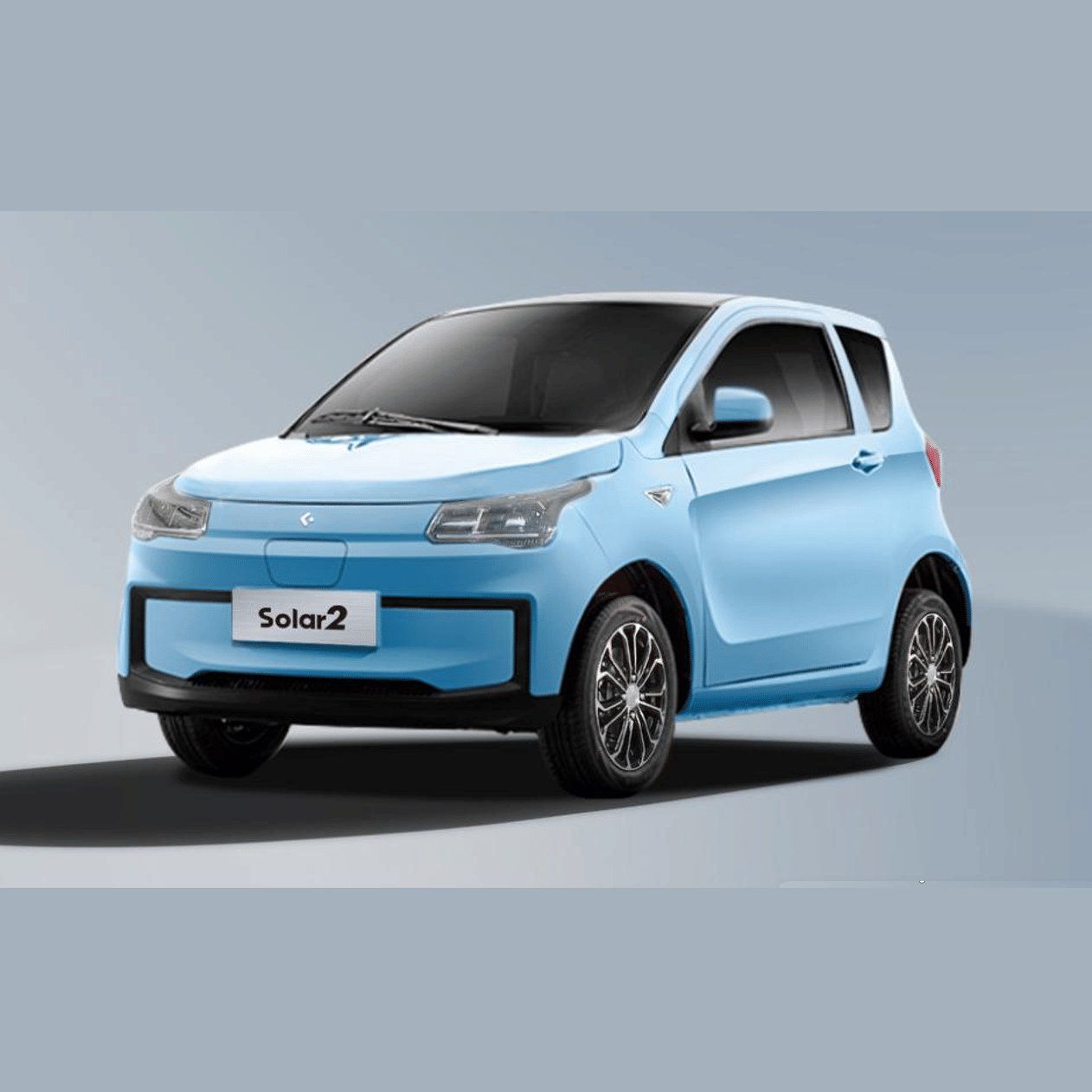
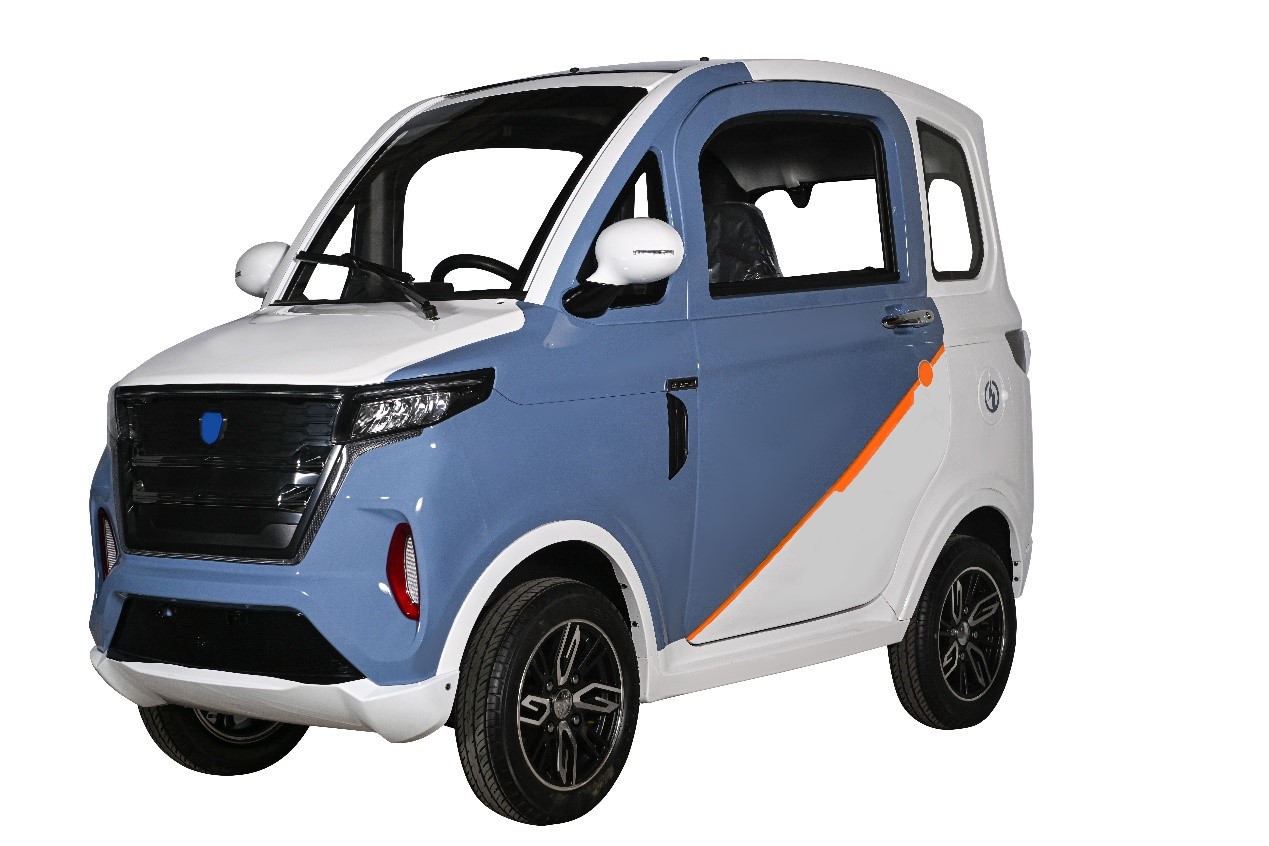
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric cars with eec certification
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), navigating the complexities of EEC certification can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Sourcing electric cars with EEC certification not only assures compliance with stringent European standards but also opens doors to lucrative markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide is designed to equip you with the essential knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, covering a wide range of topics including the types of electric vehicles available, their applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
As you delve into this comprehensive resource, you will uncover the critical factors influencing the EEC certification process, such as the importance of component certifications, the role of an authorized EU representative, and the implications of regulatory compliance on market access. Furthermore, we will discuss cost considerations and provide strategies for evaluating potential suppliers, ensuring that you can confidently navigate the global market for electric cars.
By leveraging the insights within this guide, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, streamline their procurement processes, and ultimately enhance their competitive advantage. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or any other emerging market, this guide serves as a vital tool for harnessing the full potential of electric vehicles in your business strategy.
Understanding electric cars with eec certification Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) | Fully electric, no internal combustion engine, longer range | Logistics, public transport, fleet sales | Pros: Zero emissions, low operating costs. Cons: Higher initial cost, charging infrastructure needed. |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) | Combines electric and gasoline propulsion, versatile range | Corporate fleets, urban delivery services | Pros: Flexibility in fuel options, reduced range anxiety. Cons: More complex systems, maintenance costs may vary. |
