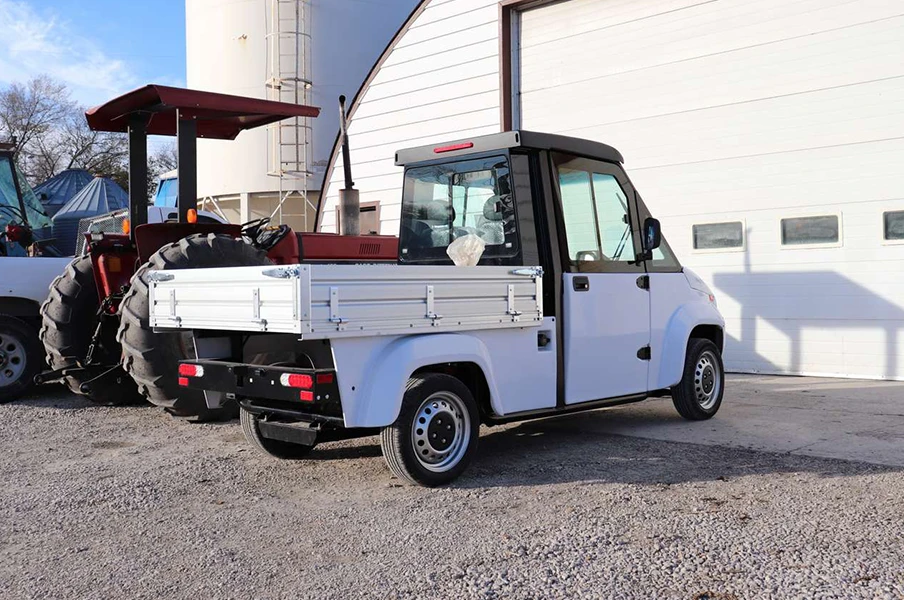
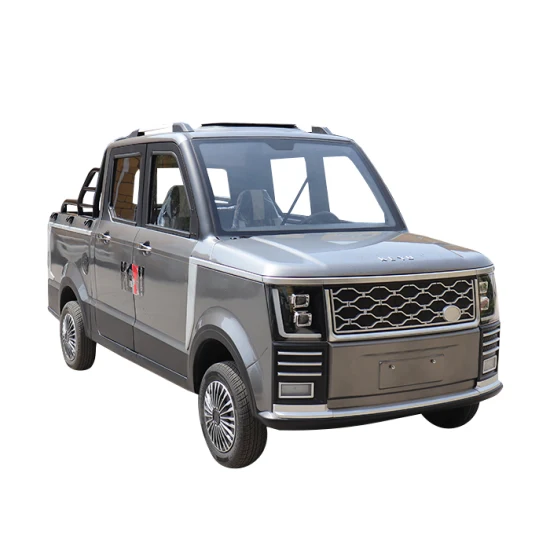
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for low speed electric truck
In the rapidly evolving landscape of logistics and transportation, sourcing low-speed electric trucks has become a pivotal challenge for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining operational efficiency. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Nigeria and Brazil) seek sustainable solutions, understanding the diverse applications and types of low-speed electric trucks is crucial. This guide serves as an essential resource for navigating the complexities of the global market, providing insights into vehicle specifications, customization options, and practical applications ranging from urban deliveries to facility maintenance.
The comprehensive scope of this guide includes an exploration of various low-speed electric truck models, their operational advantages, and an in-depth analysis of supplier vetting processes. Additionally, we address cost considerations and potential financing options, equipping buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By highlighting key features such as zero emissions, street legality, and versatility across different terrains, this guide empowers businesses to invest wisely in electric utility vehicles. Ultimately, it aims to facilitate a smoother transition to eco-friendly transportation, ensuring that organizations can thrive in a competitive global market while contributing to a sustainable future.
Understanding low speed electric truck Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extended Cab Truck | Additional passenger space, versatile cargo capacity | Facilities maintenance, construction sites | Pros: Increased capacity; Cons: May be bulkier. |
| Electric Panel/Cargo Van | Enclosed cargo space, customizable shelving | Urban deliveries, logistics | Pros: Secure transport; Cons: Limited payload. |
| Crew Cab Truck | Seating for multiple passengers, spacious interior | Shuttle services, event transportation | Pros: Comfort for passengers; Cons: Higher cost. |
| Electric Passenger Window Van | Designed for passenger transport with window access | Public transport, employee shuttles | Pros: Comfortable ride; Cons: Less cargo space. |
| Utility Vehicle | Open bed for transporting tools and equipment | Landscaping, maintenance tasks | Pros: Versatile use; Cons: Exposed cargo area. |
What Are the Characteristics of Extended Cab Trucks?
Extended cab trucks are ideal for businesses needing both passenger and cargo capacity. With additional seating and a versatile bed, they are particularly suited for facilities maintenance and construction sites where team collaboration is essential. When purchasing, consider the balance between passenger space and vehicle size, as a larger truck may be less maneuverable in tight urban settings.