| Electric Pedal-Assisted Bicycles (EPACs) | Lightweight, designed for urban commuting, lower speed limits | Urban mobility solutions, last-mile delivery | Pros: Eco-friendly, low cost of operation. Cons: Limited range, not suitable for all terrains. |
| Electric Light Commercial Vehicles (eLCVs) | Designed for cargo transport, optimized for urban logistics | Delivery services, municipal operations | Pros: Cost-effective for short hauls, lower emissions. Cons: Limited payload capacity, range constraints. |
| Two-Wheel Electric Vehicles (e-motorcycles) | Lightweight, suitable for traffic-congested areas, lower speeds | Ride-sharing, delivery services | Pros: Maneuverable, lower purchase costs. Cons: Limited cargo capacity, less stability than larger vehicles. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) for B2B buyers?
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are entirely powered by electricity, making them ideal for businesses focused on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints. They typically offer longer ranges and lower operating costs compared to traditional vehicles, making them suitable for logistics and public transport sectors. When considering BEVs, B2B buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including charging infrastructure requirements and potential government incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
How do Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) serve diverse business needs?
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) provide the flexibility of both electric and gasoline propulsion, making them suitable for corporate fleets and urban delivery services. Their dual-fuel capability helps mitigate range anxiety, allowing businesses to complete longer journeys without relying solely on electric charging. B2B buyers should consider the balance between electric and gasoline usage, as well as the potential for reduced fuel costs and emissions.
What advantages do Electric Pedal-Assisted Bicycles (EPACs) offer for urban mobility?