How Do Electric Panel/Cargo Vans Benefit Urban Deliveries?
Electric panel or cargo vans offer enclosed spaces that can be fitted with customizable shelving, making them perfect for urban deliveries and logistics. Their design prioritizes security and organization, allowing businesses to transport goods safely. Buyers should assess their specific cargo needs and consider the trade-off between secure transport and limited payload capacity.
What Makes Crew Cab Trucks Ideal for Shuttle Services?
Crew cab trucks provide ample seating for multiple passengers, making them an excellent choice for shuttle services or event transportation. Their spacious interiors ensure comfort during transit. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate their budget against the benefits of passenger comfort and the potential for higher operational costs.
Why Choose Electric Passenger Window Vans for Public Transport?
Electric passenger window vans are specifically designed for transporting groups, featuring window access for passenger comfort. They are suitable for public transport and employee shuttles, providing a pleasant travel experience. Buyers should consider the vehicle’s capacity against the need for cargo space, as these vans prioritize passenger comfort.
What Are the Advantages of Utility Vehicles for Maintenance Tasks?
Utility vehicles are characterized by their open beds, making them ideal for transporting tools and equipment in landscaping and maintenance tasks. Their versatility allows businesses to adapt them to various functions. However, buyers should be aware of the exposed cargo area, which may not be suitable for all types of materials, especially those needing protection from the elements.
Key Industrial Applications of low speed electric truck
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of low speed electric truck | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery in urban areas | Enhances delivery efficiency while reducing emissions | Consider battery range, payload capacity, and urban compliance regulations. |
| Facilities Management | Onsite maintenance and transportation | Improves operational efficiency with lower operational costs | Evaluate customization options for specific tasks and terrain adaptability. |
| Agriculture | Transporting goods within large farms | Streamlines logistics and reduces labor costs | Assess durability and off-road capabilities for diverse terrains. |
| Hospitality and Tourism | Guest transport within resorts | Enhances guest experience while promoting sustainability | Look for comfort features and customization to fit the resort’s branding. |
| Construction | Material transport on job sites | Increases productivity with eco-friendly operations | Focus on load capacity, battery life, and adaptability to rough terrain. |
How are Low Speed Electric Trucks Used in Logistics and Delivery?
Low speed electric trucks are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery in urban settings. Their compact size and zero-emission capabilities allow businesses to navigate congested city streets efficiently. By adopting these vehicles, companies can significantly reduce their carbon footprint while enhancing delivery speed. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to consider the vehicle’s battery range and compliance with local regulations to ensure seamless operations in densely populated areas.
What Role Do Low Speed Electric Trucks Play in Facilities Management?
In facilities management, low speed electric trucks serve as essential tools for onsite maintenance and transportation of goods. These vehicles facilitate the movement of personnel and equipment within large facilities, such as factories, hospitals, or campuses. The benefits include reduced operational costs and improved efficiency. For B2B buyers, customization options tailored to specific tasks—like tool storage or passenger capacity—are critical for maximizing utility in diverse environments, particularly in the Middle East and Europe where facility layouts may vary significantly.
How Are Low Speed Electric Trucks Beneficial in Agriculture?
Within the agricultural sector, low speed electric trucks are employed for transporting goods across extensive farm operations. Their ability to operate quietly and without emissions makes them ideal for transporting produce without disturbing the local ecosystem. This not only streamlines logistics but also helps farmers reduce labor costs associated with traditional transport methods. Buyers in regions like Brazil should prioritize durability and off-road capabilities to handle various terrains and weather conditions, ensuring reliable performance throughout the agricultural cycle.
How Do Low Speed Electric Trucks Enhance Guest Experiences in Hospitality and Tourism?
In the hospitality and tourism industries, low speed electric trucks are used for transporting guests within resorts and tourist attractions. These eco-friendly vehicles not only improve the guest experience by providing comfortable, convenient transportation but also align with sustainability goals. For international buyers, especially in regions with a strong emphasis on eco-tourism, considering comfort features and options for branding customization can significantly enhance the appeal of these vehicles to guests.
What Advantages Do Low Speed Electric Trucks Offer in Construction?
In construction, low speed electric trucks are invaluable for transporting materials and equipment across job sites. Their zero-emission operation aligns with increasing regulatory pressures for sustainability in construction practices. These vehicles can boost productivity by reducing the time spent on material transport. Buyers should focus on load capacity, battery life, and the ability to navigate rough terrains, particularly in regions like Africa where construction sites may present unique challenges.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘low speed electric truck’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range for Urban Deliveries
The Problem: Many businesses in urban environments rely on low speed electric trucks for last-mile deliveries. However, a common challenge arises when these vehicles don’t offer sufficient range to complete daily routes without frequent recharging. For B2B buyers, this limitation can lead to operational inefficiencies, delayed deliveries, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers. Companies may find themselves needing to invest in additional vehicles or face logistical nightmares when planning routes that require more distance than their electric trucks can handle.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing low speed electric trucks with robust battery options and extended range capabilities. When evaluating vehicles, consider models that offer various battery pack sizes, allowing customization based on specific operational needs. For example, vehicles like the MAX-EV LSV provide multiple battery capacity options to increase range significantly. Additionally, creating strategic charging stations at key delivery points can help maintain operational flow. Implementing a vehicle management system that tracks battery levels and optimizes routes based on real-time data can also enhance efficiency and reliability in urban logistics.
Scenario 2: Vehicle Customization for Diverse Operational Needs
The Problem: Companies often operate in varied environments that require specific configurations of low speed electric trucks. For instance, a facility maintenance team may need a truck equipped with tool storage, while a food delivery service may require insulated cargo space. B2B buyers frequently struggle to find vehicles that can adapt to these diverse needs, leading to inefficient use of resources and potential underperformance in various tasks.
The Solution: When purchasing low speed electric trucks, it’s crucial to choose models that offer extensive customization options. Buyers should look for manufacturers that provide modular designs, allowing for the addition of features such as cargo boxes, shelving, or specialized storage compartments. For example, the Club Car Urban allows for different bed configurations and customization to fit specific business needs. Additionally, engaging with manufacturers to discuss bespoke solutions can ensure that the vehicles are tailored precisely to operational requirements. This approach not only maximizes the utility of the vehicle but also streamlines workflows, reducing the need for multiple vehicle types.
Scenario 3: Compliance with Local Regulations and Safety Standards
The Problem: Operating low speed electric trucks in different regions often comes with a maze of compliance requirements, including safety standards, street legality, and environmental regulations. B2B buyers may find it challenging to navigate these requirements, risking fines or operational shutdowns if vehicles are not compliant. This complexity is particularly pronounced in markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where regulations can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on local regulations before selecting low speed electric trucks. Engaging with local authorities or consulting industry experts can provide insights into the necessary compliance requirements. Furthermore, sourcing vehicles from manufacturers known for adhering to international safety and emissions standards can simplify the process. For instance, choosing trucks that meet street-legal requirements, such as those equipped with necessary safety features like seatbelts, lights, and signals, can ensure compliance. Additionally, implementing regular training for staff on local regulations and vehicle operation can foster a culture of safety and compliance within the organization.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for low speed electric truck
What Are the Key Materials Used in Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
When selecting materials for low-speed electric trucks, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material can significantly influence performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of low-speed electric trucks, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
Steel is widely used in the chassis and structural components of low-speed electric trucks due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high tensile strength, good impact resistance, and excellent weldability, making it suitable for heavy loads and rugged applications.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and readily available, which lowers manufacturing costs. Its durability ensures a long service life, even under harsh conditions.
Cons: Steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can be a significant issue in humid or coastal environments. It is also heavier than alternative materials, potentially affecting the vehicle’s efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength makes it ideal for load-bearing components, but its weight may limit the vehicle’s speed and energy efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local environmental conditions that may necessitate additional corrosion protection.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
Aluminum is increasingly favored for its lightweight properties, which enhance the energy efficiency of electric trucks. It boasts excellent corrosion resistance and is easily machined, making it suitable for various components, including body panels and structural supports.
Pros: The reduced weight of aluminum contributes to better battery efficiency and range, which is crucial for electric vehicles. Its natural resistance to corrosion minimizes maintenance needs.
Cons: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, which can increase initial manufacturing costs. It also has lower tensile strength, requiring careful design to ensure structural integrity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly beneficial in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the body and frame of the truck.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards and are sourced from reputable suppliers to avoid quality issues.
How Does Composite Material Benefit Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are becoming popular in low-speed electric trucks for their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. These materials can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: Composites offer excellent durability and can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, enhancing energy efficiency.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, leading to higher production costs. Additionally, repair and recycling options for composites are limited compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for non-structural components, such as body panels and interior fittings, where weight savings are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific manufacturing standards for composites in their region and consider the availability of repair services.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer in Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
Plastics are commonly used in low-speed electric trucks for components such as dashboards, interior fittings, and some exterior parts. They are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be produced in various colors and finishes.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be easily molded into complex shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They also provide good insulation properties.
Cons: Plastics may not offer the same level of durability as metals or composites, particularly under extreme conditions. They can also degrade over time due to UV exposure.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-load-bearing applications, contributing to overall weight reduction without compromising structural integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety and environmental regulations is critical, especially in regions with strict standards for plastic materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Low-Speed Electric Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for low speed electric truck | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Body panels and structural supports | Lightweight, enhances efficiency | Higher cost than steel | Med |
| Composite | Body panels and interior fittings | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Plastic | Dashboards and non-load-bearing parts | Cost-effective and design flexibility | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and local market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for low speed electric truck
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Low Speed Electric Trucks?