Electric Pedal-Assisted Bicycles (EPACs) are designed for urban commuting and last-mile delivery, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses seeking eco-friendly transport options. Their lightweight design and lower speed limits make them ideal for navigating congested city streets. Buyers should assess the operational costs, including maintenance and battery replacements, as well as the suitability of EPACs for their specific delivery routes and urban environments.
How can Electric Light Commercial Vehicles (eLCVs) enhance urban logistics?
Electric Light Commercial Vehicles (eLCVs) are specifically designed for cargo transport within urban areas. They provide a sustainable alternative for businesses focused on reducing emissions while maintaining efficient logistics operations. When evaluating eLCVs, B2B buyers should consider payload capacity, range limitations, and overall cost-effectiveness for short-haul deliveries, as well as compliance with local environmental regulations.
What should B2B buyers know about Two-Wheel Electric Vehicles (e-motorcycles)?
Two-Wheel Electric Vehicles (e-motorcycles) are increasingly popular for ride-sharing and delivery services due to their maneuverability and lower purchase costs. They are particularly effective in urban environments where traffic congestion is common. However, B2B buyers should be mindful of their limited cargo capacity and stability compared to larger vehicles. Assessing local regulations and rider safety measures is also essential for businesses considering e-motorcycles for commercial use.
Key Industrial Applications of electric cars with eec certification
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Cars with EEC Certification | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery solutions in urban areas | Reduced operational costs and environmental impact | Need for EEC-certified vehicles that comply with local regulations and standards. Consider suppliers with a proven track record in reliability and service. |
| Agriculture | Transporting goods and personnel within farms | Enhanced efficiency and sustainability in operations | Focus on vehicles with EEC certification to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards. Look for models suited for rough terrain and heavy loads. |
| Public Transport | Electric buses for city transit systems | Lower emissions and operational costs for municipalities | Ensure EEC certification is in place for all components. Assess the availability of maintenance and support services in the region. |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Shuttle services for hotels and resorts | Improved guest experience and reduced carbon footprint | Source vehicles that meet EEC standards and are comfortable for passengers. Consider the aesthetic and branding alignment with the hotel or resort. |
| Construction | On-site transport of materials and personnel | Increased productivity and reduced diesel costs | Prioritize EEC-certified vehicles that can handle rugged conditions and heavy loads. Evaluate the lifecycle costs, including maintenance and energy consumption. |
How are Electric Cars with EEC Certification Applied in Various Industries?
In the logistics and delivery sector, electric cars with EEC certification are increasingly used for last-mile delivery solutions in urban environments. They address the growing demand for sustainable transport options while significantly reducing operational costs associated with fuel consumption. Businesses must ensure that the vehicles sourced comply with local regulations, and reliability is crucial for maintaining delivery schedules.
In agriculture, these electric vehicles facilitate the transport of goods and personnel across expansive farming areas. Their use enhances operational efficiency by providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional fuel-powered vehicles. Buyers should focus on models that are EEC-certified to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards, particularly in regions where agricultural practices are closely regulated.
Public transport systems are adopting electric buses equipped with EEC certification to reduce emissions and operational costs. These vehicles not only contribute to a cleaner environment but also align with the global shift towards sustainable public transport solutions. Municipalities must ensure that all components of these buses meet EEC standards and that adequate maintenance services are accessible locally.
In the tourism and hospitality industry, electric shuttles are becoming a popular choice for transporting guests within resorts and hotels. These vehicles enhance the guest experience by offering a quieter and more eco-friendly option. Sourcing EEC-certified vehicles is essential to comply with regulatory requirements, and businesses should also consider the vehicle’s design to align with their branding.
Lastly, in the construction industry, electric vehicles are utilized for the on-site transport of materials and personnel. They provide a cleaner alternative to diesel-powered options, which can be particularly beneficial in urban construction projects where emissions are a concern. Buyers should prioritize EEC-certified vehicles capable of handling heavy loads and rugged conditions while evaluating total lifecycle costs, including maintenance and energy efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric cars with eec certification’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex EEC Certification Requirements
The Problem: For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa and the Middle East, understanding the intricate requirements of EEC certification can be daunting. The certification process involves various components, including the need for a unique World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), compliance with ISO standards, and the acquisition of E-MARK certificates for individual parts. This complexity can lead to delays in product launch, increased costs, and potential penalties for non-compliance, ultimately impacting market entry and competitiveness.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the certification landscape, B2B buyers should prioritize establishing a robust relationship with a certified compliance consultant who specializes in EEC regulations. This expert can provide tailored guidance on the specific documentation and standards required for their electric vehicles. Additionally, buyers should invest in a comprehensive checklist that outlines all necessary steps in the certification process, including sourcing E-MARK certified components from reliable suppliers. By keeping a close eye on the expiration dates of certifications and scheduling regular audits, companies can ensure ongoing compliance and avoid disruptions in their market access.