The manufacturing process for low speed electric trucks (LSEVs) involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
Material preparation is the initial phase where raw materials are sourced and processed. Common materials include high-strength steel for the chassis, lightweight aluminum for body components, and advanced polymers for insulation and interior finishes. The selection of materials is crucial as it impacts the vehicle’s weight, durability, and overall efficiency.
Additionally, battery components, specifically lithium-ion cells, are procured from specialized suppliers to ensure optimal performance. The quality of these materials significantly affects the LSEVs’ range and charging efficiency, making supplier evaluation critical for manufacturers.
How Are Low Speed Electric Trucks Formed?
In the forming stage, materials undergo various processes such as cutting, bending, and welding to create the vehicle’s structure. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including laser cutting and robotic welding, are often employed to enhance precision and consistency.
For instance, robotic welding ensures strong joints, which are essential for vehicle safety and longevity. This stage is also where components like the drivetrain are integrated, ensuring that the electric motor and battery systems are seamlessly incorporated into the chassis.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like for Low Speed Electric Trucks?
The assembly stage is where all the prepared components come together. Skilled technicians follow detailed assembly line protocols to install major systems such as the electrical, mechanical, and safety features. This phase may include:
- Integration of the Electric Drivetrain: The electric motor and battery management systems are installed with care to ensure optimal performance.
- Installation of Safety Features: Essential components like seatbelts, lights, and braking systems are installed to comply with international safety standards.
- Final Assembly of Body Components: Body panels and interiors are fitted, ensuring that all parts align correctly for both functionality and aesthetics.
Automation plays a significant role in the assembly process, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. However, skilled labor remains crucial for tasks that require a high level of craftsmanship.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in Low Speed Electric Truck Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the vehicle’s appearance and protect against environmental factors. Techniques may include:
- Painting and Coating: Advanced painting technologies ensure a durable finish that is resistant to scratches and corrosion. Eco-friendly paints are often chosen to align with the sustainability goals of electric vehicles.
- Quality Inspections: Each vehicle undergoes thorough inspections to ensure that all components function as intended. This includes testing electrical systems, brakes, and overall vehicle integrity.
The finishing stage is not just about aesthetics; it also involves ensuring that the vehicle meets regulatory compliance for emissions and safety.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated Into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing low speed electric trucks. It ensures that every vehicle produced meets the required standards for safety, performance, and sustainability. Key international standards, such as ISO 9001, guide the QA processes, ensuring a systematic approach to quality management.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards serve as benchmarks for quality assurance and can significantly influence purchasing decisions. For low speed electric trucks, buyers should be aware of:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Certification: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For components like engines and batteries, API standards ensure reliability and performance.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the credibility and reliability of manufacturers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This prevents subpar materials from entering the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, various checks are performed to ensure that each component is correctly installed and functioning. This includes testing electrical systems and ensuring proper alignment of parts.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed vehicle undergoes comprehensive testing, including performance, safety, and emissions testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities and quality processes directly. This firsthand evaluation can reveal insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Manufacturers should provide documentation detailing their quality control measures, test results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality practices and product reliability.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential, especially when sourcing from regions with varying standards. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers adhere to local regulations and international standards relevant to their region.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Understanding these cultural differences can help facilitate smoother negotiations and expectations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: International shipping can introduce risks to product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics strategies to mitigate these risks.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure reliable, high-quality low speed electric trucks that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘low speed electric truck’
When considering the procurement of low-speed electric trucks (LSEVs), a structured approach can help ensure that your investment aligns with your operational needs and sustainability goals. This checklist offers a practical guide for B2B buyers, facilitating informed decision-making throughout the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Operational Requirements
Understanding your specific operational needs is the cornerstone of sourcing the right low-speed electric truck. Consider factors such as payload capacity, range, and the types of terrain the vehicle will navigate.
– Payload Capacity: Determine how much weight the vehicle must carry, which will influence the truck’s specifications.
– Range: Assess how far the vehicle needs to travel on a single charge, particularly for last-mile delivery or facility maintenance.
Step 2: Research Available Models and Features
Explore the various models of low-speed electric trucks available in the market. Different manufacturers offer unique features that can enhance your operational efficiency.
– Customization Options: Look for vehicles that allow for modifications tailored to your specific business needs, such as cargo configurations or additional safety features.
– Performance Specifications: Evaluate aspects like top speed, battery life, and charging options to ensure they meet your requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews and ratings to gauge the supplier’s track record.
– Post-Sale Support: Investigate the availability of maintenance services and warranty options.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Low-speed electric trucks must comply with local transportation regulations, which can vary significantly by region. Confirm that the vehicles are street-legal and meet safety standards.
– Safety Features: Ensure the trucks are equipped with necessary safety features such as seatbelts, lights, and signals.
– Licensing Requirements: Research any specific licensing or registration needed to operate these vehicles in your area.
Step 5: Assess Environmental Impact and Sustainability
As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, consider the environmental impact of the vehicles you plan to purchase. Low-speed electric trucks should contribute to reducing your carbon footprint.
– Zero Emissions: Verify that the vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
– Energy Efficiency: Look for trucks with advanced battery technologies that enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers and models, request detailed quotes to compare pricing effectively.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential resale value.
– Leasing vs. Buying: Explore leasing options as an alternative to outright purchases, which can provide flexibility in managing capital expenditures.
Step 7: Conduct a Test Drive
Finally, arrange for test drives of shortlisted models to assess their performance firsthand.
– Handling and Comfort: Evaluate how easy the vehicle is to drive and whether it meets comfort standards for your operators.
– Load Capacity Testing: If possible, test the truck with a load similar to what it will carry in regular operations to ensure it meets your performance expectations.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for low-speed electric trucks, ensuring that your choice aligns with your operational needs and sustainability objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for low speed electric truck Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
When sourcing low-speed electric trucks (LSEVs), understanding the cost structure is essential. Key components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials in LSEVs consist of high-quality steel, aluminum, and advanced lithium-ion battery systems. The cost of these materials fluctuates based on global market trends, impacting overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled technicians involved in assembly, quality control, and maintenance. Regions with higher labor costs may influence the final price, so consider sourcing from areas with competitive labor markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes operational costs associated with running a manufacturing facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for production can be significant, especially for custom specifications. Investing in high-quality tooling can enhance production efficiency and product quality over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure the reliability and safety of LSEVs, which is crucial for compliance with international standards. Adequate QC measures may incur additional costs but are vital for long-term performance.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering vehicles to buyers can vary greatly depending on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. Efficient logistics planning can help manage these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding the market landscape and competitive pricing can aid in negotiating favorable terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Low-Speed Electric Truck Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of low-speed electric trucks:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also facilitate better pricing arrangements.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features, such as specialized cargo beds or enhanced battery systems, can significantly impact costs. Buyers should assess the value of customization against their operational needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can affect both the initial cost and the long-term reliability of the vehicle. High-quality materials may result in higher upfront costs but can offer better durability and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service levels play a crucial role in pricing. Engaging with reputable suppliers can lead to better support and long-term relationships.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to customs, tariffs, and insurance. This awareness is critical for international transactions, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Low-Speed Electric Truck Prices?
Buyers looking to secure favorable pricing should consider the following tips:
-
Conduct Market Research: Familiarize yourself with current market prices and competitor offerings. This knowledge will strengthen your negotiation position.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the long-term savings associated with electric vehicles, such as lower fuel and maintenance costs. Highlighting TCO can justify a higher initial investment.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable terms.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If negotiations do not meet your budgetary constraints, be prepared to explore other suppliers. This mindset can enhance your bargaining power.
-
Consider Local Incentives: Investigate any local or regional incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can offset initial costs. Many governments offer grants or tax breaks for environmentally friendly vehicles.
Conclusion: What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should approach sourcing with a comprehensive understanding of costs and pricing dynamics. Given the diversity of regional markets, it is crucial to account for local regulations, logistical challenges, and potential tariffs. Engaging with knowledgeable suppliers who understand these nuances will facilitate a smoother procurement process.
Disclaimer: Prices for low-speed electric trucks can vary widely based on specifications, market conditions, and supplier terms. Always request detailed quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing low speed electric truck With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives in Electric Transport Solutions
When considering transportation solutions for urban and industrial applications, businesses are often faced with a range of options. Low-speed electric trucks (LSEVs) offer an eco-friendly and efficient means of transport, but they are not the only solution available. This analysis explores various alternatives that may fit specific operational needs, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and ideal use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Low Speed Electric Truck | Electric Cargo Bike | Traditional Gasoline Truck |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 25 mph, 1,500 lbs payload capacity | Up to 20 mph, 400 lbs payload capacity | 60+ mph, 2,000+ lbs payload capacity |
| Cost | $19,950 – $22,308 | $2,000 – $5,000 | $25,000 – $50,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; street legal | Minimal infrastructure; easy to park | Requires fuel stations; higher parking costs |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal moving parts | Very low; basic repairs only | Moderate; regular servicing needed |
| Best Use Case | Urban deliveries, facility maintenance | Short-distance deliveries in congested areas | Long-haul transport and heavy-duty tasks |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Cargo Bike: A Versatile and Cost-Effective Option
Electric cargo bikes are a practical alternative for businesses that require short-distance deliveries, particularly in congested urban areas. They can easily maneuver through traffic and require minimal parking space, which is a significant advantage in cities with high vehicle density. The low acquisition cost and minimal maintenance requirements make them an appealing choice for startups or small businesses. However, they come with limitations in payload capacity and speed, making them unsuitable for heavier loads or longer distances.