Scenario 2: Managing Supply Chain Challenges for Certified Components
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of sourcing E-MARK certified components consistently. Many manufacturers face difficulties in finding suppliers that provide certified parts, leading to potential inconsistencies in product quality and the risk of losing their EEC certification if a non-compliant component is used. This situation can result in costly recalls, reputational damage, and lost sales opportunities, especially in competitive markets.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, buyers should develop strategic partnerships with multiple suppliers of E-MARK certified components. This approach diversifies the supply chain and reduces dependency on a single source, ensuring a more stable supply of compliant parts. Additionally, buyers can implement a vendor management system that monitors supplier certifications and performance metrics. Regular communication and collaboration with suppliers can facilitate faster response times for quality issues and help establish contingency plans for sourcing alternative components if needed.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Market Entry Barriers in Diverse Regions
The Problem: B2B buyers looking to export electric cars with EEC certification often encounter varying regulatory requirements and market entry barriers across different regions, such as Europe and South America. These discrepancies can lead to confusion and additional costs, as buyers must adapt their products to meet local standards while ensuring compliance with EEC regulations. This complexity can slow down the go-to-market process and hinder competitive positioning.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct comprehensive market research to understand the specific regulatory landscape in each target region. Leveraging the expertise of local consultants familiar with both EEC and regional requirements can streamline the compliance process. Buyers should also consider modular vehicle designs that allow for easy adaptation to meet different regulatory standards without overhauling the entire product. Additionally, engaging in trade shows and industry networks can provide valuable insights into local market dynamics and help build relationships with regional stakeholders, facilitating smoother entry into new markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric cars with eec certification
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) that require EEC certification, it is essential to consider properties that influence performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, steel, carbon fiber, and thermoplastics. Each material presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact the manufacturing process and end-product suitability.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Car Manufacturing?
Aluminum is widely used in electric vehicles due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. These properties make aluminum ideal for structural components, battery enclosures, and body panels. The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved energy efficiency and extended driving range, which are critical for EV performance.
Pros and Cons: While aluminum is durable and resistant to corrosion, it can be more expensive than traditional steel. Manufacturing processes for aluminum, such as extrusion and die-casting, may also require specialized equipment, increasing complexity. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN can add to the initial costs but ensures quality and safety.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Design?
Steel remains a popular choice for electric vehicle construction, particularly for structural components and safety features. High-strength steel variants provide excellent durability and impact resistance, essential for passenger safety. Additionally, steel is readily available and cost-effective, making it an attractive option for manufacturers.
Pros and Cons: Although steel is less expensive than aluminum, it is heavier, which can negatively affect the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Corrosion resistance can be an issue unless treated with coatings or galvanized processes. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local steel standards (e.g., JIS, DIN) when sourcing materials.
How Does Carbon Fiber Enhance Performance in Electric Vehicles?
Carbon fiber is increasingly being utilized in high-performance electric vehicles due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. This material is particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in battery housings and chassis components. The use of carbon fiber can significantly enhance vehicle performance and efficiency.
Pros and Cons: Despite its impressive properties, carbon fiber is costly and requires complex manufacturing techniques, such as autoclaving or resin infusion. This can limit its use to premium vehicle segments. For international buyers, understanding the specific compliance requirements for carbon fiber components is crucial, as different regions may have varying standards.
What Advantages Do Thermoplastics Offer for Electric Cars?
Thermoplastics are increasingly being adopted in electric vehicle production due to their versatility, lightweight nature, and ease of manufacturing. These materials are often used for interior components, battery casings, and exterior panels. Thermoplastics can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros and Cons: While thermoplastics are generally less expensive and easier to work with than metals, they may not offer the same level of durability and heat resistance. Additionally, their long-term performance can be affected by environmental factors. Buyers should ensure that the selected thermoplastics meet relevant international standards for safety and environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars with EEC Certification
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric cars with eec certification | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components, battery enclosures, body panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing processes | High |
| Steel | Chassis, safety features, structural components | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, potential corrosion issues | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | High-performance chassis, battery housings | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, battery casings, exterior panels | Versatile, lightweight, easy to mold | Limited durability, affected by environmental factors | Medium |
By understanding the properties and implications of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and compliance requirements in the electric vehicle market.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric cars with eec certification
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
The manufacturing process for electric cars, particularly those seeking EEC certification, involves several critical stages designed to ensure product quality and compliance with international standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates advanced techniques that align with stringent safety and environmental regulations.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Cars?
Material preparation is the foundational step in manufacturing electric vehicles. This phase focuses on sourcing high-quality materials that meet both EEC standards and the specific requirements of electric vehicle production. Common materials include lightweight metals like aluminum for the chassis and high-strength steel for structural components, as well as advanced composites for body panels.
During this stage, suppliers must provide documentation proving compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems. B2B buyers should verify that suppliers maintain traceability of materials and adhere to specifications that fulfill EEC requirements.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Electric Vehicle Production?
Forming techniques involve shaping the prepared materials into components that will be assembled into the final vehicle. Common methods include stamping, extrusion, and casting, which are utilized to create parts such as the vehicle frame, battery housing, and motor mounts.
Advanced forming techniques, such as hydroforming and 3D printing, are increasingly adopted to enhance design flexibility and reduce material waste. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific forming technologies employed by manufacturers, as these can significantly impact the performance and durability of the electric vehicle.
How Is the Assembly of Electric Cars Conducted?