Traditional Gasoline Truck: Power and Capacity at a Cost
Traditional gasoline trucks offer unmatched power and payload capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and long-haul transport. They can handle larger loads and operate at higher speeds, which is advantageous for businesses with extensive delivery needs. However, the higher initial investment, ongoing fuel costs, and environmental concerns associated with emissions may deter environmentally conscious companies. Additionally, the maintenance requirements can be more demanding compared to electric alternatives, impacting operational costs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right transport solution depends on various factors, including operational requirements, budget, and sustainability goals. Low-speed electric trucks provide a balanced approach for urban environments, combining eco-friendliness with adequate performance for medium payloads. If your operations demand shorter delivery distances with agility, an electric cargo bike could be the most cost-effective option. Conversely, if high capacity and speed are essential, traditional gasoline trucks may still be necessary despite their higher costs and environmental impact. Evaluating these factors will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and values.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for low speed electric truck
What Are the Key Technical Specifications for Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
When considering low-speed electric trucks (LSEVs), it’s crucial to understand the technical specifications that define their performance and utility. Here are some key properties:
-
Maximum Speed (MPH)
Most LSEVs are designed to operate at a maximum speed of 25 mph, making them ideal for urban and industrial environments. This speed limit ensures safety while facilitating efficient transport within confined spaces. For B2B buyers, understanding speed capabilities is essential for compliance with local regulations and meeting operational needs. -
Payload Capacity (lbs)
The payload capacity refers to the maximum weight that the vehicle can carry, typically ranging from 1,000 to 2,200 lbs. This specification is vital for businesses that require transportation of goods, as exceeding this limit can lead to vehicle damage and increased operational costs. Buyers should evaluate their logistical needs to select a truck that can handle their specific cargo requirements. -
Battery Type and Capacity (kWh)
LSEVs commonly utilize lithium-ion batteries, offering superior energy density and longevity. Battery capacity, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), directly affects the vehicle’s range and operational efficiency. For instance, a truck with a 24 kWh battery may provide a range of 60-100 miles on a single charge. Understanding battery specifications is crucial for businesses to plan charging schedules and ensure adequate operational range. -
Drive Type
Many LSEVs come with options for either two-wheel drive (2WD) or four-wheel drive (4WD). The drive type impacts traction and maneuverability, especially in varied terrains. For businesses operating in rough conditions, a 4WD option may be necessary to ensure reliable performance. Selecting the appropriate drive type can enhance efficiency and safety in specific operational contexts. -
Turning Radius (ft)
The turning radius indicates how tightly the vehicle can maneuver, which is particularly important for urban settings. A smaller turning radius (often around 10-15 ft) allows for easier navigation in crowded environments. For B2B buyers, this specification is critical for ensuring that the vehicle can operate effectively in tight spaces, such as loading docks or narrow streets.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Low-Speed Electric Trucks?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in the procurement process. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to the company that manufactures the original product, including components of LSEVs. When dealing with OEMs, buyers can ensure quality and compatibility of parts, which is critical for maintenance and repairs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ helps buyers assess the feasibility of bulk purchases and manage inventory costs effectively. For businesses looking to scale operations, knowing the MOQ can influence purchasing decisions. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific goods or services. In the context of LSEVs, sending an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and negotiate terms, ensuring they secure the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses mitigate risks and manage logistics effectively during cross-border transactions. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with acquiring and operating a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel (or electricity), and depreciation. For B2B buyers, evaluating TCO is crucial for making informed financial decisions regarding fleet investments. -
Warranty Period
This term describes the timeframe during which the manufacturer will cover repairs or replacements for defects. Understanding warranty terms is essential for buyers to gauge long-term reliability and safeguard their investments in LSEVs.
By grasping these technical specifications and industry terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing low-speed electric trucks, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and sustainability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the low speed electric truck Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Low Speed Electric Truck Market?
The global low-speed electric truck (LSEV) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of environmental regulations, urbanization, and technological advancements. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions regulations, especially in urban areas, prompting businesses to shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) to comply with these standards. This shift is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where urban centers are expanding rapidly, and the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions is on the rise.
Emerging technologies in battery efficiency and electric drivetrains are also transforming sourcing trends. Companies are increasingly seeking LSEVs equipped with advanced lithium-ion batteries that offer longer ranges and shorter charging times, making them more practical for daily operations. Additionally, the rise of telematics and fleet management software is enabling businesses to optimize their vehicle usage, reduce operational costs, and enhance overall efficiency.
For international B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with manufacturers offering customizable options to meet specific business needs. Buyers should focus on evaluating suppliers not just on cost but on the overall value, including the potential for customization, after-sales support, and the sustainability of their operations.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Business in the Low Speed Electric Truck Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the low-speed electric truck sector, influencing both consumer preferences and corporate responsibility initiatives. As businesses increasingly prioritize reducing their carbon footprint, investing in LSEVs is a strategic move. These vehicles produce zero emissions, contributing to cleaner air and supporting corporate sustainability goals.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming imperative for B2B buyers. Companies are expected to ensure that their supply chains uphold environmental and social standards. This includes sourcing materials that are environmentally friendly and verifying that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
In this landscape, buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and commit to sustainable practices. Engaging with manufacturers who offer green certifications not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also positions businesses as leaders in sustainability within their respective industries.
What is the Brief Evolution of Low Speed Electric Trucks in the B2B Context?
The low-speed electric truck market has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from niche applications to mainstream commercial use. Initially, LSEVs were primarily used in specialized sectors like golf courses and gated communities. However, advancements in battery technology and electric drivetrains have expanded their applications to urban logistics, facility maintenance, and last-mile delivery services.
The evolution has been further accelerated by increasing urbanization and the pressing need for sustainable transport solutions. As cities strive to reduce congestion and pollution, LSEVs are becoming essential tools for businesses seeking efficient and eco-friendly transportation options. This shift not only reflects changing market demands but also underscores the growing importance of sustainability in B2B operations.
International buyers can capitalize on this trend by investing in LSEVs that align with their operational needs while also contributing to broader environmental goals. Understanding the historical context of LSEVs can provide valuable insights into their future trajectory and potential applications across various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of low speed electric truck
-
How do I choose the right low-speed electric truck for my business needs?
Selecting the right low-speed electric truck involves assessing your specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as payload capacity, range, and terrain compatibility. Evaluate the types of tasks the vehicle will perform—whether it’s for urban deliveries, maintenance, or transportation. Additionally, check for customization options that can enhance functionality, such as different cargo bed sizes or additional features like backup cameras and storage compartments. Engaging with suppliers to discuss your needs can also provide valuable insights and recommendations. -
What is the best low-speed electric truck for urban deliveries?
The ideal low-speed electric truck for urban deliveries should offer maneuverability, a compact design, and sufficient cargo space. Models like the Club Car Urban are designed specifically for last-mile logistics, equipped with features that support efficiency in tight spaces. Look for trucks that can accommodate diverse cargo loads and have a top speed of around 25 mph to comply with street regulations. Ensure the vehicle has good battery life and can operate in various weather conditions to meet delivery schedules reliably. -
What customization options are available for low-speed electric trucks?
Customization options for low-speed electric trucks vary by manufacturer but often include different cargo bed configurations, passenger seating arrangements, and optional features such as enhanced lighting, sound systems, and storage solutions. Some suppliers allow for bespoke designs tailored to specific industry needs, such as mobile food delivery or facility maintenance. Engaging with the manufacturer to discuss your specific requirements can help you create a vehicle that perfectly aligns with your business operations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for low-speed electric trucks?
Minimum order quantities for low-speed electric trucks can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific model. Many manufacturers may require a MOQ of 1-5 units for standard models, while custom configurations may necessitate larger orders. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for single-unit purchases or bulk discounts. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing low-speed electric trucks internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of low-speed electric trucks typically range from upfront payments to installment plans. Many suppliers may require a deposit of 30-50% at the time of order, with the balance due prior to shipping. It’s important to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and consider the implications of currency exchange rates. Establishing clear terms in your contract can help mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for low-speed electric trucks?
Ensuring quality assurance involves selecting reputable suppliers who adhere to international manufacturing standards. Request certifications and quality control documentation to verify that the vehicles meet safety and performance criteria. Additionally, consider conducting factory inspections or third-party audits before shipment. Establishing a clear return policy and warranty terms can also safeguard your investment and provide peace of mind regarding product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when importing low-speed electric trucks?
When importing low-speed electric trucks, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Engaging a freight forwarder can help streamline the logistics process, ensuring compliance with local laws. It’s also important to plan for transportation within your country upon arrival, including any necessary permits for road use. Understanding lead times for delivery and potential delays can help manage expectations and operational planning. -
Are low-speed electric trucks suitable for diverse terrains and weather conditions?