Assembly is a critical stage where all individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically follows a well-defined sequence to ensure that each part is correctly positioned and secured. Key assembly techniques include robotic automation for precision and consistency, as well as manual assembly for complex components that require human expertise.
During assembly, manufacturers must conduct various quality checks to ensure that components fit together correctly and function as intended. B2B buyers should assess the assembly processes of potential suppliers, focusing on their use of automated systems and quality control measures.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Electric Vehicles?
Finishing processes in electric vehicle manufacturing encompass several steps designed to enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal and protect its components. Common finishing techniques include painting, coating, and surface treatment. These processes not only contribute to the vehicle’s appearance but also ensure compliance with environmental standards by using low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials.
In addition to aesthetics, finishing processes often include performance testing, such as battery integration and thermal management assessments. B2B buyers should verify that manufacturers employ eco-friendly finishing techniques that align with EEC environmental regulations.
Which International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the production of electric vehicles, especially for those seeking EEC certification. Key international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and ISO 14001 for environmental management, play a crucial role in guiding manufacturers. Compliance with these standards ensures that the vehicles produced are not only safe but also environmentally friendly.
Industry-specific certifications, such as CE and E-mark certifications, further verify that the vehicles meet stringent EU regulations concerning safety, noise, and emissions. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to these standards, as they reflect a dedication to quality and regulatory compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Vehicle Production?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each vehicle meets the required specifications. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection assesses the quality of raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide certification for materials to ensure compliance with EEC standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing, this phase involves monitoring production processes to catch defects early. This may include regular measurements and tests of components as they are assembled.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before vehicles are shipped, a comprehensive inspection is performed to confirm that the final product meets all specifications and regulatory requirements. This includes functionality tests, safety assessments, and emissions checks.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers who have robust QC processes in place and are willing to share their QC reports and methodologies.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are several effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, QC measures, and overall operational standards of potential suppliers. These audits can reveal insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports can provide transparency regarding the supplier’s QC practices. These documents should outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC, along with any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes. These agencies can conduct tests that verify compliance with EEC and other international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
When sourcing electric vehicles with EEC certification, international B2B buyers must navigate various nuances related to quality control. These include:
-
Local Regulations: Buyers should be aware of specific local regulations in their respective markets, as these can influence the compliance requirements for electric vehicles.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural approaches to quality and manufacturing can impact supplier relationships. Buyers should consider these differences when negotiating terms and establishing expectations.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: Ensuring a consistent supply of E-mark certified components is critical for maintaining the validity of EEC certification. Buyers should assess the supply chain practices of manufacturers to mitigate risks associated with component sourcing.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish successful partnerships in the electric vehicle market, ultimately ensuring compliance and maintaining high-quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric cars with eec certification’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), obtaining EEC certification is essential for manufacturers and suppliers aiming to access the European market. This practical sourcing guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure electric cars that meet EEC certification requirements. Following this guide will help streamline your procurement process and ensure compliance with critical regulations.
Step 1: Understand EEC Certification Requirements
Before initiating your sourcing process, familiarize yourself with the EEC certification requirements. This certification is crucial for ensuring that electric vehicles comply with safety and environmental standards set by the European Union. Key components include obtaining a World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ISO certification, and E-MARK certifications for various vehicle components.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly define the technical specifications that align with your market needs and compliance requirements. Consider factors such as vehicle range, battery capacity, and safety features. This step is vital as it helps in narrowing down potential suppliers who can meet your exact requirements, ensuring that the products will perform effectively in your intended environment.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in electric cars with EEC certification. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize platforms such as trade shows, industry publications, and online directories to gather information on suppliers’ capabilities and reputations.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, verify their certifications, including EEC, ISO, and any other relevant quality assurance certifications. This step is critical to ensure that the suppliers adhere to the necessary standards and regulations, safeguarding your investment and compliance with EU laws. Request documentation and check for any recent audits or certifications.
Step 5: Evaluate Quality Control Processes
Assess the quality control (QC) processes that potential suppliers have in place. A robust QC system indicates that the manufacturer prioritizes product quality and consistency. Inquire about their testing protocols, frequency of inspections, and how they handle quality issues. This diligence will help avoid costly product recalls and ensure that you receive vehicles that meet your specifications.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Field Tests
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the electric vehicles to assess their performance and suitability for your market. Conduct field tests under various conditions to evaluate factors such as battery life, charging time, and overall user experience. This hands-on evaluation is crucial to ensure that the vehicles will meet the expectations of your end users.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
After confirming your supplier and product quality, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that all contractual terms are clearly defined, including warranty, after-sales support, and any penalties for non-compliance. A well-structured contract protects both parties and facilitates a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric cars with EEC certification efficiently, ensuring compliance and enhancing market entry opportunities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric cars with eec certification Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
When sourcing electric cars with EEC certification, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials directly impacts the overall cost. High-grade components, such as lithium batteries and advanced electronic systems, may increase initial costs but offer better performance and longevity. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between cost and quality.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower wage rates may provide initial savings, but it’s crucial to assess the skills and expertise of the workforce to ensure quality assembly and compliance with EEC standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, but buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s operational efficiency to gauge potential savings.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific vehicle designs can be a significant upfront investment. This cost should be amortized over the expected production volume, so buyers should consider their anticipated order quantities when negotiating tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC system is vital to meet EEC certification requirements. While it may add to the overall cost, effective QC processes help avoid costly recalls and enhance product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, shipping methods, and associated tariffs. Buyers should factor in these costs early in the sourcing process to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market conditions. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric cars with EEC certification:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate favorable terms based on their purchasing volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized features can drive costs up. Buyers should balance their requirements with budget constraints, considering that extensive customization may extend lead times and increase costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications like EEC or ISO can significantly affect pricing. Investing in certified components may incur higher upfront costs but can enhance overall vehicle quality and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and handling costs. Understanding these terms can prevent misunderstandings and additional costs during the import process.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on upfront costs, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, warranty, and operational efficiency. This perspective can lead to better long-term value.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Request quotes from several manufacturers to create a competitive bidding environment. This approach can uncover pricing discrepancies and leverage better deals.