Many low-speed electric trucks are designed to handle various terrains, but suitability often depends on specific models and features. Look for vehicles equipped with robust tires and enhanced suspension systems for off-road capabilities. Additionally, consider options such as all-weather tires and heating systems for cold climates. Engaging with suppliers about the intended usage and local conditions can help you choose a vehicle that meets your operational demands effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Low Speed Electric Truck Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Vantage – Electric Trucks and Vans
Domain: vantagevehicle.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Vantage – Electric Trucks and Vans, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Club Car – Urban Electric Truck
Domain: clubcar.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Club Car Urban
Type: LSV (Low-Speed Vehicle) / Electric Truck
MSRP: Starting at $25,680 for LSV
Capacity: Up to 1,400 lbs (with Lithium)
Speed: Street-legal, up to 25 MPH
Versions: XR (non street-legal) and LSV (street-legal)
Standard Features (both XR and LSV Models): All Season Road Tires, Premium Instrument Cluster, Headlights, Rear Lights, Horn, Bench Seat, Lockable Storage Locke…
3. Westward Industries – MAX-EV LSV
Domain: westwardindustries.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Product Name: MAX-EV LSV (Low Speed Electric Utility Vehicle)\nType: Electric Utility Vehicle (EUV)\nSeating Capacity: 2 and 4-seater options\nStarting Price: $19,950 (USD)\nLeasing Options: Available\nPayload Capacity: Up to 1,500 lbs\nDrivetrain: Electric drivetrain with permanent magnetic advanced motor\nBattery Options: Standard lithium-ion batteries ranging from 8 kWh to 24 kWh\nEstimated Ran…
4. Scooter Carz – Truck Golf Car 4 Seater LSV
Domain: scootercarz.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Truck Golf Car 4 Seater LSV Low Speed Vehicle”, “Model”: “60v Coco Truck Golf Cart”, “Features”: {“Air Conditioning”: “Optional ($249.95)”, “Steering Wheel Position”: “Left side”, “Certificate of Origin”: “Included”, “Charger”: “110v with 3 prong USA plug included”}, “Dimensions”: {“Length”: “2400 mm (94 inches)”, “Width”: “1200 mm (47 inches)”, “Height”: “1620 mm (64 inches)”}, …
5. TELO – All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘TELO MT1’, ‘type’: ‘All-Electric Mini Truck’, ‘dimensions’: {‘length’: ‘152 inches’, ‘width’: ’73 inches’, ‘height’: ’67 inches’}, ‘bed_size’: {‘length’: ’60-96 inches’, ‘width’: ’56 inches’, ‘height’: ’18 inches’}, ‘seating_capacity’: ‘2, 5, or 8 seats’, ‘performance’: {‘acceleration_0_to_60’: ‘6.0 seconds’, ‘power’: ‘300 hp’, ‘drivetrain’: ‘2WD’, ‘payload_capacity’: ‘2,000 lbs’, ‘towin…
6. GEM – eL XD Electric Utility Vehicle
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GEM eL XD Electric Utility Vehicle
– Payload Capacity: 1,415 lbs
– Towing Capacity: 1,250 lbs
– Range: Up to 78 miles between charges
– Seating: 1-2 passengers
– Dimensions: Length 146 in, Width 55.5 in, Height 73 in
– Bed Dimensions: 70 in long, 48 in wide
– Turning Radius: 194 in
– Wheelbase: 114 in
– Front Suspension: MacPherson Strut with 5.6 in travel
– Rear Suspension: Independent Trailing A…
7. Raymond West – Low-Speed Electric Vehicles
Domain: raymondwest.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Low-Speed Electric Vehicles from ICON® EV ECO family, including EPIC Carts, Cruise Car Inc, and utility vehicles. Key offerings include: 2-Seater Golf Carts (EPIC Cart E20), 4-Seater Golf Carts (variety of options), 6-Seater Golf Carts (EPIC Cart E60), I20 Series (2-Seater), I40 Series (4-Seater), I60 & I80 Series (6 to 8-Seater). Features include high performance, customization options, and suita…
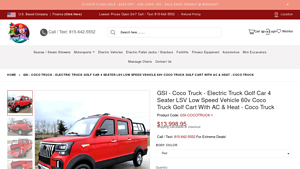
8. GSI – Coco Truck Electric Golf Cart
Domain: importjunkies.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Product Name: GSI – Coco Truck – Electric Truck Golf Car 4 Seater LSV Low Speed Vehicle 60v Coco Truck Golf Cart With AC & Heat
Product Code: GSI-COCOTRUCK-1
Regular Price: $13,998.95
Dimensions: 3900x1450x1650mm / 154x57x65in
Motor: 4000W
Controller: 30 Tubes
Tire: 145 Vacuum
Brake: Four Wheel Disc Brake
Drive Way: RWD
Maximum Cruising Range: 70-130km / 43-81 miles
Body Structure: 4 Doors & 4 Sea…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for low speed electric truck
In the evolving landscape of transportation, low-speed electric trucks (LSEVs) present a compelling opportunity for businesses across diverse sectors. Their zero-emission operation not only supports corporate sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets. Strategic sourcing of these vehicles can yield significant cost savings, improved operational efficiency, and compliance with local regulations, particularly in urban areas where emissions standards are stringent.
As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider integrating LSEVs into their fleets, it is crucial to evaluate the unique customization options available, such as payload capacity and battery life. Investing in the right model can lead to enhanced productivity, particularly for last-mile delivery and facility maintenance applications.
Looking forward, the demand for low-speed electric trucks is anticipated to grow, driven by both regulatory pressures and market trends favoring sustainability. Companies that strategically source these vehicles will not only stay ahead of compliance requirements but also position themselves as leaders in innovation and environmental stewardship. Embrace the future of transportation by exploring the potential of low-speed electric trucks to transform your operations today.