-
Understand Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends, including material costs and technological advancements, to anticipate pricing fluctuations and negotiate more effectively.
-
Build Strong Relationships: Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable conditions and priority service.
-
Consider Local Regulations: In regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, local import regulations and tariffs can affect pricing. Understanding these factors can help buyers navigate costs effectively.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for electric cars with EEC certification can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate and current pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric cars with eec certification With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Electric Cars with EEC Certification
In the evolving landscape of sustainable transportation, electric cars with EEC (European Economic Community) certification stand out for their compliance with stringent safety and environmental standards. However, international B2B buyers have multiple options to consider when evaluating transportation solutions. This section compares electric cars with EEC certification against alternative solutions, providing valuable insights for businesses looking to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Cars With EEC Certification | Hybrid Vehicles | Public Transportation Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, low emissions | Moderate efficiency, reduced emissions | Variable, depending on system design |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment; potential savings on fuel | Moderate initial cost; savings on fuel and maintenance | Generally lower cost per passenger, but depends on infrastructure |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires EEC compliance, potentially complex | Easier to implement in existing infrastructure | Often requires significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized service; low ongoing costs | Moderate maintenance needs; parts may be more accessible | Regular maintenance needed for vehicles and infrastructure |
| Best Use Case | Urban environments, eco-conscious businesses | Businesses with mixed driving needs | High-density areas, cost-sensitive operations |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Vehicles?
Hybrid vehicles combine internal combustion engines with electric propulsion, offering a middle ground between traditional vehicles and fully electric options. They often provide better fuel efficiency than gasoline-only vehicles and can be more cost-effective in regions where charging infrastructure is lacking. However, they still rely on fossil fuels, which may not align with the sustainability goals of some businesses. Additionally, hybrid vehicles can have higher maintenance costs due to the complexity of their systems.
How Do Public Transportation Solutions Compare?
Public transportation solutions, such as buses and rail systems, can significantly reduce per-passenger costs and environmental impact in urban areas. They facilitate mass transit, which can ease congestion and lower emissions on a larger scale. However, they often require substantial investments in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance. Furthermore, the effectiveness of public transport is highly dependent on the local government’s commitment to maintaining and upgrading services, which can vary widely across regions.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Transportation Solution?
Selecting the right transportation solution involves weighing various factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance requirements. Electric cars with EEC certification are ideal for businesses prioritizing environmental compliance and sustainability, particularly in European markets. Conversely, hybrid vehicles may suit companies seeking flexibility without the need for extensive infrastructure. Finally, public transportation solutions can be advantageous for businesses operating in densely populated areas where cost efficiency and high passenger capacity are paramount. Ultimately, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals to make an informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric cars with eec certification
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
When considering electric cars with EEC certification, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some of the essential properties that influence purchasing decisions:
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity is a fundamental specification that determines the range and performance of an electric vehicle (EV). Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), it indicates how much energy the battery can store. For B2B buyers, a higher capacity translates to longer operational ranges, essential for logistics and transportation businesses. This is particularly relevant for markets where charging infrastructure may be limited.
2. Motor Power (kW)
The power of the electric motor, measured in kilowatts (kW), directly impacts the vehicle’s performance, including acceleration and speed. A more powerful motor enables quicker response times and better handling, which are critical for fleet operations. Buyers should evaluate motor power in conjunction with battery capacity to ensure optimal vehicle performance for their specific needs.
3. Vehicle Weight (kg)
The weight of an electric vehicle affects its efficiency and range. Lighter vehicles generally offer better energy efficiency and range, as less energy is required to propel them. Understanding the weight specifications helps buyers assess the vehicle’s suitability for specific applications, such as urban delivery or off-road use.
4. Charging Time (hours)
Charging time is an important consideration for B2B operations that rely on uptime. This specification indicates how long it takes to fully charge the vehicle’s battery using different charging methods (e.g., standard, fast, and supercharging). Shorter charging times enhance fleet efficiency by minimizing downtime, which is crucial for businesses that operate on tight schedules.
5. EEC Compliance Standards
The EEC certification involves adherence to specific standards that ensure vehicle safety and environmental compliance. Buyers must understand these standards, as they dictate the quality and reliability of the vehicles being procured. EEC compliance not only facilitates market entry in the EU but also enhances brand credibility in global markets.
6. Warranty and Maintenance Terms
Warranty provisions and maintenance requirements are vital for B2B buyers. A comprehensive warranty can significantly reduce the total cost of ownership by covering repairs and replacements. Additionally, understanding maintenance terms ensures that the vehicles can be serviced efficiently, minimizing operational disruptions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in the Electric Vehicle Industry?
Navigating the electric vehicle market requires familiarity with industry-specific terminology. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, understanding OEM relationships is vital for procurement, as it affects supply chain management and component quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially when negotiating bulk purchases of electric vehicles or components.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers in the electric vehicle sector, issuing an RFQ allows for comparing quotes from various manufacturers, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, facilitating smoother logistics for electric vehicle imports.
5. Type Approval
Type approval is a certification process that verifies that a vehicle meets regulatory standards for safety and environmental impact. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to ensure compliance with EEC regulations before entering the European market.
6. E-MARK Certification
E-MARK certification indicates that a vehicle or component complies with European safety and environmental standards. For international buyers, this certification is essential for accessing the EU market and ensuring product quality and reliability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing electric vehicles with EEC certification, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes and market success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric cars with eec certification Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics for Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
The electric vehicle (EV) market is undergoing a transformative phase, driven by a combination of regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. The European Union’s EEC certification acts as a gateway for electric cars to enter one of the most regulated automotive markets globally. This certification not only ensures compliance with safety and environmental standards but also serves as a benchmark of quality that can enhance a product’s marketability.
Emerging trends indicate a growing demand for electric vehicles that prioritize sustainability and innovation. In regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure for electric vehicles is still developing, there’s an increasing push for local manufacturing and assembly to reduce costs and improve accessibility. Additionally, technological advancements in battery production, charging infrastructure, and vehicle design are reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are now looking for suppliers who can offer not only compliant vehicles but also scalable solutions that cater to local market needs.
Moreover, the global shift towards renewable energy sources is influencing the sourcing landscape. Buyers are increasingly seeking partnerships with manufacturers who utilize sustainable practices and materials in their production processes. This trend is expected to gain momentum as governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and consumers become more environmentally conscious.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B in the Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional; they are integral to the B2B landscape, especially in the electric vehicle sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials for electric cars is significant, with issues ranging from resource extraction to carbon emissions during production. Buyers are increasingly held accountable for their supply chains, prompting a demand for transparency and ethical practices. This is particularly relevant for international buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where local regulations may be evolving to include stricter environmental standards.
To meet these demands, manufacturers are focusing on sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and ensuring responsible sourcing of critical components like lithium for batteries. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with companies that hold such certifications, as this not only mitigates risk but also enhances brand reputation.
Furthermore, the rise of ‘green’ certifications and eco-labels is influencing purchasing decisions. Products that are certified as environmentally friendly can appeal to consumers who prioritize sustainability, thereby providing a competitive edge in the market. Buyers who incorporate ethical sourcing into their procurement strategies are not only contributing to environmental protection but are also positioning themselves to meet the evolving expectations of their customers.
What Is the Historical Context of Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
The history of electric vehicles and their certification can be traced back to the early 21st century when the global automotive industry began to recognize the need for cleaner, more sustainable transportation options. The European Union established the EEC certification framework to ensure that vehicles sold in its markets meet stringent safety and environmental standards. This certification process has evolved over the years, adapting to advancements in technology and changes in consumer expectations.
Initially focused on conventional vehicles, the EEC certification now encompasses electric vehicles, reflecting the growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable mobility solutions. The implementation of the new standard 168/2013 in 2016 marked a significant milestone, introducing more detailed classifications and requirements for electric vehicles, thereby enhancing the integrity of the certification process.
As electric vehicles continue to gain traction globally, understanding the historical context of EEC certification provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the regulatory landscape, helping them navigate market complexities and make strategic sourcing decisions that align with both compliance and consumer demand.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric cars with eec certification
-
How do I ensure my electric vehicle complies with EEC certification requirements?
To ensure compliance with EEC certification for electric vehicles, start by obtaining a unique World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) for vehicle identification. Ensure that all vehicle components, such as lights and tires, have E-MARK certifications. An ISO certificate that outlines your production scope is also essential. Lastly, appoint an authorized representative based in the EU to facilitate the certification process and maintain communication with regulatory bodies. -
What are the key benefits of sourcing electric cars with EEC certification for my business?
Sourcing electric cars with EEC certification opens the door to the European market, providing access to a high-demand customer base. It establishes credibility and trust with consumers, as EEC certification signifies adherence to stringent safety and environmental standards. Additionally, certified vehicles reduce the risk of recalls and associated costs, ensuring a more stable revenue stream for your business. -
What is the typical timeline and cost for obtaining EEC certification for electric vehicles?
The process of obtaining EEC certification typically takes between three to six months. Costs can exceed $20,000 per model, which includes testing and documentation fees. Budgeting for these expenses is crucial, as they can impact your pricing strategy and overall market entry timeline. Engaging with a specialized consultant can help streamline the process and potentially reduce costs. -
How do I vet suppliers of electric cars with EEC certification?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with proven experience in obtaining EEC certification. Request documentation of their certifications and compliance records. Conduct thorough background checks, including references from previous clients, to evaluate their reliability and quality of products. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes firsthand. -
Can I customize electric cars to meet specific market needs while ensuring EEC compliance?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for electric vehicles while maintaining EEC compliance. It is vital to discuss your specific requirements upfront with the supplier to ensure that any modifications do not compromise the vehicle’s certification status. Be aware that any significant changes may require re-evaluation and possible re-certification, which could affect timelines and costs. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing electric cars with EEC certification?
Minimum order quantities for electric vehicles can vary significantly by supplier and model. Typically, MOQs may range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the manufacturer’s production capacity and your negotiation power. Discussing your needs directly with suppliers can sometimes lead to flexibility in MOQs, especially for long-term partnerships or bulk orders. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of electric cars with EEC certification?
Payment terms can vary widely but often include options such as upfront payments, letter of credit arrangements, or staggered payments tied to delivery milestones. It is essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly documented in your purchase agreement to avoid disputes later. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars with EEC certification?
When importing electric cars, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling automotive imports to navigate the complexities of international shipping. Additionally, be aware of any tariffs, taxes, and compliance documentation required by your country’s customs authority to prevent delays in delivery.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Electric Cars With Eec Certification Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Facebook – BAW MINI EV
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electric cars | BAW MINI EV WITH EEC CERTIFICATION
2. EEC L6e Certification – Budget-Friendly Electric Cars
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: EEC L6e Certification Electric Vehicle, 4 wheels, budget-friendly electric car options.
3. EDACAR – EEC Electric Car
Domain: m.edacarev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: EDACAR EV Co., Ltd. introduces the EEC electric car, designed as an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles. Key features include:
– Zero emissions and an efficient electric motor, reducing carbon footprint.
– Advanced technology and stylish design for a smooth and quiet ride, ideal for urban commuting.
– Cutting-edge safety features and smart connectivity o…
4. CyberSwitching – Commercial Dual EV Charging Stations
Domain: cyberswitching.com
Introduction: Electric Vehicle Chargers: 1. Commercial Dual EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID – Price: $3,290.00 – $3,890.00 2. Commercial Dual 48A EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE3 Level-2 with display, RFID, CTEP – Price: $3,490.00 – $4,090.00 3. Commercial Dual EV Charging station, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID – Price: $2,890.00 (Original price: $2,890…
5. Accio – Top-Selling Electric Vehicles
Domain: accio.com
Introduction: Top-Selling Electric Vehicles in the EEC: 1. Tesla Model Y – Price Range: $44,990–$59,990, Key Features: Autopilot, 319-mile range, Ranking: #3 Luxury Compact SUV. 2. Ford Mustang Mach-E – Price Range: $37,995–$54,495, Key Features: 300-mile range, dual-motor performance, Ranking: #1 Compact SUV. 3. Hyundai Ioniq 5 – Price Range: $39,600–$44,600, Key Features: 300-mile range, modular interior, Ran…
6. Yunrong – EEC Certified Electric Cars
Domain: yunronev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer: Taizhou Yunrong Technology Co., Ltd.
Specialization: EEC Certified Electric Cars
Key Features:
– Eco-friendly transportation solution with zero emissions
– Comfortable and smooth driving experience
– Advanced manufacturing techniques for reliability and durability
– Commitment to quality and sustainability
– Continuous investment in research and development
Product Range:
– BYD Yan…
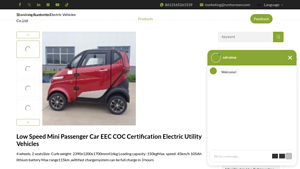
7. Runhorse – Low Speed Electric Utility Vehicle
Domain: runhorseev.com
Introduction: Low Speed Mini Passenger Car EEC COC Certification Electric Utility Vehicle
– Size: 2390x1200x1700 mm
– Curb Weight: 416 kg
– Loading Capacity: 150 kg
– Max Speed: 45 km/h
– Battery: 105Ah lithium battery
– Max Range: 115 km
– Charging Time: Full charge in 3 hours with fast charger
– Capacity: 2 seats
– Power System: A/C Motor 60V 3000W
– Brake System: Hydraulic System (Front Disc, Rear Drum)
– Su…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric cars with eec certification
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) with EEC certification represents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. Understanding the intricacies of EEC certification, which ensures compliance with stringent European safety and environmental standards, is crucial for sourcing quality electric vehicles. This certification not only facilitates access to the lucrative European market but also enhances product credibility, enabling businesses to build trust with consumers.
Strategic sourcing of EEC-certified electric cars allows companies to mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and quality assurance. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who have a proven track record of obtaining EEC certifications and maintaining high standards across their supply chains. This approach not only ensures compliance but also positions businesses to leverage competitive advantages in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, the demand for sustainable transportation solutions is set to grow exponentially. International buyers are encouraged to act now by engaging with certified manufacturers and exploring innovative electric vehicle options that align with regional needs. By doing so, businesses can not only enhance their product offerings but also contribute to a greener future while capitalizing on emerging market trends.